Search
Search
New study will assess fecal transplants in treatment of pancreatic cancer
Pancreatic cancer is an aggressive disease that affects up to six-thousand Canadians a year and is the third leading cause of cancer deaths. In a new study a multidisciplinary team of scientists at Lawson Health Research Institute are examining the microbiome in the gut, as a possible gateway to improving treatment outcomes.
“Pancreatic cancer is very hard to treat, partially because when it’s detected, the cancer is usually in a later stage and spreads very quickly,” explains Dr. John Lenehan, Medical Oncologist at London Health Sciences Centre’s London Regional Cancer Program (LRCP) and Associate Scientist at Lawson. “Our best chemotherapy treatments for the average patient, will give them a little less than a year to live.”
With the goal of improving treatments for these patients the research team led by Dr. Saman Maleki, Scientist at Lawson, is studying whether changing the gut microbiome can result in better response to cancer treatments. “We know that the microbiome plays an important role in patients’ response to various forms of systemic treatments such as immunotherapy and chemotherapy for different cancers,” says Dr. Maleki.

Dr. John Lenehan, Dr. Jeremy Burton and Dr. Saman Maleki
This unique study will happen in three stages. The first stage is an observational study to examine fecal samples of 52 patients at LRCP with advanced pancreatic cancer. The second stage will focus on using the samples from these patients in preclinical models to test new combinations of treatments. The final stage of the study will focus on intervention through human clinical trials by modifying a patient’s microbiome with something called a fecal transplant prior to treatment.
“The microbiome is involved in many aspects of cancer development and these organisms aren’t just living in the gut but also within the tumor,” says Dr. Michael Silverman, Lawson Scientist and Chair/Chief of Infectious Diseases at LHSC and St. Joseph’s Health Care London. “We believe that by giving people a fecal transplant, we can change the bacteria that live within the tumor and gut and then optimize the immune response to both the tumour and to treatment, with the goal of improving patient outcomes.”
Dr. Michal Silverman, Lawson Associate Scientist
Fecal transplants involve collecting stool from a healthy donor, preparing it in a lab and safely transplanting it to the patient, in this case with a capsule. The goal is to transplant the donor’s microbiome so that healthy bacteria will colonize in the patient’s gut. “If you think of microbiome, each bacterium is like a little factory and all together they are a giant factory within us producing things we need,” explains Dr. Jeremy Burton, Lawson Scientist who specializes in human microbiome research. “Over time, a person’s diet, medications, and lifestyle can change the microbiome and it can have a big impact to the rest of our body.”
The research team was recently awarded a $450,000 Catalyst 2021 grant from the Weston Family Foundation to conduct this study, which is the first in the world focusing on prospectively modifying the microbiome in pancreatic cancer patients for treatments and outcomes.
“We normally don’t see this in one study where we go through the full spectrum of learning from patients, to looking at treatments, and then moving to a final intervention stage,” explains Dr. Maleki. “This has not been tried in pancreatic cancer before, but we think leveraging the microbiome and improving the immune response can potentially move the needle in this patient population.”
The team is recruiting both pancreatic cancer patients, as well as healthy volunteers for fecal transplant samples. Those interested in helping with fecal transplant donations can contact Dr. Seema Parvathy at 519-646-6100 ext. 61726 or email seemanair@@email
New tool shows promise in helping people manage traumatic brain injuries once pace at a time
Mild traumatic brain injuries (mTBI), including concussions, may come with lasting effects that can alter a person’s life. Although a person with a mTBI may appear fine on the outside, many have to pace their day-to-day activities in order to allow the time needed for the brain to properly heal.
For 42-year-old Cindy Vanderveen who lives with post-concussion syndrome, every day tasks can become quite a challenge. Cindy who had multiple concussions over the years, experienced her mTBI symptoms in July of 2020 after an intense workout. Not knowing what was happening, she assumed she was having a stroke or seizure.
“I had issues with my vision; everything looked distorted. I had problems speaking (aphasia) and couldn’t eat or drink without choking on my food,” explains Cindy. “Everything I used to enjoy doing, gardening, cycling, working, it just stopped and my entire life was put on hold.”
