Search
Search
Third clinical trial launched to study whether type 2 diabetes can go into remission
Since launching two years ago, an innovative study that aims to induce remission of type 2 diabetes has captured the attention of hundreds of Londoners. For those with type 2 diabetes like Greg Ackland and Jocelyne Chauvin, the idea of stopping all medications has translated from a dream to a reality through participation in the REMIT study at Lawson Health Research Institute (Lawson).
With a family history of type 2 diabetes, Greg Ackland was first diagnosed over six years ago when he underwent an operation for a hernia. He developed a mild infection and, while being treated, his care team discovered his blood sugar levels were high.
Ackland started treatment and was eventually taking four pills per day. “I watched the progression of my medications and thought ‘I’m losing this battle,’” says 51 year-old Ackland.

Above: Greg Ackland, research participant in the REMIT study
He saw information about the REMIT study on the local news and after meeting the criteria he was enrolled. The outcomes have been incredible. Ackland has now stopped all medications and his blood sugar levels are good. He has recommitted to exercise which has resulted in weight loss and muscle gain.
“I’m glad I jumped at the opportunity to participate in this trial,” says Ackland. “I’ve reset myself.”
Lawson is one of seven Canadian sites taking part in the REMIT study, which is considered a significant departure in strategy in the care of people with type 2 diabetes. The study consists of a series of clinical trials that tests an aggressive approach in recently diagnosed patients. The first two trials in London saw significant interest in participation from those with type 2 diabetes. A third REMIT trial is now being launched providing another opportunity for individuals with type 2 diabetes to take part.
“The goal of the REMIT study is to take a proactive approach to help people early in the disease, normalize their blood sugars for a period of 12 weeks and then slow the progression of the disease and the need for additional medications,” says Dr. Irene Hramiak, Lawson researcher, endocrinologist, and Chief of the Centre for Diabetes, Endocrinology and Metabolism at St. Joseph’s Health Care London. “We want to know if we can induce remission, for how long and whether it matters what combination of medications we use.”
The standard treatment for people with type 2 diabetes is to start on a single medication, which is then followed by the addition of more drugs and insulin as the disease progresses. In the REMIT study, patients receive intensive treatment early in their care journey that consists of two diabetes medications plus insulin at bedtime for three months to see if remission can be induced. In addition, patients are supported to make lifestyle changes with a diet and 30 minutes of exercise each day.
“When I saw a gentleman on the news talking about the REMIT study and how it allowed him to stop taking all medications, I thought ‘cool!’” says Jocelyne Chauvin. The 62 year-old Londoner was first diagnosed with type 2 diabetes three years ago after a regular checkup. While it was difficult news, she had a family history of the disease and health issues before her diagnosis.

Above: Jocelyne Chauvin, research participant in the REMIT study
“I started taking one pill a day and was told I’d be up to four pills a day within six months,” says Chauvin. “But with good nutrition and exercise I worked hard to stay on one pill a day for three years.”
After hearing about the study, she contacted the research team and, after meeting the criteria, was enrolled in April 2017. Chauvin has now stopped all medications and says she feels much better. She exercises more and her blood sugar levels are close to normal.
“This is my first time participating in a clinical trial and I’m very excited about my experience,” says Chauvin.
REMIT is being led by the Population Health Research Institute (PIHR), a joint institute of McMaster University and Hamilton Health Sciences. The study follows a PHRI pilot study of early aggressive treatment that resulted in up to 40 per cent of intervention group participants with type 2 diabetes going into remission and not needing any diabetes treatment for at least three months.
“The idea of putting type 2 diabetes into remission is changing the way we think about the disease. It has a strong appeal to both those with type 2 diabetes and clinicians,” says Dr. Hramiak. “It’s changing the paradigm of when and how to use medication for type 2 diabetes.”
Those who would like more information about the trial can call 519-646-6100 ext. 65373.
Tom Miller
Tom Miller, MD
Associate Professor, Schulich School of Medicine and Dentistry
Neuromuscular Function
Dr. Thomas Miller is a physiatrist at Parkwood Institute and an Associate Professor in the Schulich School of Medicine and Dentistry at Western University in the Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation. Dr. Miller completed his medical degree at Queen’s University in 1989, and then completed subsequent training in physical medicine & rehabilitation at the University of Ottawa and a fellowship in clinical neurophysiology at University of New South Wales in Australia.
Dr. Miller is the Medical Director of the neuromusculoskeletal rehabilitation program at Parkwood Institute, Director of the Electrodiagnostic laboratory, consultant physiatrist with the Hand and Upper Limb Centre. He is also the co-director of the Peripheral Nerve Clinic at Parkwood Institute, a multidisciplinary assessment and treatment program for major nerve injury. Specific areas of academic research include peripheral nerve injury and its rehabilitation, spasticity rehabilitation and the neurophysiological assessment of function and mobility.

Top 12 research stories of 2022
As the research institute of London Health Sciences Centre (LHSC) and St. Joseph’s Health Care London, our teams impact the lives of people in Ontario, Canada and around the globe with groundbreaking studies, world firsts and translational research that enhances care, health and wellbeing. Here are some of Lawson Health Research Institute’s top research highlights of 2022.
Researchers looking to better personalize treatment for PTSD

In a new study through Lawson and Western University’s Schulich School of Medicine & Dentistry, scientists are looking at a form of treatment called deep brain reorienting (DBR) for those suffering from post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Read more.
Virtual care associated with significant environmental and patient cost savings

A new study by researchers at ICES, Lawson and Western finds that virtual care during the COVID-19 pandemic led to a significant reduction in carbon dioxide emissions and patient travel-related expenses, such as gasoline, parking or public transit costs. Read more.
Novel test that could easily diagnose blast injury created by local scientists

In a world first, researchers at Lawson and Defence Research and Development Canada have developed a breath test that could be used to diagnose repetitive blast injury – a mild traumatic brain injury resulting from pressure changes that occur during explosions. The device will soon go through clinical trials to validate its efficacy. Read more.
