Search
Search
Dalton L. Wolfe
Dalton L. Wolfe, PhD
Lawson Scientist, Parkwood Institute Research
Implementation Science and Education; Spinal Cord Injury
Dalton Wolfe is a Scientist at Lawson Health Research Institute, an Assistant Professor in the Faculty of Health Science and leads the Research 2 Practice (R2P) team, which is a unique research program within Parkwood Institute that focuses on strategies for generating evidence and implementing best practice within rehabilitation. Professor Wolfe’s primary research interest is in the area of knowledge mobilization and best practice implementation with a focus on physical activity and activity-based therapies in spinal cord injury and brain injury rehabilitation.
Professor Wolf also co-leads the Ontario SCI Implementation, Evaluation and Quality Care Consortium, which focuses on implementation of quality indicators towards the enhancement of care across the 5 academic health centres involved in SCI rehabilitation in Ontario. As part of the Parkwood Rehabilitation Innovations in Mobility Enhancement initiative (PRIME), Professor Wolfe is focused on enhancing clinical decision-making to improve locomotor and other movement-related outcomes with activity-based therapies such as robotic, manual and FES-assisted therapies. As with many of the R2P initiatives this involves implementation science and participatory research methods to put in place practice-based research infrastructure that enables iterative knowledge generation as well as implementation. Trainees work alongside clinicians, administrators and persons with lived experience to tackle clinically relevant questions.

Dementia doesn’t have to be your destiny
Tackling a “dirty dozen” list of health and lifestyle factors can go a long way in lowering the risk of dementia, say London experts.
Many people could greatly improve their odds against developing dementia by making four, low-cost lifestyle changes – today.
In the first study of its kind, researchers at Lawson Research Institute (Lawson) and Western University have found that about half of dementia cases in Canada can be influenced by 12 lifestyle factors.
Topping the “dirty dozen” list across Canadians’ lifespan, and especially notable from mid-life onwards, are physical inactivity, hearing loss, obesity and hypertension.
The solutions:
- Get off the couch and get moving
- Tackle hearing loss early
- Lose weight
- Get assessed and treated for high blood pressure
“While lifestyle changes aren’t a magic pill to prevent all dementias, they’re an empowering way to reduce the overall risk,” says Lawson researcher and study lead author, Surim Son, a Western University PhD candidate who with the dementia research program at St. Joseph’s Health Care London (St. Joseph’s).
“We’re talking about significant benefits to Canadian health and health systems,” adds Son.
The findings could also have profound implications in refocusing health policy priorities. The Public Health Agency of Canada is already highlighting the study as part of its resources for national health policy advisors, she notes.
This study is the first to weigh Canadians’ lifestyles and habits against 12 potentially modifiable risk factors for dementia, and the first globally to include sleep disruption on the list.
Son’s paper, published in The Journal of Prevention of Alzheimer’s Disease, builds on a 2017 study in the Lancet that shows 12 modifiable risk factors throughout the course of life could contribute to 40 per cent of dementias around the world.
But Canada’s numbers are considerably higher because more of us indulge in weightier lifestyle risks. For example, four of every five older Canadian adults don’t exercise regularly; one in three is obese or has hypertension; and one in five has hearing loss.
"If half of the dementia cases in Canada are linked to modifiable lifestyle risk factors, this suggests that, today, prevention may be the most effective form of treatment," says Dr. Manuel Montero-Odasso, co-author of the paper and Director of the Brain & Gait Lab at St. Joseph’s Parkwood Institute.
“Dementia doesn’t have to be your destiny, even if that’s part of your genetic story. Our results from the SYNERGIC Trial shows almost everyone can change their risk factors and improve their cognitive resilience,” says Montero-Odasso, who was recently awarded a $2.4-million Canadian Institutes of Health Research grant to train professionals in risk reduction and care for people living with cognitive impairment.
Montero-Odasso’s advice: “Go out for a walk and keep moving. Get a hearing assessment. Keep your blood pressure in check. It’s low-cost and easy to implement. It’s good for your body health, even beyond improving your brain health and reducing your dementia risk.”