Cindy was referred to the Acquired Brain Injury (ABI) program at St. Joseph’s Health Care London where she was encouraged to try a new research tool called MyBrainPacer™App, created to help those living with an mTBI.
The app was created at Lawson Health Research Institute – the institute of St. Joseph’s Health Care London – a team looking to better assist and treat those living with a mTBI. It was made possible by funding provided by the Cowan Foundation and other community supporters through St. Joseph’s Health Care Foundation.
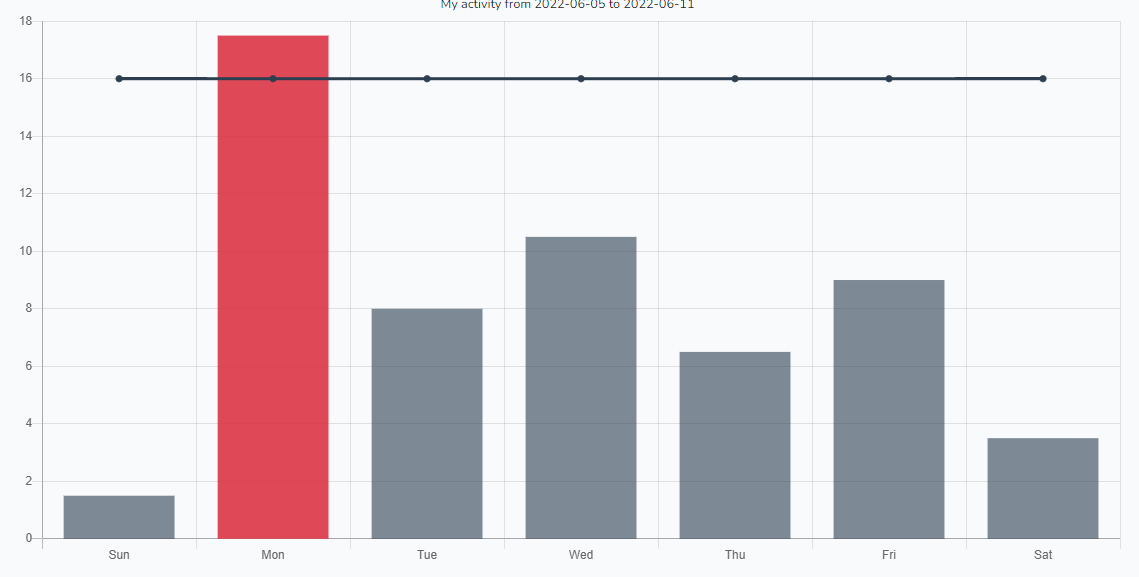
“By documenting activity levels over time, patients and their clinicians can better understand what activities are linked to worsening symptoms, which they can therefore avoid,” explains Dr. Dalton Wolfe, Lawson Scientist.

The online application is part of a study which allows Dr. Wolfe and his team to track the efficacy of the app. Much like point tracking used by dieters to monitor food choices, through MyBrainPacer™ App, users can assign values to tasks like driving, grocery shopping, screen use and exercise so they can plan and pace their daily activity. Individual users are given a total number of points per day that will keep their persisting symptoms in the ‘safe range’. As users track their symptoms through the app, the app adjusts the daily point value to what is best for the user. The app is based on St. Joseph’s Pacing and Planning Program, which has helped hundreds of concussion patients achieve their recovery goals.
“By putting the app in the hands of patients and the clinicians who treat them, the app has the potential to give us data that traces the recovery patterns of patients and how that relates to the activities that they participate in over time,” adds Dr. Wolfe. “This will enable us to document safe levels of activity for persons with specific characteristics or symptom profiles, which could be the key to unravelling better treatment strategies.”
After using the app for some time, Cindy has noticed a positive change. “In the beginning I wasn’t able to drive farther than five minutes at a time,” remembers Cindy. “Once I began to use the app to plan and track my activities, my symptoms dramatically decreased.”
Currently anyone with a mTBI can enroll as a study participant on the MyBrainPacer™ App and use the tool. The research team is hoping to enroll approximately five-thousand users over time to allow for a large evaluation population.
“Without the app, there is no way to keep track of the hundreds of trajectories of patient recoveries,” says Dr. Wolfe. “This information is vital to understand what is working in terms of future therapeutic approaches.”