Local researchers using artificial intelligence to lead the way in bedside lung imaging
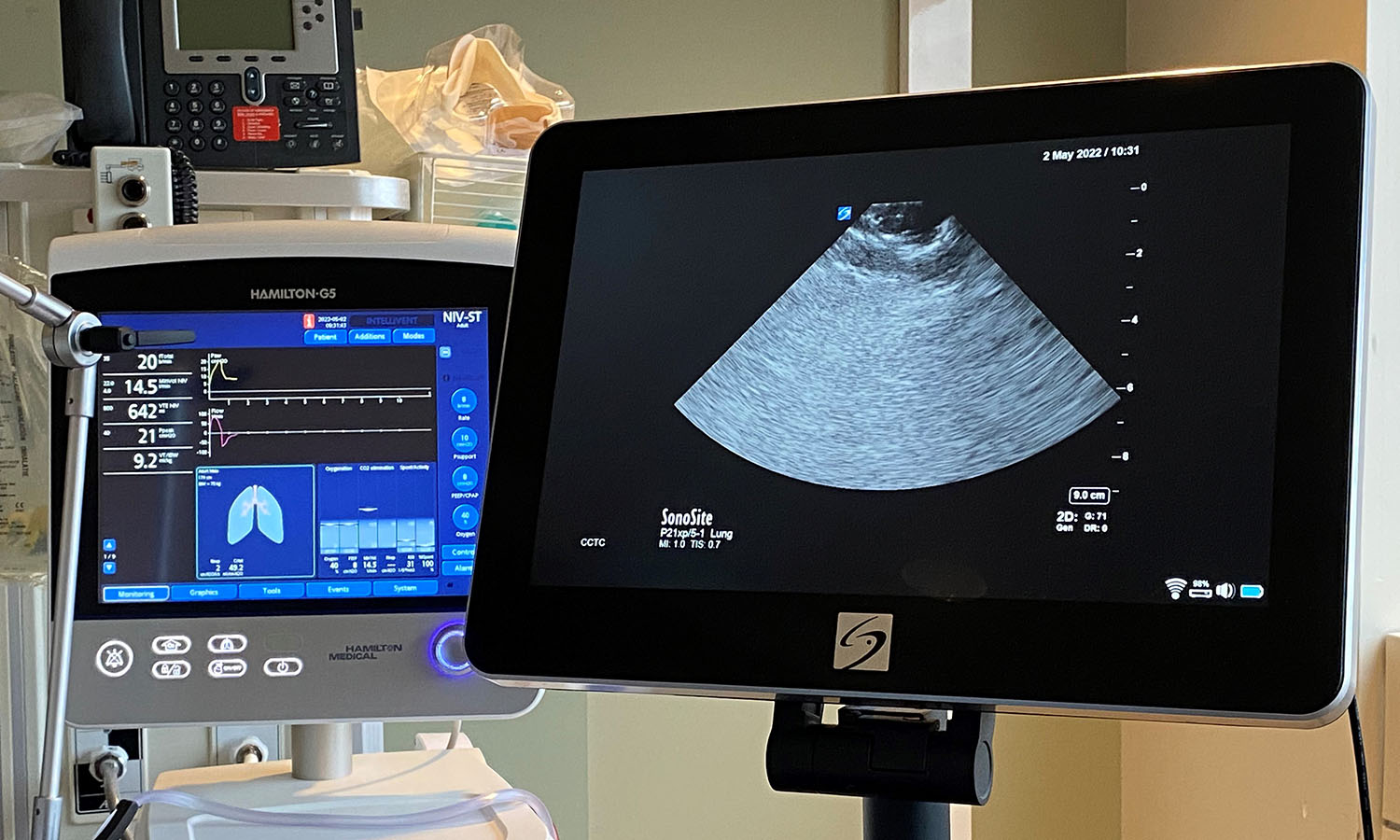
A team at Lawson is testing a new form of artificial intelligence (AI), paired with portable ultrasound machines, to image and identify lung concerns in real time, right at the beside of critically ill patients. Approximately 100 critical care patients at LHSC will be part of this study. Read more.
New tool shows promise in helping people manage traumatic brain injuries one pace at a time
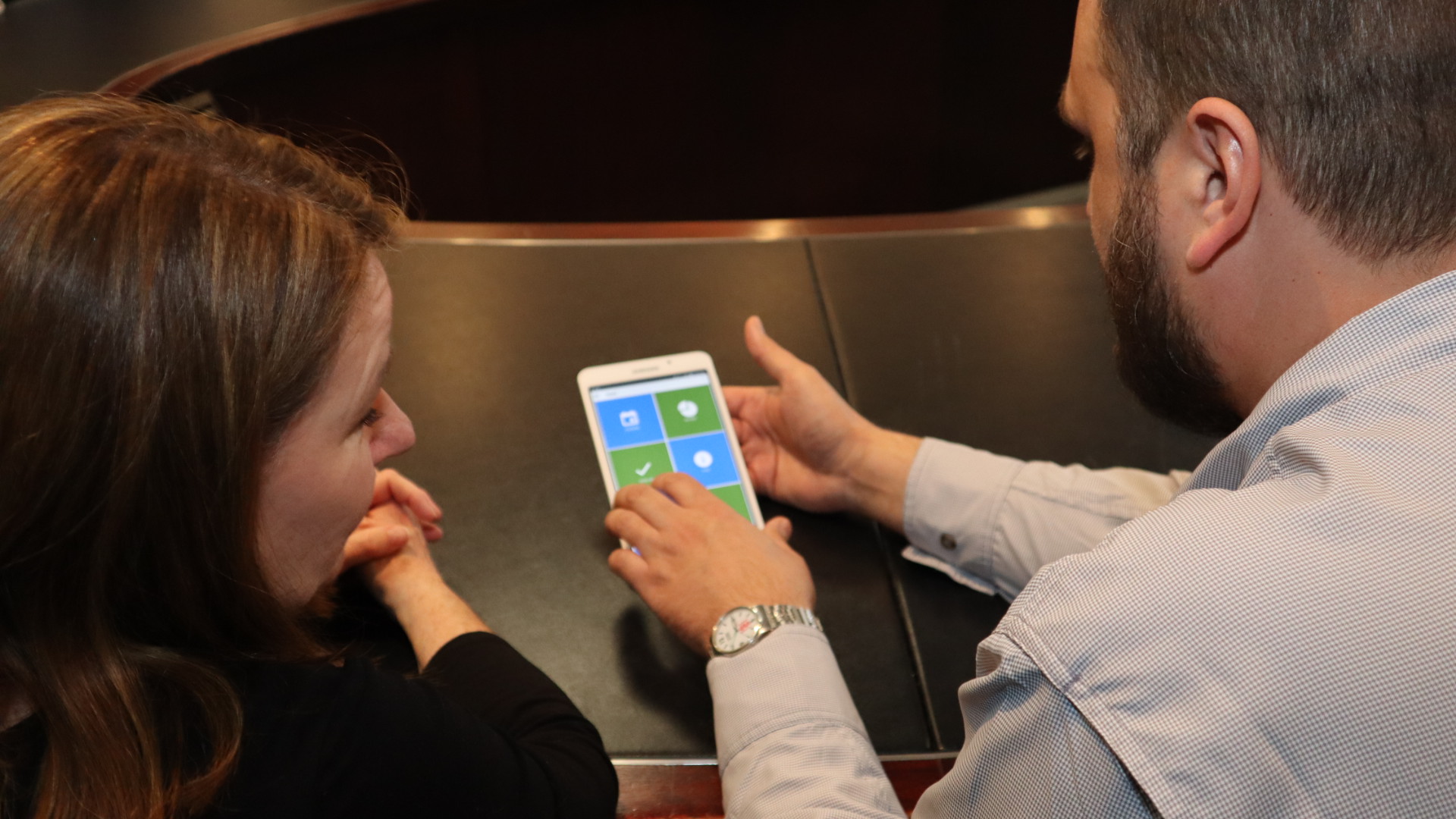

A team at Lawson has developed a new app called MyBrainPacer™ which aims to better assist and treat those living with mild traumatic brain injuries (mTBI), including concussions. mTBI may come with lasting effects that can alter a person’s life. Although a person with a mTBI may appear fine on the outside, many have to pace their day-to-day activities in order to allow the time needed for the brain to properly heal. Much like point tracking used by dieters to monitor food choices, through MyBrainPacer™ App, users can assign values to tasks like driving, grocery shopping, screen use and exercise so they can plan and pace their daily activity. Read more.