The 12 potential modifiable factors (based on a study of 30,000 Canadians over the age of 45), weighted from most significant factor to least:
- Physical inactivity
- Hearing loss
- Obesity
- Hypertension
- Traumatic brain injury
- Depression
- Less education in early life
- Sleep disturbances
- Diabetes
- Smoking
- Excessive alcohol
- Social isolation
Dr. Arlene MacDougall appointed Director of Research and Innovation for St. Joseph’s Mental Health Care
Dr. Arlene MacDougall has been appointed as Director of Research and Innovation for mental health care at St. Joseph’s Health Care London and Lawson Health Research Institute.
She will oversee and facilitate all mental health care research at both Parkwood Institute and Southwest Centre for Forensic Mental Health Care, working to develop strong local and global partnerships, engage patients and their caregivers in research activities, and foster trans-disciplinary approaches to research.
Her goal is to build on existing research strengths in mood disorders, suicide and smart technology. She also will look to develop research links between Mental Health and Parkwood Institute’s other major research programs, Cognitive Vitality and Brain Health, and Mobility and Activity.
Dr. MacDougall joined Lawson and the Department of Psychiatry at the Schulich School of Medicine & Dentistry, Western University in 2013 working with the Prevention and Early Intervention Program for Psychoses at London Health Sciences Centre. Last year she was cross appointed to the Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics at Schulich.
“I come to this new role with a great deal of optimism, energy and enthusiasm. Parkwood Institute Research has a number of established strengths in the mental health care field as well as potential for new streams of research and innovation,” says Dr. MacDougall. “I look forward to working with researchers, staff, and patients and their supporters, as well as academic and community partners, to make Parkwood Institute a leading centre in Canada for mental health research.”
Parkwood Institute Research is a Lawson program that represents inter-disciplinary clinical research and focuses on the advancement of innovations and discoveries that directly improve patient care.
Dr. MacDougall will continue her own program of research, which includes recovery-oriented interventions for people with serious mental illness locally and in Africa. She is leading local studies on the use of mindfulness meditation and participatory video interventions to promote recovery among youth with early psychosis. She is also leading a project based in Kenya using social businesses and a low cost psychosocial rehabilitation toolkit to create meaningful employment, promote social inclusion and support the overall functioning and recovery of people with serious mental illness in low income settings.
Most recently she has been involved in developing and leading initiatives that use social innovation approaches to tackle complex mental health system challenges both locally and globally.
At Western, she is the Director of Global MINDS (Mental Health Incubator for Disruptive Solutions) @ Western, an educational and research initiative that supports students, faculty and community stakeholders to create solutions that will reduce the global burden of mental disorders. Global MINDS is focused on innovating for low and middle income countries and for marginalized communities in Canada. Another initiative, MINDS of London-Middlesex, is working with multiple local stakeholders to collaboratively establish a social innovation lab and use collective impact approaches that will lead to solutions that address complex challenges in the local mental health system.
Dr. MacDougall began her new role on February 1, 2017 and joins Drs. Michael Borrie and Tim Doherty as Joint/Acting Beryl and Richard Ivey Research Chair in Aging, Mental Health, Rehabilitation and Recovery. She also joins Lawson’s Research Executive Committee as Assistant Director (interim) for Parkwood Institute Research, Mental Health.
Easing the pressure for patients with chronic wounds
Chronic wounds represent a significant burden in Canada. Between four and 30 per cent of patients develop a chronic wound, depending on the health care setting. Over 85 per cent of all Spinal Cord Injury (SCI) survivors will experience health complications related to pressure ulcers, injuries to the skin and underlying tissue resulting from prolonged pressure. These types of wounds can significantly reduce participation in meaningful activities and overall quality of life.
Research from around the world shows that electrical stimulation can help speed the healing of pressure ulcers. This therapy is currently done by a trained health care provider and is not readily available for people across Canada.Electrical stimulation therapy (E-Stim) is a wound treatment that involves applying low levels of electrical current to the wound bed and surrounding tissues. It stimulates several healing processes, promotes local circulation and prevents infections.
The E-Stim Collaboration: A Best Practice Implementation Project for Better Pressure Ulcer Care aims to improve the coordination of pressure ulcer care and promote the use of evidence-informed wound treatments for people living with SCI. In particular, the research project is studying how to best provide E-Stim to people with pressure ulcers, in their own communities.
“Over the years I’ve seen the serious impact pressure ulcers have on the lives of people with spinal cord injury and other health challenges. This is what drives my commitment to not only develop best practice guidelines, but also to ensure they are put into action,” says Dr. Pamela Houghton, Associate Scientist, Lawson and Professor, School of Physical Therapy at Western University. “Advances in technology make it possible for more people with care needs to live at home.”