“I still have bad days, and some tasks are harder than others,” adds Cindy. “But through using the MyBrainPacer™ App I am able to do more activities independently and I’m 90 per cent back to who I was.”
Anyone interested in enrolling to use the app can do so by visiting mybrainpacer.ca
Senior Media Relations Consultant
Communications & Public Engagement
T: 519-685-8500 ext. 73502
Celine.zadorsky@lhsc.on.ca
New tool shows promise in helping people manage traumatic brain injuries one pace at a time
LONDON, ON- A team at Lawson Health Research Institute and St. Joseph’s Health Care London, has created a new online tool called MyBrainPacer™ App to help assist people living with a mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI).
mTBI’s, including concussions, may come with lasting effects that can alter a person’s life. Although a person with an mTBI may appear fine on the outside, many have to pace their day-to-day activities in order to allow the time needed for the brain to properly heal. That’s where the MyBrainPacer™ App can come into play as a helpful resource.
“By documenting activity levels over time, patients and their clinicians can better understand what activities are linked to worsening symptoms, which they can therefore avoid,” explains Dr. Dalton Wolfe, Lawson Scientist.
The online application is being used as a research tool, allowing Dr. Wolfe and his team to track its efficacy. Much like point tracking used by dieters to monitor food choices, through MyBrainPacer™ App, users can assign values to tasks like driving, grocery shopping, screen use and exercise so they can plan and pace their daily activity. Individual users are given a total number of points per day that will keep their persisting symptoms in the “safe range.” As users track their symptoms through the app, the app adjusts the daily point value to what is best for the user. The app is based on St. Joseph’s Pacing and Planning Program, which has helped hundreds of concussion patients achieve their recovery goals.
“By putting the app in the hands of patients and the clinicians who treat them, the app has the potential to give us data that traces the recovery patterns of patients and how that relates to the activities that they participate in over time,” adds Dr. Wolfe. “This will enable us to document safe levels of activity for persons with specific characteristics or symptom profiles, which could be the key to unravelling better treatment strategies.”
After a number of concussions, study participant Cindy Vanderveen, has been using the app to manage her brain injury and has noticed a positive change.
“In the beginning I wasn’t able to drive farther than five minutes at a time,” remembers Cindy. “My care team at St. Joseph’s recommended MyBrainPacer™ App to help me plan and pace my day. Once I began to use the app to plan and track my activities, my symptoms dramatically decreased. I still have bad days and some tasks are harder than others, but through using MyBrainPacer™ App, I am able to do more activities independently and I am 90 per cent back to who I was.”
Currently anyone with an mTBI can enroll as a study participant on the MyBrainPacer™ App by visiting mybrainpacer.ca. The research team is hoping to enroll approximately five-thousand users.
The creation of the app has been made possible by funding provided by the Cowan Foundation and other community supporters through St. Joseph’s Health Care Foundation.
Lawson Health Research Institute is one of Canada’s top hospital-based research institutes, tackling the most pressing challenges in health care. As the research institute of London Health Sciences Centre and St. Joseph’s Health Care London, our innovation happens where care is delivered. Lawson research teams are at the leading-edge of science with the goal of improving health and the delivery of care for patients. Working in partnership with Western University, our researchers are encouraged to pursue their curiosity, collaborate often and share their discoveries widely. Research conducted through Lawson makes a difference in the lives of patients, families and communities around the world. To learn more, visit www.lawsonresearch.ca.
