Search
Search
National award honours innovator Frank Prato’s excellence in medical physics
Dr. Frank Prato is a man of many firsts:
First in Canada to conduct magnetic resonance brain imaging. A pioneer in magnetic resonance cardiac imaging. Driving force behind the installation of Canada’s first PET/MR scanner. Founder of the Canadian Organization of Medical Physicists (COMP) while president of the Canadian College of Medical Physicists.
And while Dr. Prato admits to a competitive streak that constantly propels him to break new ground in medical physics, the renowned, prolific researcher is keen to note these innovations have been part of a larger team effort.
“My career has been filled with opportunities to work with and train some spectacular scientists who have made major contributions across Canada and around the world,” he says. “I’m proud of the whole group that has developed over the years and the support St. Joseph’s has provided.”
Chief Medical Physicist at St. Joseph’s Health Care London (St. Joseph’s), Dr. Prato has been awarded the 2024 COMP Gold Medal, the organization’s highest award for outstanding career achievement.
“Dr. Prato’s ground-breaking work in the field of medical physics has not only advanced the scientific community but also significantly impacted patient care in Canada and beyond,” says COMP President Boyd McCurdy, “His pursuit of innovation and excellence exemplifies the highest standards of our profession, and we celebrate his outstanding contributions to medical physics with admiration and gratitude.”

Dr. Prato is also Assistant Scientific Director and Imaging Program Leader at Lawson Health Research Institute (Lawson) and professor of medical imaging and medical biophysics at Western University.
“I have worked with Frank for 36 years now and have come to recognize him as one of the finest people I know,” says Dr. Ting-Yim Lee, Director of PET/CT Research at Lawson, medical physicist at St. Joseph’s Hospital, and one of the nominators of Dr. Prato for the award.
“Frank is unfailingly helpful and authentic, a great listener and a tenacious problem-solver. He demonstrates excellence and professionalism in medical physics locally, nationally and internationally.”
Dr. Lee cites Dr. Prato’s leadership in being “at the forefront of numerous international innovations in nuclear medicine and diagnostic radiology.”
Throughout his 48 years as a medical physicist, Dr. Prato has been inspired by the potential of technology’s reach into human health.
“I’ve always wanted to work in an area where we can do research, with a vision of what’s going to be important in patient health. I get excited about being on the leading edge of discovery that’s embedded in patient care.”
Critical advancements in nuclear medicine and diagnostic radiology, thanks to the work of Dr. Prato and his St. Joseph’s/Lawson team, have included:
- Introducing the first bone mineral density imaging procedure on a patient in Canada, a tool now essential for managing osteoporosis.
- Performing the first magnetic resonance brain imaging in Canada, setting a national standard.
- Pioneering magnetic resonance cardiac imaging techniques, enhancing the understanding of myocardial scarring and blood flow assessment.
- Introducing the first PET/CT and PET/MR scanners in Canada, revolutionizing molecular imaging and proving the economic value of advanced imaging technologies.
- Imaging the brains of premature infants, a world first.
- Developing Canada’s first self-sustaining cyclotron infrastructure.
- Conducting the world’s first MRI-compatible, high-resolution brain PET scan.
- Early diagnosis and treatment of dementia, mental illness and prostate cancer.
Dr. Prato’s leadership extends beyond his technical achievements. As the founder of COMP, an organization that now includes more than 800 professionals, he played a crucial role in establishing the organization, advocating for medical physicists' independent voice and professional growth.
His tenure as President and board member of the Canadian College of Physicists in Medicine (CCPM) was marked by significant advancements, including enhancing certification processes and establishing reciprocity with the American Board of Medical Physics. Dr. Prato also received the Valuable Service Award from CCPM in 2002 and was named a Fellow of COMP in 2013.
Earlier this spring, Dr. Prato received a Dean’s Award of Excellence for Research Faculty from Western University’s Schulich School of Medicine & Dentistry. He is also the sole Canadian to have won the d'Arsonval Award, an international honour from the Bioelectromagnetics Society.