The pilot project in the South West LHIN has a unique model that builds capacity in the community and taps into the lived experience of people with pressure ulcers and SCI. It brings together the expertise of researchers, clinicians and managers from academia, hospital centres and community care.
Partners include the Parkwood Institute Research program at Lawson Health Research Institute, Western University, Saint Elizabeth’s Health Care Research Centre, Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre and the South West Community Care Access Centre. An interdisciplinary specialized team, called SCIPUT, has been established within the Spinal Cord Injury Rehabilitation program provided at Parkwood Institute, St. Joseph’s Health Care London.
“Our collaborative team is using the PLAN-DO-STUDY-ACT quality improvement model. This allows us to learn from each cycle and make adjustments as we go,” says Dr. Houghton. “We have just completed the first cycle and are reporting on lessons learned.” Funded by the Rick Hansen Foundation, the team hopes this will set the stage for a larger cross-country initiative.
Those interested in participating can contact phoughto@uwo.ca. The study is open to:
- Individuals with an open pressure ulcer and with a condition that causes limited mobility and/or requires a wheelchair;
- Those who are able and willing to participate in treatment plan, and communicate feedback; and,
- People who are eligible to receive services from South West CCAC.
|
Image
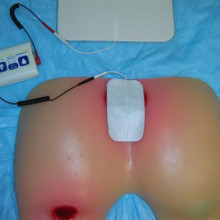
Electrical stimulation (E-Stim) directly stimulates several wound healing processes, promotes local circulation and prevents wound infections. It produces faster healing and wound closure. A trained health care provider applies low levels of electrical current to the pressure ulcer using specialized equipment. |
Embracing health research this holiday season
Community members, patients and families, and those working in the health field attended a special open house on November 28 by research groups at Lawson Health Research Institute. Together, they celebrated the holiday spirit and the gift of hope that is made possible through hospital-based research.
A part of St. Joseph’s Health Care London, Parkwood Institute represents the next era in care, recovery and rehabilitation. Across the site, clinical and research teams in different disciplines and specialties collaborate not only with each other but also with patients and families.
“Many people in the community know the high-quality and compassionate care that is supported by the various clinical teams at Parkwood Institute, but aren’t aware of the research happening at this site,” says Dr. Cheryl Forchuk, Beryl and Richard Ivey Research Chair in Aging, Mental Health, Rehabilitation and Recovery, and Assistant Scientific Director at Lawson.
“Lawson researchers at Parkwood are tackling important challenges with highly innovative and meaningful solutions that help improve care and quality of life.”
For the past three years, the open house gives guests a more in-depth understanding of hospital-based research and its impact. Dr. Forchuk notes that it is a great chance to talk to the researchers and their teams, and to learn about research in a really fun and interactive way. Guests may also learn about opportunities to participate in studies, as the research teams rely on people in the community getting involved.

There were 12 interactive program displays from Parkwood Institute Research, a Lawson program, in the areas of cognitive vitality and brain health, mobility and activity and mental health:
- Cognitive Clinical Trials Group (CCTG)
- Collaboration of Rehabilitation Research Evidence (CORRE)
- Gait and Brain Lab
- Geriatric Mood Disorders Lab
- MacDonald Franklin OSI Research Centre (Occupational Stress Injury)
- Mental Health Nursing Research Alliance (MHNRA)
- Mental Health INcubator for Disruptive Solutions (MINDS) of London
- Neuropsychiatry and Therapeutic Brain Stimulation Research Group
- Occupational Therapy and Spiritual Care Research Lab
- R2P (Research to Practice)
- Rehabilitation Mental Health
- Wound Care
The open house had a festive theme and many of the exhibits involved a problem solving or interactive elements to encourage learning and foster teamwork.
Karen Vecchio, federal Member of Parliament for Elgin-Middlesex-London, was among the over 200 people in attendance.

At the open house, from left: Dr. Cheryl Forchuk, MP Karen Vecchio and Roy Butler, St. Joseph's Vice President.
“London is a great community to conduct research,” explains Dr. Forchuk. “We are a mid-size city surrounded by rural areas, in many ways reflecting Canada as a whole. A lot of our projects cover the country with multiple sites and results found here by our leading experts are being implemented in health centres and national strategies in this country and around the world.”