Study shows a decline in Veterans' mental health throughout the pandemic

When it comes to mental health conditions, Veterans are an at-risk population, often having higher rates of depression and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). When the COVID-19 pandemic hit, scientists at Lawson wanted to understand its effects on this already at-risk population. They found that more than half of Canadian Veterans reported a decline in their mental health. Read more.
Growing evidence that PSMA imaging improves prostate cancer detection
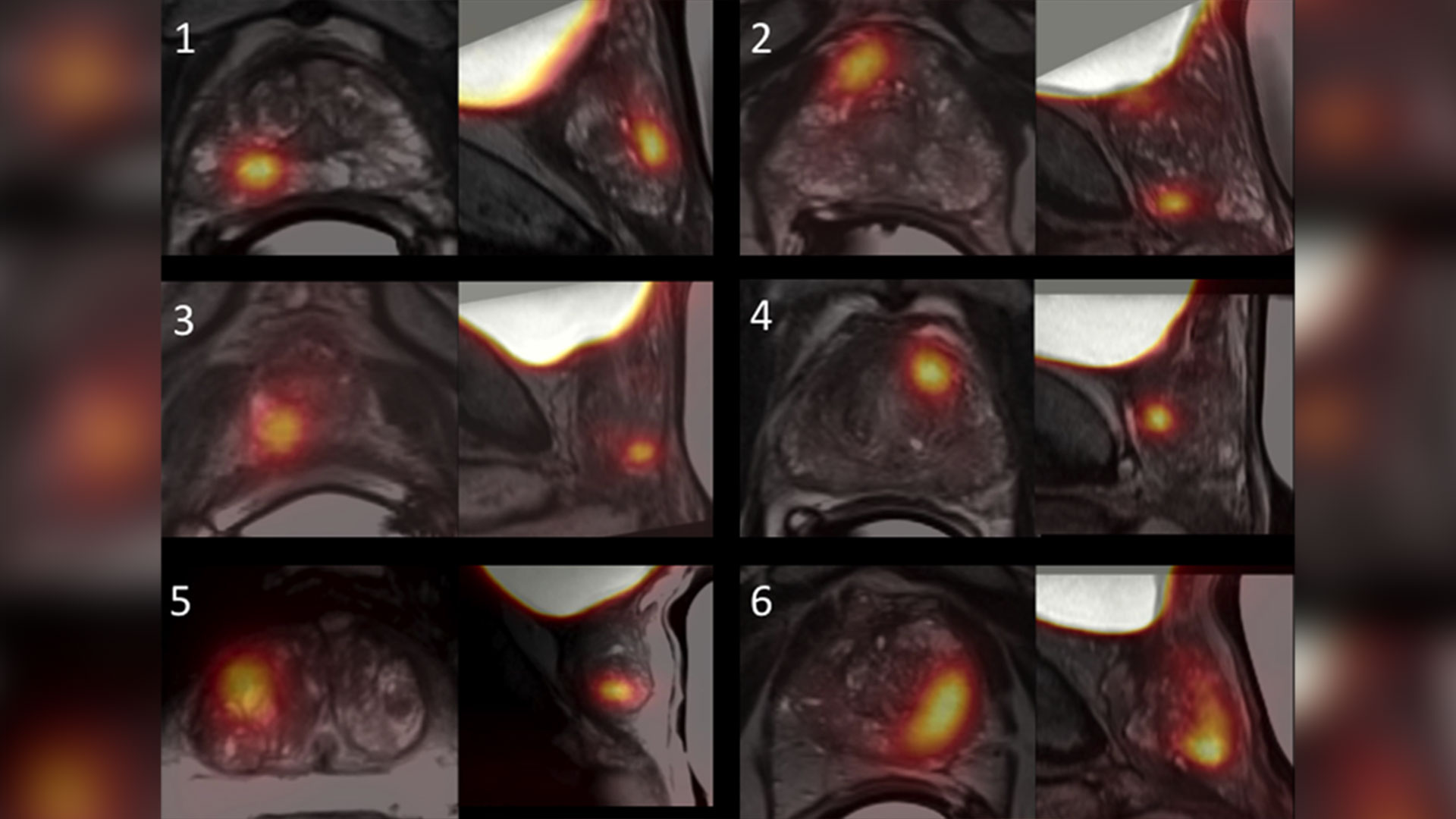
Scientists at Lawson are leading the way in using specialized imaging to detect prostate cancer – the fifth leading cause of cancer death in men around the world. Early evidence indicates that PSMA PET scans have changed how prostate cancer is being treated, but more work is underway to understand the impact of those treatment changes. Read more.