Renowned for compassionate care, St. Joseph’s Health Care London is a leading academic health care centre in Canada dedicated to helping people live to their fullest by minimizing the effects of injury, disease and disability through excellence in care, teaching and research. Through partnership with Lawson Health Research Institute and our collaborative engagement with other health care and academic partners, St. Joseph’s has become an international leader in the areas of: chronic disease management; medical imaging; specialized mental health care; rehabilitation and specialized geriatrics; and surgery. St. Joseph’s operates through a wide range of hospital, clinic and long-term and community-based settings, including: St. Joseph’s Hospital; Parkwood Institute; Mount Hope Centre for Long Term Care; and the Southwest Centre for Forensic Mental Health Care. www.sjhc.london.on.ca
St. Joseph’s Health Care Foundation gathers, grows and grants philanthropic funds to enable St. Joseph’s Health Care London to pursue excellence in care, teaching and research. Through donor support, the foundation contributes to advances in the delivery of patient care, specialized equipment, research initiatives and capital funds at St. Joseph’s Hospital, Parkwood Hospital, Mount Hope Centre for Long Term Care, Regional Mental Health Care London and Southwest Centre for Forensic Mental Health Care and Lawson Health Research Institute. As one of the largest charitable organizations in Southwestern Ontario, St. Joseph’s Health Care Foundation is an accredited member of Imagine Canada’s Ethical Trustmark Program, which recognizes the foundation’s commitment to ethical fundraising and donor accountability. www.sjhcfoundation.org
Senior Media Relations Consultant
Communications & Public Engagement
T: 519-685-8500 ext. 73502
Celine.zadorsky@lhsc.on.ca
New transportation resource for youth in crisis
LONDON, ON – Transitional aged youth in Middlesex County now have access to a free transportation resource to access mental health services. Called the County Transport initiative, it will help youth ages 16 to 25 in Lucan, Parkhill, Exeter and Strathroy-Caradoc get the mental health care they need, when they need it.
County Transport is being coordinated by MINDS of London-Middlesex, a program of Lawson Health Research Institute, in partnership with the Canadian Mental Health Association (CMHA) of Elgin-Middlesex, Star Taxi and Middlesex County through the Lucan and Parkhill Libraries.
“Through our collaborative work, we’ve heard from many youth that transportation is a barrier for them when trying to access mental health services when in crisis. Youth in rural areas find this very challenging since most services are not close to their location,” says Romaisa Pervez, Research Assistant at MINDS of London-Middlesex.
MINDS, a Mental Health INcubator for Disruptive Solution, is a social innovation lab with a mission to address the complexity of the mental health care system. Youth with lived experience, community members and researchers work together to understand and help those living with mental health challenges in London-Middlesex by designing, piloting and testing innovative solutions developed locally.
“We do not have the exact numbers of Transitional Aged Youth (TAY) living in rural Middlesex who would benefit from access to the County Transport Initiative, but we know that mental health services in rural communities are limited and that access to the services available in larger city centres is challenging due to transportation difficulties,” explains Cathy Burghardt-Jesson, Warden for Middlesex County. “Transportation from Middlesex to London, where the majority of mental health resources are located, is underdeveloped as there are limited bus routes and schedules. This leaves little in the way of affordable transit options for TAY in crisis.”
Youth in crisis who connect with CMHA’s Reach Out 24/7 line at www.reachout247.ca or by phone at 519-433-2023 will be supported and assessed by the Crisis Line staff. If it is determined that a visit to the London Crisis Centre is needed, the CMHA Crisis worker will ensure a smooth transition from the Crisis Line to the Star Taxi Service. The youth will be provided with free transportation to and from CMHA’s Mental Health and Addictions Crisis Centre located at 648 Huron Street.
To ensure the safety and wellbeing of the youth accessing this service, Star Taxi drivers have received training developed by CMHA regarding mental health and crisis de-escalation, as well as suicide prevention training by Living Works.
Funding for the initiative has been provided by St. Joseph’s Health Care Foundation and the generous support of individual donors in the community.
“With additional funding, the initiative could be scaled up to reach as many youth as possible in Middlesex County and beyond. We want to see all youth in rural areas who want to access mental health services able to do so, by removing the barriers of location and transportation,” adds Pervez. They will be collecting information regarding use of the transportation service and youth experience to refine and improve the initiative.
-30-
Lawson Health Research Institute is one of Canada’s top hospital-based research institutes, tackling the most pressing challenges in health care. As the research institute of London Health Sciences Centre and St. Joseph’s Health Care London, our innovation happens where care is delivered. Lawson research teams are at the leading-edge of science with the goal of improving health and the delivery of care for patients. Working in partnership with Western University, our researchers are encouraged to pursue their curiosity, collaborate often and share their discoveries widely. Research conducted through Lawson makes a difference in the lives of patients, families and communities around the world. To learn more, visit www.lawsonresearch.ca.