A dedicated mentor, Dr. Prato has guided more than 60 Masters of Science students, PhD students and Post-Doctoral Fellows, many of whom have won awards and secured prominent positions in the field. His mentorship has been instrumental in the success of numerous scientists within the Imaging Program at Lawson, contributing to a legacy of innovation for years to come.
“At 78 years old,” he says, “I am pleased to say I have achieved things at St. Joseph’s that will far outlast me.”
New Alzheimer’s research aims to improve treatment and support for patients with agitation
Two new interventional studies have been brought to London, focused on improving quality of life for patients with Alzheimer’s disease and their caregivers. Both hope to improve upon standard approaches to treating agitation, a core symptom of Alzheimer’s.
Agitation is a significant source of stress for patients and caregivers. It is complex and difficult to treat. Often, families do not know about this particular symptom of Alzheimer’s and are not properly trained on how to manage care while dealing with agitation.
“These studies are designed to have a direct impact on patients, families and care providers, to improve quality of life and function in those suffering from agitation due to Alzheimer’s,” says Dr. Amer Burhan, Associate Scientist at Lawson Health Research Institute (Lawson) and Geriatric Neuropsychiatrist, St. Joseph’s Health Care London (St. Joseph’s).
Parkwood Institute, a part of St. Joseph’s, is one of multiple sites participating in these studies across Canada and the United States.
One study aims to identify patients early in their diagnosis, while they are living at home or in the community, and apply a comprehensive psychosocial approach, with or without medication, to help with the management of agitation. “We hope to identify participants and have them participating in our program before they experience a crisis due to agitation,” explains Dr. Burhan.
Psychosocial intervention is a way of helping patients and caregivers understand the reasons for agitation. Agitation can develop due to a wide range of causes. For example, patients may just be bored and need help to find something meaningful to occupy their time, they could be upset about something in their current environment, or may be suffering from physical discomfort or pain.
Interventions can include communicating with patients in a manner that creates calm, scheduling meaningful activities, and maintaining routine and rhythm in life. The research team will connect with families early after diagnosis to give them the tools and support they need.
Initially, participants will be treated using structured psychosocial intervention to help reduce and manage their agitation. After three weeks, they will be reassessed and if significant agitation continues to persist, the patient will be randomly selected to receive either a placebo, or medication known as S-Citalopram to treat agitation while they continue to receive psychosocial care.
Sylvia Wilson is the wife of one of the study participants. By enrolling in this trial, she feels she has gained a much better understanding of her husband’s disease, and is grateful for the support that study participants receive.
“My husband typically does not like going to visit doctors, but Dr. Burhan and his team are great,” says Wilson. “They understand agitation, and other symptoms of the disease very well, and I notice a difference in his mood with the treatment he receives through the study.”
Participants are still able to receive care from their primary physician and care teams, with the study providing an added layer of support.
Another study is focused on Alzheimer’s patients who are admitted to hospital or living in long-term care. The aim is to standardize the approach to care for agitation related to Alzheimer’s. After baseline assessment, participants will be randomized to receive the current treatment as per usual, or an integrated care pathway derived from evidence-informed treatment guidelines. These include washing out medications that have not helped, adding individualized behavioral and environmental support, and if medications are needed, use a specific set of medications and dosages based on best evidence.
“Better understanding agitation is a growing area of interest in geriatric research. The work being done locally is part of an international effort to create a paradigm shift in treating patients with Alzheimer’s disease and agitation,” explains Dr. Burhan.
Researchers are ready to offer these studies to patients and their families, hoping to make these treatment protocols an integral part of care for patients with agitation due to Alzheimer’s disease. Those interested in learning more about these studies can contact Dr. Burhan at @email or call 519-646-6100 x. 48170.
In the media: Study on 'agitation' in Alzheimer's patients seeks participants
New form of expanded dialysis improves quality of life, study finds
LONDON, ON – In a published study, a hospital research team from Lawson Health Research Institute has found that expanded dialysis, a new method that removes a broader range of toxins from the body, can improve quality of life in chronic kidney disease patients who struggle with the side effects of traditional dialysis.