Leveraging virtual reality to manage pain in paediatric patients
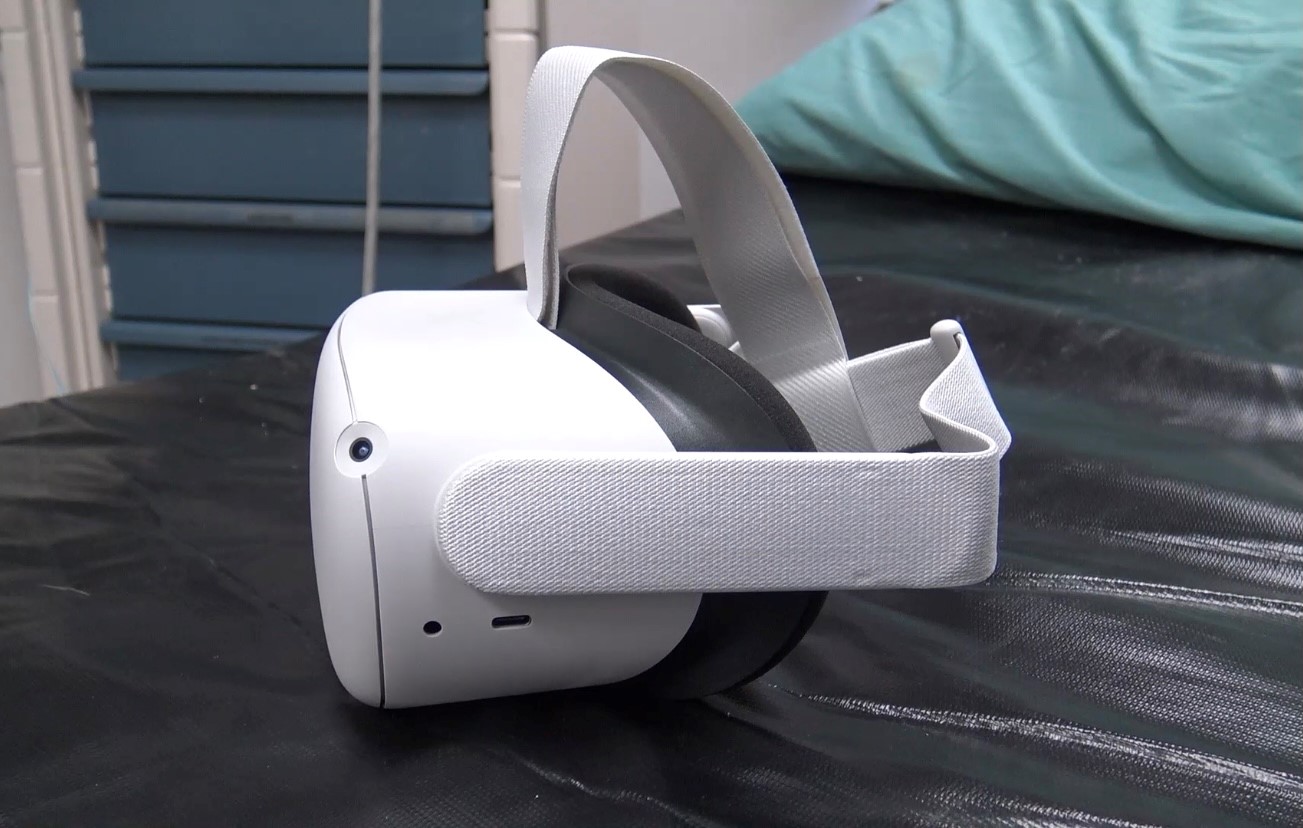

A study underway through Lawson and Children’s Hospital at LHSC is using virtual reality (VR) to help paediatric patients during painful and distressing procedures. The study is focusing on paediatric patients who need port access. A port is a little reservoir that sits underneath the skin that allows access to blood or medication with the use of a needle. Ports are most commonly used in paediatric cancer patients. Read more.
Team players: FMT and microbiome research could have widespread impact

There is still much to learn about the human microbiome and its role in fighting disease, but ongoing studies at Lawson, including a focus on fecal microbial transplants (FMT), are making strides in harnessing this complex system. FMT is being studied in connection with conditions as varied as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, rheumatoid arthritis, atherosclerosis, HIV, cancer and multiple sclerosis. Read more.
London researchers adapt MRI technology to image salt within the kidneys
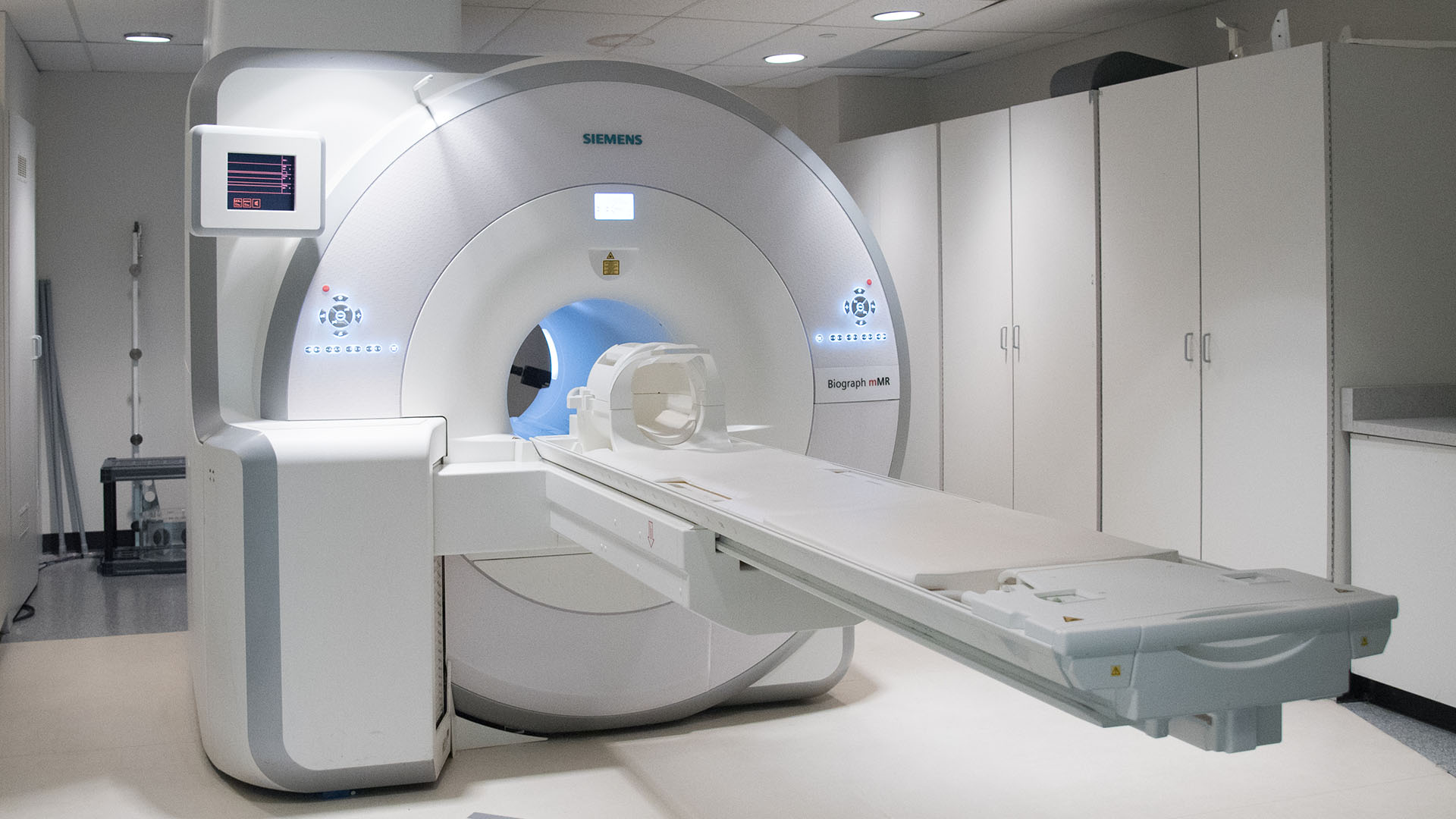
Scientists at Lawson have adapted PET/MRI technology to accurately image salt within the kidneys of patients with kidney disease. Imaging salt within the kidneys has never been accurately accomplished in patients with kidney disease, but Dr. McIntyre and his team developed new technology and software that was adaptable to a PET/MRI machine at St. Joseph’s. Read more.