Senior Media Relations Consultant
Communications & Public Engagement
T: 519-685-8500 ext. 73502
Celine.zadorsky@lhsc.on.ca
New transportation resource for youth in crisis
Transitional aged youth in Middlesex County now have access to a free transportation resource to access mental health services. Called the County Transport initiative, it will help youth ages 16 to 25 in Lucan, Parkhill, Exeter and Strathroy-Caradoc get the mental health care they need, when they need it.
County Transport is being coordinated by MINDS of London-Middlesex, a program of Lawson Health Research Institute, in partnership with the Canadian Mental Health Association (CMHA) of Elgin-Middlesex, Star Taxi and Middlesex County through the Lucan and Parkhill Libraries.
“Through our collaborative work, we’ve heard from many youth that transportation is a barrier for them when trying to access mental health services when in crisis. Youth in rural areas find this very challenging since most services are not close to their location,” says Romaisa Pervez, Research Assistant at MINDS of London-Middlesex.

Romaisa Pervez, Research Assistant at MINDS of London-Middlesex, is leading the County Transport initiative.
MINDS, a Mental Health INcubator for Disruptive Solution, is a social innovation lab with a mission to address the complexity of the mental health care system. Youth with lived experience, community members and researchers work together to understand and help those living with mental health challenges in London-Middlesex by designing, piloting and testing innovative solutions developed locally.
“We do not have the exact numbers of transitional aged youth living in rural Middlesex who would benefit from access to the County Transport Initiative, but we know that mental health services in rural communities are limited and that access to the services available in larger city centres is challenging due to transportation difficulties,” explains Cathy Burghardt-Jesson, Warden for Middlesex County.
“Transportation from Middlesex to London, where the majority of mental health resources are located, is underdeveloped as there are limited bus routes and schedules. This leaves little in the way of affordable transit options for youth in crisis.”
Youth in crisis who connect with CMHA’s Reach Out 24/7 line at www.reachout247.ca or by phone at 519-433-2023 will be supported and assessed by the Crisis Line staff. If it is determined that a visit to the London Crisis Centre is needed, the CMHA Crisis worker will ensure a smooth transition from the Crisis Line to the Star Taxi Service. The youth will be provided with free transportation to and from CMHA’s Mental Health and Addictions Crisis Centre located at 648 Huron Street.
To ensure the safety and wellbeing of the youth accessing this service, Star Taxi drivers have received training developed by CMHA regarding mental health and crisis de-escalation, as well as suicide prevention training by Living Works.
Funding for the initiative has been provided by St. Joseph’s Health Care Foundation and the generous support of individual donors in the community.
“With additional funding, the initiative could be scaled up to reach as many youth as possible in Middlesex County and beyond. We want to see all youth in rural areas who want to access mental health services able to do so, by removing the barriers of location and transportation,” adds Pervez.
They will be collecting information regarding use of the transportation service and youth experience to refine and improve the initiative.
New treatment for critically ill COVID-19 patients with sepsis is one step closer to potentially saving lives
LONDON, ONTARIO – It’s a human protein called annexin A5, and it’s being studied as a potential therapy for COVID-19 patients with sepsis. Annexin A5 is a protein produced inside the human body with unique anti-coagulation (preventing blood clots) and anti-inflammatory properties that could help in the fight against sepsis.
Sepsis is a life-threatening condition that occurs when the body’s response to an infection turns into an overwhelming inflammatory response. The inflammatory response can cause damage to organs such as the heart, liver, lungs, and even the brain. Unfortunately, most critically ill COVID-19 patients develop sepsis. “With COVID initially, it is in the airway and then in the lungs, then from there the inflammatory response in fact spreads to the whole body,” says Dr. Qingping Feng, Lawson Scientist and Ivey Chair in Molecular Toxicology at Western University's Schulich School of Medicine & Dentistry. “Sepsis causes major organ dysfunction and carries a high mortality unfortunately.”
“For patients with severe COVID-19 disease, what we see is major respiratory failure in the lungs as the primary site in the body,” says Dr. Claudio Martin, Intensive Care Physician at London Health Sciences Centre (LHSC) and Associate Scientist at Lawson. “When the pandemic started, there was no proven treatment for sepsis, including sepsis as a result of COVID-19. Based on clinical trials during the pandemic, we now use steroids and other treatments to try to help, but the results and effects aren’t dramatic and we see patients who have these treatments and still progress and end up in critical care.”