In a clinical trial led by Dr.Chris McIntyre, Nephrologist at London Health Sciences Centre (LHSC) and Scientist at Lawson, dialysis patients at LHSC were administered expanded dialysis through a new dialyzer made by Baxter International Inc.
The dialyzer, called THERANOVA, has precisely-made pores that allow larger sized toxic chemicals to be filtered from the blood while retaining essential molecules such as albumin. “The chemicals that can now be filtered out can cause inflammation, malnutrition and the buildup of waste,” explains Dr. McIntyre. “With traditional dialysis treatments, we haven’t been as successful at removing those chemicals and some patients experienced significant side effects.”
These larger molecules that the THERANOVA dialyzer is able to filter out are believed to be associated with inflammation, cardiovascular disease and chronic symptoms like fatigue. Study participant Robert Wahby has chronic kidney disease and has been on dialysis for about five years. He is no stranger to these symptoms. “I was hoping that trying this new dialyzer would help get rid of some of my symptoms. My appetite was down, I was a little weak and I was hoping I would sleep better.”
As part of the clinical trial, Wahby started to immediately notice a positive difference when administered dialysis through the THERANOVA dialyzer. “I felt better, I was eating more and I had a better night’s sleep.”
His wife, Marlene Wahby, also noticed promising changes. “His sleeping patterns have gotten better and he feels better when he comes home. When he was on the traditional dialysis, he got very jumpy and didn’t feel well at all after treatments.”
This study was conducted for three months with 28 patients. Along with receiving the expanded dialysis treatment, the research participants were monitored through the London Evaluation of Illness (LEVIL) app, developed by Dr. McIntyre with the help of patient input.
“One of our big research challenges is measuring the quality of life on dialysis,” says Dr. McIntyre. “Conventional measures take time and may not be as accurate, so by asking questions through the app every day we were able to get a true idea of how patients were feeling.”
By using the LEVIL app, the team was able to determine that patients that had a poorer quality of life at the start of the study significantly improved in the areas of general wellbeing, energy and sleep after approximately four to eight weeks of expanded dialysis.
Now that the first phase of this study has been completed and published in Kidney Medicine, the next phase will include 60 dialysis patients for up to six months of treatments using the THERANOVA dialyzer. This second phase will be a multicentered clinical study led by Lawson, University of Toronto and Humber River Hospital.
-30-
Senior Media Relations Consultant
Communications & Public Engagement
T: 519-685-8500 ext. 73502
Celine.zadorsky@lhsc.on.ca
New national strategy to tackle dementia
Researchers in London, Ontario have been awarded $1.345 million over five years through the second phase of the Canadian Consortium on Neurodegeneration in Aging (CCNA), announced today as part of Canada’s first national dementia strategy. CCNA is a collaborative research program tackling the challenge of dementia and other neurodegenerative illnesses.
A Dementia Strategy for Canada: Together We Aspire focuses on preventing dementia, advancing therapies and finding a cure, as well as improving quality of life for people living with dementia and caregivers.
Clinician researchers from across the country working together
Dr. Manuel Montero-Odasso, Scientist at Lawson Health Research Institute, is world renowned for his findings on the relationship between cognition and mobility in the elderly, and gait as a predictor of frailty and dementia. He leads the Mobility, Exercise and Cognition (MEC) Team in London, comprised of top researchers in the areas of mobility, exercise and brain health.

“Evidence from other countries with dementia strategies shows that coordinated, targeted efforts at the national level improves results for all aspects of dementia care and also for research,” says Dr. Montero-Odasso, also a geriatrician and Director of the Gait and Brain Lab at Parkwood Institute, a part of St. Joseph’s Health Care London.
CCNA was purpose-built to synergize dementia research within the Canadian context. Phase I saw the creation of infrastructure fostering collaboration amongst Canadian researchers, and there are now 20 teams built around important research topics.
“This kind of effective national collaboration by scientists and clinicians from many disciplines gives the CCNA a cutting edge in research, prevention, treatment and management of all forms of dementia,” explains Dr. Montero-ODasso. “We created a national network of researchers form west to east coast with a high level of expertise to deliver lifestyle interventions to improve cognition and slow down progression to dementia. I feel privileged working with such excellent investigators and leading this important endeavour locally.”