London researchers discover novel method to diagnose long COVID
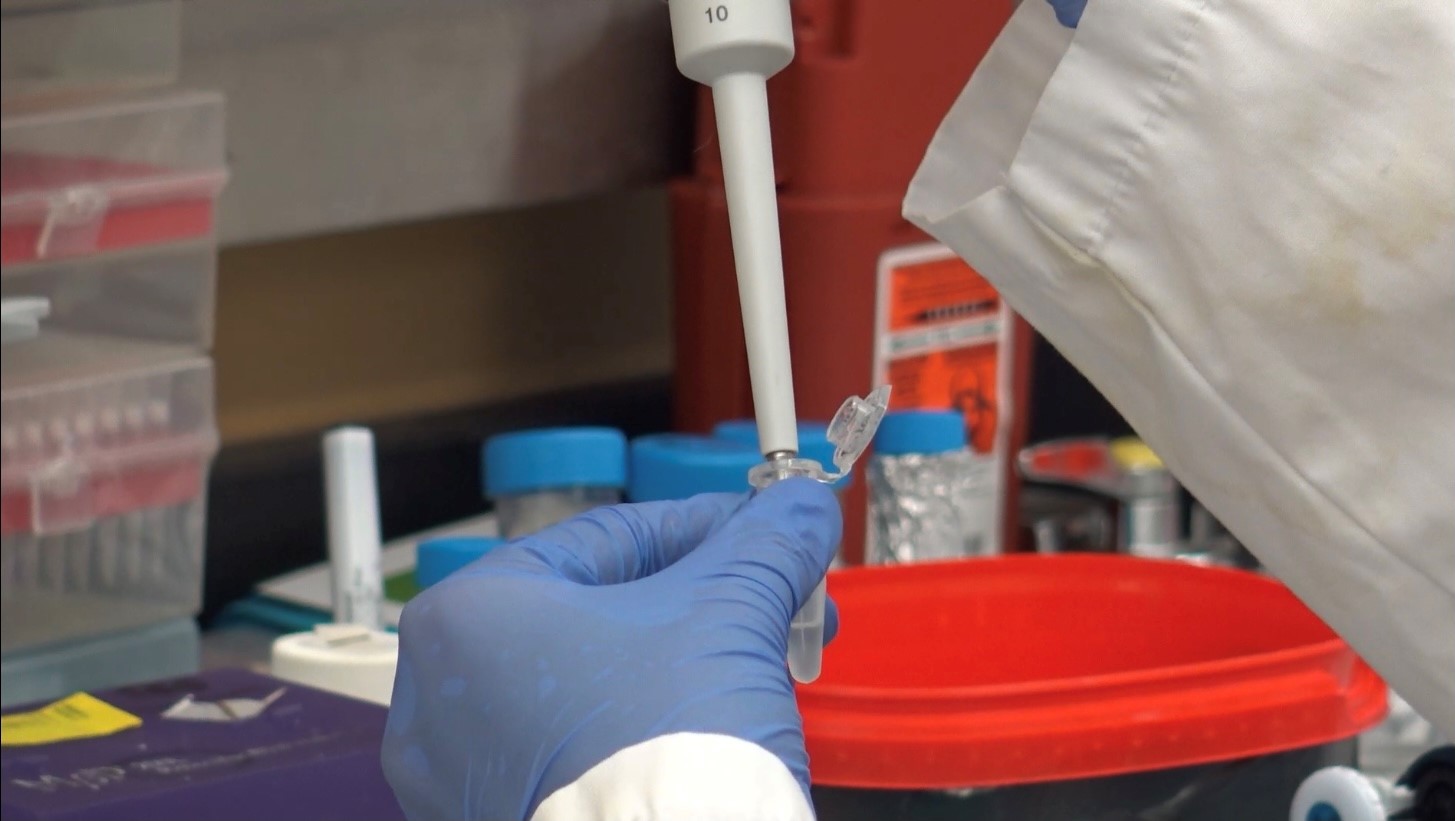
Published in Molecular Medicine, researchers at Lawson have found that patients with post-COVID-19 condition (long COVID) have unique biomarkers in their blood. The team is now working on developing a first of its kind blood test that could be used to diagnose long COVID. The discovery could also lead to new therapeutics for this condition. Read more.
Largest trial ever done in hemodialysis care examines optimal dialysis temperature
Published in the Lancet findings from a large clinical trial through Lawson, ICES Western and Western University suggest that lowering dialysis temperatures does not lead to improved patient outcomes, despite previous studies suggesting otherwise. Read more.
To learn more about Lawson research studies, please visit our News and Media page
Senior Media Relations Consultant
Communications & Public Engagement
T: 519-685-8500 ext. 73502
Celine.zadorsky@lhsc.on.ca
Two new research chairs announced for imaging
In a historical-first, St. Joseph’s Health Care Foundation and Western University announced two research chairs that are a critical step toward new approaches in imaging research and patient care in London and around the world. The combined value of both innovative new research chairs is $6.5M, which will be endowed in perpetuity to advance imaging research at Western University and Lawson Health Research Institute.
The research chairs have been named after the two scientists who are revolutionizing health care through their groundbreaking imaging research – Drs. Ting-Yim Lee and Frank Prato.
“These Chairs build on the legacy of exceptional imaging leadership across our academic, research and healthcare organizations. They are a critical step towards new approaches in medical technology and hospital-based research that will revolutionize patient care,” says Dr. Gillian Kernaghan, President and CEO, St. Joseph’s Health Care London.
Research teams in the city are using state-of-the-art imaging technology to help clinicians better predict and diagnose illnesses before their unset. And uncover why, and how, illness forms to one day find a cure to some of the most devastating diseases in the world.
“We’ve come to know medical imaging as one of the cornerstones of innovation and discovery at Lawson, and the two new research chairs represent two monumental leaps forward in the field of imaging research,” adds Dr. David Hill, Lawson Scientific Director.
The Ting-Yim Lee Chair in Cardiac Computerized Tomography (CT) Imaging Research has been established through the generosity of Ting-Yim and Maggie Lee and a joint funding collaboration between St. Joseph’s Foundation and Western University.