However, Dr. Feng and his team have found in a pre-clinical study that annexin A5 can inhibit inflammation and improve organ function and survival when treating sepsis. This discovery was made right here in London and now the research team has launched a clinical trial with critically ill COVID-19 patients at LHSC, using a manufactured form of annexin A5.
Enrollment has begun with the goal to have 60 patients participate in the clinical trial. “Patients are receiving standard treatment and then those enrolled will also receive the annexin,” says Dr. Martin. “It’s a placebo blinded clinical trial, so patients will either get a lower dose of annexin, a higher dose of annexin or a placebo.”
If the clinical trial shows promising results the team plans on expanding into a larger phase three trial with not just COVID-19 patients with sepsis, but other sepsis patients as well. “If in fact Annexin A5 is shown to be effective in sepsis, this will be a huge benefit for society because sepsis is the leading cause of death worldwide,” adds Dr. Feng.
The drug is currently being produced through a partnership with Suzhou Yabao Pharmaceutical R&D Co. Ltd., based in China, Lawson Health Research Institute, and WORLDiscoveries. “Our long-standing partnership with Suzhou Yabao has enabled annexin A5 drug development to proceed to this point,” says Kirk Brown, Manager of Business Development, Lawson Health Research Institute. “We are now in a unique position through this trial to offer a potential life-saving treatment for this emergent global disease, with the objective of soon expanding to all cause septic patients.”
-30-
Lawson Health Research Institute is one of Canada’s top hospital-based research institutes, tackling the most pressing challenges in health care. As the research institute of London Health Sciences Centre and St. Joseph’s Health Care London, our innovation happens where care is delivered. Lawson research teams are at the leading-edge of science with the goal of improving health and the delivery of care for patients. Working in partnership with Western University, our researchers are encouraged to pursue their curiosity, collaborate often and share their discoveries widely. Research conducted through Lawson makes a difference in the lives of patients, families and communities around the world. To learn more, visit www.lawsonresearch.ca.
WORLDiscoveries is the business development arm of London’s extensive research network and the bridge between local invention and global industry. Born out of a partnership between Western University, Robarts Research Institute and Lawson Health Research Institute (collectively known as the Partners), WORLDiscoveries draws upon a mix of industry connections, sector-specific market knowledge and business development expertise, to help researchers and local inventors commercialize their discoveries through licensing and new company spin-offs.
Senior Media Relations Consultant
Communications & Public Engagement
T: 519-685-8500 ext. 73502
Celine.zadorsky@lhsc.on.ca
New urinary microbiome study could be first step in providing personalized care to patients with ureteral stents
LONDON, ONTARIO - For patients with kidney stones, ureteral stents (hollow devices placed in the ureter – the tube between the kidney and bladder) can be used temporarily to relieve urinary obstruction. Despite the use of antibiotics, ureteral stents often become encrusted with minerals and coated with bacteria. This can lead to complications like infection and the need for replacement surgery.
Published today in Cell Reports Medicine, researchers at Lawson Health Research Institute and Western University conducted a novel microbiome study to examine bacteria associated with ureteral stents. They found that nearly all the stents, whether visibly coated or not, had unique bacterial profiles that were most associated with a patient’s medical condition rather than antibiotic use. For patients with ureteral stents, they may benefit from a personalized approach to care and antibiotic treatment.
The study included 241 patients from St. Joseph’s Health Care London. The research team collected and analyzed patient urine samples and ureteral stents following surgical removal, as well as relevant patient information such as antibiotic use and history of infections.
“We wanted to know which bacteria were present and whether the bacteria found in urine samples corresponded to the bacteria found on a patient’s stent,” explains Dr. Kait Al, Postdoctoral Fellow at Lawson and at Western’s Schulich School of Medicine & Dentistry. “We found that there was a bacterial community present on almost all stents, even if they were not visibly affected, and that it differed from the bacterial community found in a patient’s urine.”
These findings challenge long-held beliefs that the urinary tract is a sterile environment devoid of bacteria.