Dr. Ting Yim Lee is a scientist and professor of the Schulich School of Medicine & Dentistry, medical physicist at St. Joseph’s Health Care London and a scientist with Lawson’s Imaging program. Through his leadership, The Ting-Yim Lee Chair in Cardiac Computerized Tomography (CT) Imaging Research will transform the way clinicians diagnose, and prevent, severe tissue damage in persons who have experienced a cardiac event.
“Over the past 28 years, St. Joseph’s and Western have created opportunities for me and supported my research endeavor in many ways. I feel this gift is the best way to repay the help that I have received. We are onto something that is worthwhile and successful. By setting up this Chair, there would be a significant person – a clinician-scientist – to lead the next phase of the cardiac CT program. I am really humbled that the institutions see the value in this research and have contributed to guarantee that we have the necessary leader to carry forth this development,” says Dr. Lee.
This Chair represents the next phase of CT imaging research, focused on developing software and new methods that will save people’s lives.
The Dr. Frank Prato Research Chair in Molecular Imaging has been established to further enhance scientific understanding in the specialty of molecular imaging – building upon St. Joseph’s internationally-recognized leadership in imaging excellence.
Dr. Frank Prato is a scientist and professor of the Schulich School of Medicine & Dentistry, Chief Medical Physicist at St. Joseph’s Health Care London and the Founder and Program Leader of Lawson’s Imaging Program. Through his visionary leadership, The Dr. Frank Prato Research Chair in Molecular Imaging will improve the way clinicians effectively diagnose disease and actively correct the course of treatments in real time for life-threatening illnesses.
“I am truly honoured to have this Research Chair in Molecular Imaging named after myself. Over the past 40 years I have been privileged to work with outstanding people and incredible resources. Today Medical Imaging has become a cornerstone of care at St Joseph's Hospital. Here at St Joseph's we realize patient stewardship includes research as an essential part of the patient care continuum and that discovery, through research, leads to improved patient care. The holder of this chair will help lead us into the next frontier of medical imaging directly benefiting our local, national and global communities,” says Dr. Prato.
This Chair represents the next phase of precision medicine using molecular imaging to distinguish between varying forms of dementias, cancers, and to detect the early onset of cardiac disease and diabetes before symptoms emerge.
“With this historic announcement, we are marking a new phase of partnership and collaboration between our institutions and celebrating the generosity of donors who have helped create two significant research chairs,” explains Dr. Amit Chakma, President and Vice-Chancellor, Western University. “Together we will ensure that London remains at the forefront of medical imaging research and teaching.”
These Chairs will also have a greater role to play in the local health care community by attracting, and retaining, the research talent needed to innovate the way London’s hospitals and Western tackle the most pressing health issues Canadians face today.
Understanding the COVID-19 virus through health research
In the early months of the COVID-19 pandemic, there was little known about the virus that was causing the COVID-19 illness. Hospital researchers in London, Ontario, through Lawson Health Research Institute, quickly got to work to study and better understand the SARS-CoV-2 virus. Lawson is the research arm of London Health Sciences Centre (LHSC) and St. Joseph’s Health Care London.
“When the pandemic hit, we were well prepared in London to start research studies. We had existing expertise, laboratories and teams through the hospitals, Lawson and Western University that could be mobilized quickly,” explains Dr. Douglas Fraser, Critical Care Physician at LHSC and Scientist at Lawson. “Patients started coming to hospital with COVID-19 and we began research that involved collecting human samples and bringing them to the lab for analysis.”
Dr. Fraser, who is also a Professor at Western’s Schulich School of Medicine & Dentistry, led the research team studying the samples from COVID-19 patients in hospital. “We learned very quickly that COVID-19 patients were experiencing a strong inflammatory response to the virus. We looked at the molecules involved because many of these are signaling molecules to the immune system.”

Dr. Douglas Fraser, Critical Care Physician (LHSC) and Lawson Scientist
“By studying the molecules, we were able to determine the pathways. This is important because it also points to how we should be targeting our diagnostics and therapeutics,” adds Dr Fraser.
As a hospital research institute, Lawson is uniquely positioned to address the medical questions posed by a new virus. Its Clinical Research Services (LCRS) and Center for Clinical Investigation and Therapeutics (CCIT) teams responded rapidly when researchers initiated COVID-19 studies, including Dr. Fraser’s study to examine the immune response in patients with COVID-19.
“Starting a clinical trial usually takes a certain amount of time to put together, but the pandemic created a perfect storm,” explains Sue Tereschyn, Manager of LCRS at Lawson. “Clinical researchers had to develop studies at a speed they have never seen, and they needed implementation support at the same speed. In Dr. Fraser’s case, we needed samples from the Intensive Care Unit (ICU) and we were processing samples from COVID-19 patients seven days a week. A high level of skill was needed.”
Dr. Fraser and his team soon became the first in the world to understand the immune response and several pathophysiological features of the virus. This work led to a critical understanding of how the virus was impacting patients and potential avenues for therapy.
“It’s important to understand what’s happening in the body when someone has COVID-19 because that gives us information as to why some patients don’t do well and why others recover,” shares Dr. Fraser. “This helps us know who is vulnerable to COVID-19 and how to best offer treatments in the future.”
Read about Dr. Fraser's COVID-19 research:
- Researchers team up with Diagnostics Biochem Canada to study COVID-19
- Study identifies biomarkers that could be used in a quick, inexpensive COVID-19 blood screening tool
- Researchers unravel two mysteries of COVID-19
Work is also underway to find the unique fingerprint that the COVID-19 virus can leave on the lungs. Hospital researchers at Lawson have developed and tested an artificial neural network for diagnosing COVID-19.

Dr. Robert Arntfield, Medical Director, Critical Care Trauma Centre (LHSC) and Lawson Researcher
“The lung ultrasound techniques and the findings of COVID-19 by looking at the lungs didn’t initially look unique when compared to other conditions like pneumonia. Our group wanted to investigate whether or not there were differences that were possibly subvisible,” says Dr. Robert Arntfield, Medical Director of Critical Care Trauma Centre at LHSC and Lawson Researcher. “Through our work, we were able to show that in fact artificial intelligence could outperform a trained clinician in identifying a COVID-19 lung from a similar affected lung that was not due to COVID-19.”
This new technique just scratches the surface of the beneficial use of AI when it comes to medical imaging for patients. “It shone a light on the idea that there were hidden details within all the noise of the image,” adds. Dr. Arntfield. “When you can input that into a machine that is extremely portable the way ultrasounds are, you have a precise diagnostic machine that you can take anywhere a tablet can go.”
The team is now expanding on these findings with further research. Lawson has recently approved Dr. Arntfield’s “Project Deep Breath” which aims to go beyond COVID-19 and explore multiple conditions where lung ultrasounds and AI can be paired together.
Unique imaging research by Lawson sparks international collaboration
The Bioelectromagnetics and Human Threshold Research Group at Lawson Health Research Institute has an international reputation and expertise on human brain response to time-varying magnetic fields (MFs). This pioneering research has inspired an international collaboration to duplicate Lawson Imaging’s unique experimental expertise in Europe.
The team is now working with EuroMov, a research centre located in France, to duplicate the scientific approach and techniques in a new lab. The goal is to double research capabilities and further stimulate scientific knowledge in this area.
Fluctuating MF induces electric fields and currents in conductive tissues. Above a certain threshold, these fields and currents will change the physiological electric activity within neuronal tissues. Lawson’s team is currently the only one in the world stimulating participants with power-frequency MF of sufficient intensity to result in acute neurophysiological response. This can involve interferences with visual perception, motor output and other cognitive functions.
“An international synergy between the Bioelectromagnetics and Human Threshold Research Group at Lawson and EuroMov will increase the scope of scientific expertise for both institutions” explains Dr. Legros, Director of Bioelectromagnetics and the Human Threshold Research Group at Lawson Imaging. “Both will have access to a wide range of brain stimulation techniques and imaging modalities.”
Through this new collaboration, researchers are excited to merge their expertise and tackle questions together, opening new avenues for original research ideas and projects. This new intercontinental synergy also increases the scope of options for academic funding and international training programs for students.
Furthermore, there is great potential for reinforcing and extending the group’s industry-partnered supporting program, which already associates industry sponsors (such as Hydro-Québec, Électricité De France, Réseau de Transport d’Électricité, NationalGrid/Energy Network Association, Electric Power Research Institute) under an international consortium: the Utilities Threshold Initiative Consortium (UTIC).
The growing network of international scientists working in this field assist international regulation agencies, governments and industries to better understand the impact of electromagnetic exposure on brain activity and physical behaviour. Knowing the thresholds for human responses allows these institutions to adjust their recommendations and policies for when exposures could become unsafe for the public and workers.
The potential applications in research, industry and health care are vast, including the world of video gaming and virtual reality!
“We are excited to see discovered effects and mechanisms translated towards therapeutic applications to the benefit of patients,” says Dr. Legros. “For example, we could improve neuromodulation and neurostimulation technologies to better address movement disorders such as in Parkinson’s Disease. In another application, knowledge of the vestibular responses to stimulation may help to manage symptoms such as motion sickness.”
EuroMov is a university-based European centre for research and innovation in the science of movement. Conducting both fundamental and clinical research, it proposes innovative technological solutions allowing the capture, simulation, learning and rehabilitation of movement. EuroMov contributes to the creation of innovative starts ups and businesses in the field of health, performance, sport, human factors, and rehabilitation.
Dr. Legros is also an Associate Professor in the Departments of Medical Biophysics, Medical Imaging and Kinesiology at Western University’s School of Kinesiology, and an Associate Scientist at EuroMov.
Find out more about his research:

Above: Members of the Bioelectromagnetics and Human Threshold Research Group at Lawson.
From left to right, bottom: Shirin Davarpanah Jazi, Postdoctoral Scholar; Alicia Allen, Masters Candidate; Cadence Maureen Baker, Masters Candidate.
From left to right, top: Michael Corbacio, RA/Lab Manager); Dr. Alexandre Legros, Principal Investigator and group leader; Sebastien Villard, Postdoctoral Scholar.
Missing from the photo: Nicolas Bouisset, PhD Candidate; Lynn Keenliside; Manager Technical Services.
Unlocking boundless potential
Ashmeet Gill had her first PET/CT scan shortly after being diagnosed with Hodgkin’s lymphoma, a cancer of the body’s germ-fighting immune system. She was nervous. Claustrophobia is an issue for the young Stratford resident and the scan, necessary to determine if the cancer had spread beyond the lymph nodes in her neck, would take 34 to 45 minutes, she was told.
Wrapped in a sheet and tucked inside the tube of the PET/CT at St. Joseph’s Health Care London (St. Joseph’s), Ashmeet, then 24, steeled herself to remain calm. But near the end of the scan, a sense of panic set in.
“It was not pleasant but I endured it. I made it through.”
Ashmeet’s next PET/CT scan would be six months later, after six cycles of chemotherapy, to determine if the treatment had worked. She was terrified of another panic episode. By then, however, St. Joseph’s had a brand-new PET/CT – Canada’s first, next generation, state-of-the-art Omni Legend PET/CT from GE HealthCare.
This time, Ashmeet’s scan took “barely 15 minutes or so,” she recalled.
“I thought, seriously? I couldn’t believe I was done. I was so happy.”
With the very first patients scanned with St. Joseph’s new PET/CT machine, it was obvious the breakthrough technology was living up to high expectations.
The machine is fast – decreasing the time it took for a scan from about 45 minutes on the older system to less than 14 – head to toe. Patients are exposed to less radiation, and the ability to precisely detect disease and tiny abnormalities is outstanding.
“This is what we have been waiting for,” says Ting-Yim Lee, a pioneer in the use of machines like PET/CT to gather new, vital information about diseases. “St. Joseph’s new Omni Legend by GE HealthCare is answering the call for patients, clinicians and researchers alike.”

PET/CT is the medical ace in imaging for the assessment and treatment monitoring of cancer, neurodegenerative disorders, and metabolic and cardiovascular diseases. At St. Joseph’s, the possibilities of this technology took a giant leap forward in August 2023, thanks in part to the generosity of donors and a $1 million contribution from St. Joseph’s Health Care Foundation. With the arrival of the new system, St. Joseph’s is set to become Canada’s first national GE HealthCare centre of excellence in molecular imaging and theranostics. This two-pronged approach to diagnosing and treating cancers and other diseases merges molecular imaging with the use of radiopharmaceuticals to identify the location and extent of diseased tissues and selectively destroy the abnormal cells.
“The speed at which we can now do exams means significantly improved comfort for patients while the exceptional image quality changes the game in the hunt for cancerous lesions,” explains Ting, Director of PET/CT Research at Lawson Health Research Institute (Lawson) and medical physicist at St. Joseph’s Hospital.
“For young adults undergoing repeat PET/CT exams due to their medical conditions, managing the radiation dose is critical,” explains Dr. Narinder Paul, Lawson scientist and Chief, Medical Imaging, at St. Joseph’s. “These individuals already face an elevated life-time risk of developing cancer from radiation, and this risk further increases with additional exposures.”
For older adults, the time it takes for the examination is also of great concern. Lying still for long periods can be a hardship due to pain from bone metastases or other conditions, and is a challenge for those who have dementia, are claustrophobic or experiencing other issues, adds Dr. Paul.
“Reducing the exam time is a huge improvement in the patient experience for these individuals.”