The study revealed that the bacteria present were determined by an individual patient’s medical condition. They differed significantly based on comorbidities like irritable bowel syndrome, obesity and hypertension. Antibiotic use within the past 30 days did not seem to have an effect on the types of bacteria detected on the stents.
“While more research is needed, our study suggests that antibiotic use during the placement of these stents could one day be more conservative or targeted based on each patient’s condition,” says Dr. Jeremy Burton, Lawson Scientist and Associate Professor at Schulich Medicine & Dentistry.
The team also discovered that in patients needing multiple stents, the bacterial community remained stable over time, suggesting that infections on a patient’s previous stent could direct the course of treatment for their future device placements.
“This is the largest study of its kind, investigating bacteria both in urine and adhered to ureteral stents,” states Dr. Hassan Razvi, Urologist at St. Joseph’s, Lawson Associate Scientist and Professor at Schulich Medicine & Dentistry. “We hope this will be the first step towards personalized care, ultimately leading to fewer stent-associated infections.”
The study was made possible through the generous support of The W. Garfield Weston Foundation and St. Joseph’s Health Care Foundation.
-30-
DOWNLOADABLE MEDIA

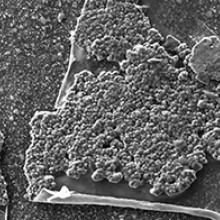
Scanning electron microscopy images showing organic material, crystals, and bacteria present on the surface of the ureteral stents.
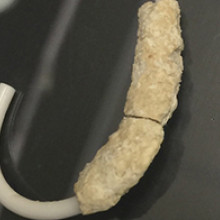
Recovered ureteral stent encrusted with minerals and bacteria.
See all Lawson Media Releases
Lawson Health Research Institute is one of Canada’s top hospital-based research institutes, tackling the most pressing challenges in health care. As the research institute of London Health Sciences Centre and St. Joseph’s Health Care London, our innovation happens where care is delivered. Lawson research teams are at the leading-edge of science with the goal of improving health and the delivery of care for patients. Working in partnership with Western University, our researchers are encouraged to pursue their curiosity, collaborate often and share their discoveries widely. Research conducted through Lawson makes a difference in the lives of patients, families and communities around the world. To learn more, visit www.lawsonresearch.ca.
Western delivers an academic experience second to none. Since 1878, The Western Experience has combined academic excellence with life-long opportunities for intellectual, social and cultural growth in order to better serve our communities. Our research excellence expands knowledge and drives discovery with real-world application. Western attracts individuals with a broad worldview, seeking to study, influence and lead in the international community.
The Schulich School of Medicine & Dentistry at Western University is one of Canada’s preeminent medical and dental schools. Established in 1881, it was one of the founding schools of Western University and is known for being the birthplace of family medicine in Canada. For more than 130 years, the School has demonstrated a commitment to academic excellence and a passion for scientific discovery.
Senior Media Relations Consultant
Communications & Public Engagement
T: 519-685-8500 ext. 73502
Celine.zadorsky@lhsc.on.ca
New urinary microbiome study could be first step in providing personalized care to patients with ureteral stents
For patients with kidney stones, ureteral stents (hollow devices placed in the ureter – the tube between the kidney and bladder) can be used temporarily to relieve urinary obstruction. Despite the use of antibiotics, ureteral stents often become encrusted with minerals and coated with bacteria. This can lead to complications like infection and the need for replacement surgery.
Published today in Cell Reports Medicine, researchers at Lawson Health Research Institute and Western University conducted a novel microbiome study to examine bacteria associated with ureteral stents. They found that nearly all the stents, whether visibly coated or not, had unique bacterial profiles that were most associated with a patient’s medical condition rather than antibiotic use. For patients with ureteral stents, they may benefit from a personalized approach to care and antibiotic treatment.

The study included 241 patients from St. Joseph’s Health Care London. The research team collected and analyzed patient urine samples and ureteral stents following surgical removal, as well as relevant patient information such as antibiotic use and history of infections.