While patients hail the new PET/CT experience, clinicians and scientists are raving about the machine’s imaging prowess. The advanced AI-driven image formation technology now empowers the precise detection of cancer within lymph nodes and other anatomical structures, “achieving remarkable accuracy even for very small lesions,” says Dr. Paul.
“The advantages we have seen so far are already impressive but what’s on the horizon in research and care – what we will be able to study and do – is even more exciting,” says Ting.
In particular, the new PET/CT is expected to be the catalyst for ground-breaking clinical research for patients facing breast cancer, Alzheimer’s disease, prostate cancer, epilepsy and obesity. Scientific exploration in these areas is currently being planned at St. Joseph’s that will pave the way for novel treatments, new, non-invasive ways to identify a patient’s risk of disease, the potential to clearly and painlessly view how treatment is working, and the ability to uncover the tiniest abnormalities at play when it comes to diseases and conditions.
The deets on PET-CT
Positron emission tomography (PET) is a medical imaging method that uses a small amount of radioactive material, called a radiotracer or radiopharmaceutical, along with a special camera and computer. This helps doctors see how organs and tissues in the body are working. The radiotracer moves through the body and collects in specific areas, showing where there might be a problem or disease. PET can also be used to check how well a patient is responding to treatment.
A computed tomography (CT) scan takes x-ray images of the body from different angles and uses computer processing to create highly detailed, cross-sectional images (slices) of the body’s structures. It is used to see things that regular X-rays can’t show.
A PET-CT machine allows both types of scans to be performed at the same time and information from these two different types of scans to be viewed on a single set of images. Together, PET-CT provides intricate views with fine details about both the body’s various structures and their functions.
Peering into the future
The following are landmark research projects nearing the starting gate at Lawson Health Research Institute made possible by St. Joseph’s Health Care London’s revolutionary new PET-CT machine.
Breast Cancer
Within the Breast Care Program at St. Joseph’s, research with the new PET-CT scanner will make breast cancer theranostics a clinical reality for the first time worldwide. In other words, it will be possible to treat breast cancer using the powerful, one-two punch of molecular imaging and radiopharmaceuticals to identify the location and extent of diseased tissues and selectively destroy the abnormal cells. Two exciting projects are on the horizon:
The one-two punch: Herceptin is a cancer medicine that interferes with the growth and spread of cancer cells in the body. HER2-positive breast cancer is a type of breast cancer that is more aggressive than other types. By using PET-CT imaging with a specialized form of Herceptin that has been chemically tagged, or "labeled," with a radioactive substance, researchers believe it’s possible for a woman to avoid undergoing a breast biopsy. They will be able to see – literally – if the radiolabeled Herceptin binds to the HER2 proteins and the extent of the HER2-positive cancer. Then, by tagging Herceptin with a therapeutic radioisotope – a special type of atom that emits radiation – the hope is to destroy the breast cancer. St. Joseph’s is investigating this approach first in animal studies before progressing into human trials.
Reducing the risk: Not all breast cancers can be effectively treated with Herceptin. For this group of patients, researchers plan to evaluate newer drugs to reduce the risk of both disease progression and death. The new PET-CT scanner will be able to monitor response from these new treatments.
Alzheimer's disease
The super sensitivity of St. Joseph’s new PET-CT will empower innovative methods to identify individuals at risk of Alzheimer’s disease, those who might benefit from treatment, and early response to treatment. The high-powered machine will allow researchers to simultaneously study both blood flow and glucose metabolism in the brain – something that has not been possible before. Both these mechanisms are believed to be contributing factors in the onset of Alzheimer’s. By measuring both at the same time, researchers hope to uncover early signs that the brain is in trouble and at risk of plaque deposits and toxic proteins that have been linked to the development of Alzheimer’s. Patients will be recruited from St. Joseph’s Aging Brain and Memory Clinic at Parkwood Institute for this ground-breaking study.
Epilepsy
Patients with uncontrolled seizures currently require a hospital stay and the implanting of electrodes deep into the brain to record brain signals that pinpoint where the epileptic seizures are originating. The hospital stay is often long as this method relies on the patient having seizures to properly record and identify the location in the brain responsible. Once the problem area is determined, surgeons intricately remove this part of the brain. Research with the new PET-CT will explore a more efficient approach – the ability to precisely reveal the brain’s seizure epicentre using non-invasive imaging looking at characteristics in the epileptic brain that is present between seizures.
Obesity
In Canada, one in four adults are currently living with obesity, a problem that is causing a surge of obesity-related health challenges. Ozempic is a ground-breaking drug that not only helps people shed weight but also slashes the risk of heart disease by an impressive 20 per cent. However, weight loss attributed to this drug is linked to a reduction in lean muscle mass and the long term effects of that muscle loss remain uncertain. Using PET-CT, researchers will explore potential alterations in muscle energy metabolism resulting from obesity treatment with Ozempic and similar drugs.
Using AI to detect lung cancer recurrence
Lung cancer is the most commonly diagnosed cancer in Canada. While the standard treatment for patients with early-stage lung cancer is surgery, up to half of these patients may develop a recurrence after their treatment.
Jaryd Christie is a Master’s candidate working with Lawson Scientist, Dr. Sarah Mattonen. Together, they are working to develop a new software that uses artificial intelligence (AI) to identify which patients are likely to have recurring cancer.
Currently, basic information like the size of the tumour is extracted from medical images such as a computed tomography (CT) scan to determine a patient’s cancer stage and prognosis. With the new technology, multiple sources of information about the patient will be extracted and used to increase accuracy for determining likelihood of recurrence.
Christie is looking to integrate multi-modal imaging, including CT and positron emission tomography (PET) with a patient’s clinical, pathological and genomic information to build the software. The AI software will find patterns from the data that is extracted and identify imaging features that are associated with recurrence after treatment.
The goal of this research is to improve the ability to identify which patients are likely to be cured. By being able to extract and combine additional information, physicians could provide aggressive treatment options for patients who need it. This would provide lung cancer patients with personalized treatments that could improve their outcomes.
“We also want to look not only at the tumour, but other places like bone marrow and non-cancerous areas in the lung, to see if these additional areas can provide information on disease progression and prognosis,” says Christie, who is completing his Master’s degree in the Department of Medical Biophysics at the Schulich School of Medicine & Dentistry at Western University. “We hope that by combining these different sources of information, we can obtain better disease characterization to more accurately determine if a patient will be cured.”
Christie received a Lawson Internal Research Fund (IRF) Studentship to conduct this research, which will be supervised by Dr. Mattonen.
“Lawson’s IRF is such an important funding opportunity for new investigators. This studentship allows me to support a student while building my research program,” adds Dr. Mattonen. “These funds will allow us to obtain preliminary data that we can use to apply for external funding.”