“We wanted to know which bacteria were present and whether the bacteria found in urine samples corresponded to the bacteria found on a patient’s stent,” explains Dr. Kait Al, Postdoctoral Fellow at Lawson and at Western’s Schulich School of Medicine & Dentistry. “We found that there was a bacterial community present on almost all stents, even if they were not visibly affected, and that it differed from the bacterial community found in a patient’s urine.”
These findings challenge long-held beliefs that the urinary tract is a sterile environment devoid of bacteria.
The study revealed that the bacteria present were determined by an individual patient’s medical condition. They differed significantly based on comorbidities like irritable bowel syndrome, obesity and hypertension. Antibiotic use within the past 30 days did not seem to have an effect on the types of bacteria detected on the stents.
“While more research is needed, our study suggests that antibiotic use during the placement of these stents could one day be more conservative or targeted based on each patient’s condition,” says Dr. Jeremy Burton, Lawson Scientist and Associate Professor at Schulich Medicine & Dentistry.
The team also discovered that in patients needing multiple stents, the bacterial community remained stable over time, suggesting that infections on a patient’s previous stent could direct the course of treatment for their future device placements.
“This is the largest study of its kind, investigating bacteria both in urine and adhered to ureteral stents,” states Dr. Hassan Razvi, Urologist at St. Joseph’s, Lawson Associate Scientist and Professor at Schulich Medicine & Dentistry. “We hope this will be the first step towards personalized care, ultimately leading to fewer stent-associated infections.”
The study was made possible through the generous support of The W. Garfield Weston Foundation and St. Joseph’s Health Care Foundation.

Dr. Kait Al, Postdoctoral Fellow at Lawson and Schulich Medicine & Dentistry
noteWORTHY – Teamwork and patients inspire clinical research assistant
St. Joseph’s celebrates people who provide exceptional care, grow stronger communities and contribute to a healthier world. Today, meet Heather LaPier, a clinical research assistant whose work helps keep clinical research running smoothly for four Lawson research scientists in diabetes and nephrology. She is a liaison among patients, researchers, clinicians, ethicists, regulatory bodies and pharmaceutical companies.
What values or people inspire your work:
I couldn’t ask for better than the physicians and researchers I work with. It’s a true team. We can bring our own ideas and expertise and know that we’re valued. We’re all good at showing appreciation for each other.
Best part of your workday:
Visiting with people receiving dialysis. They have treatment four hours a day, three times a week, so they’re used to talking with physicians and staff and we get to know them really well. They’re honest and funny – and, despite living with a chronic illness, they’re some of the most positive people I’ve ever met.
What one thing do you wish people knew about your work?
Our job is to advocate for patients and protect them, so every study is carefully designed, planned, regulated and monitored. We work to find solutions to patients’ health issues, and that means putting them first.
One big thing people should know is that participants in clinical trials and research studies get extra care and attention. Other patients have regular appointments, maybe every six months, but as a participant in research they’ll have even more frequent monitoring. So even though they’re helping advance medical knowledge generally and there’s no certainty of direct benefit to them from a specific clinical trial, they do have a whole team of people fully involved in their current care. Any time they have a question, they have direct access to an endocrinologist or nephrologist.
Why this work is meaningful to you:
It’s definitely exciting and always interesting. It can be easy to get caught up in the day-to-day tasks – but I never want to lose sight of the fact patients are living longer and better lives because of the work we’re doing. I have a front-row seat when patients come in for visits and tell us a diabetes treatment or a dialysis intervention is making them feel better.
Back-story:
My mom has been a nurse for over 30 years, so I grew up in a home where we talked about health and patient care a lot. We have a shared language. After my university degree, I applied to college for either forensic science or clinical research. I’m so glad clinical research is where I landed.
One other thing:
I love learning about the history of the Second World War, specifically naval ships and naval battles. It seems totally random, but I studied it as one of my non-science courses in university. I still find it fascinating.
Well said:
Heather is a true gem – highly skilled, creative, and an outstanding team player who expertly manages multiple research projects and investigators. She has been a game-changer for diabetes, metabolic, and chronic disease research at Lawson Research Institute, supporting everything from qualitative studies to large randomized-controlled trials with innovative designs. Our successes wouldn’t have been possible without her.
- Dr. Kristen Clemens, St. Joseph’s endocrinologist and Lawson Research Institute scientist