Preventing dementia through lifestyle changes
The MEC team has several projects in the works, but the majority of the new funding is to complete the SYNERGIC Trial, SYNchronizing Exercises and Remedies on Gait and Cognition.
This first-in-the-world clinical study is testing a triple intervention aimed at treating Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI) and delaying the onset of dementia. The SYNERGIC Trial incorporates physical exercises and cognitive training, along with vitamin D supplementation to determine the best treatment for improving mobility and cognition.
“We are looking at how interventions will work together and targeting cognitive decline at its earliest stage – individuals with MIC,” explains Dr. Montero-Odasso. “Both physical and cognitive exercises have shown promising effects for maintaining cognition, while vitamin D deficiency is associated with cognitive decline.”
A professor at Western University’s Schulich Medicine & Dentistry, Dr. Montero-Odasso partners with researchers from across the city including Dr. Rob Bartha, imaging scientist at Schulich Medicine & Dentistry and Robarts Research Institute at Western University, and Dr. Kevin Schoemaker who leads the Laboratory for Brain and Heart Health.
Study participants in the SYNERGIC Trial are asked to complete an individualized and progressive routine of exercises and cognitive training three times a week for six months, with one final assessment at 12 months. The main site for the study is Parkwood Institute with the physical exercises taking place at the Labatt Health Sciences Building on the Western campus.
To date, 138 research patients has been recruited across multiple sites in Canada.
One participant’s experience

One day, Peter Saracino saw an advertisement about a research study. They were looking for participants who were a minimum age of 60 and had minor cognitive impairment. He felt he fit the bill and he was interested in this kind of research.
“I have family members who suffered from forms of dementia and Parkinson’s Disease. I really understand how hard it hits and I liked that this study was about prevention,” explains Peter.
Going into it, Peter thought he was in pretty good shape. He has two dogs and walks them regularly. “But by going to the gym and doing the exercises and faster-paced walking, I realized that I wasn’t in as good shape as I thought. My diet was under control but I was still taking blood pressure medication. I didn’t have much energy.”
After 10 weeks in the study, he feels better than he has for over a decade. “I can garden for longer. I took two notches off my belt. I no longer take my blood pressure medication. I actually feel younger.”
He remembered that last year he slipped and fell four times, which was very unusual for him. Part of his cognitive impairment is that he had trouble with balance, and that has improved for him as well.
Peter feels that “this is exactly the kind of research that the government should be investing in – an ounce of prevention is worth a pound of cure. This kind of research leads to keeping people independent and healthier as they get older. People are happier. They feel like doing more. There is no downside to improving someone’s health through lifestyle changes, and in fact it is cost effective and helps ease the burden on the health care system.”
Looking forward
“Our preliminary analysis from SYNERGIC is giving us a strong indication that a multimodal approach, combining physical exercise, cognitive training and supplementation, has a synergistic effect. It seems the whole is greater than the sum of its parts,” says Dr. Montero-Odasso.
A major goal for the work of the MEC team in London is to translate their research findings into clinical guidelines that can be used at the front line of care. “Practitioners understand the overall importance of exercise and cognitive vitality, but we are missing more specific guidelines on what kind and how much will work for different patients. Basically, what is an effective lifestyle prescription.”

Dr. Montero-Odasso adds that “as our population ages, a comprehensive strategy is vital to ensure the growing number of those living with dementia receive the care and support they deserve. Over half a million Canadians are currently living with dementia. By 2031, this number is expected to nearly double.” More than one third of dementia cases might be preventable.
CCNA Phase II
In CCNA’s Phase II, researchers are working on analyzing the overall health of every patient in a large clinical cohort study, COMPASS-ND. This information will be used to enhance understanding of how changes in the brain affect dementia severity and ways to reduce and prevent this through lifestyle changes. Lawson is the leading recruitment site for COMPASS-ND and the London team will be instrumental in the larger lifestyle interventions moving forward.
CCNA is funded by the Government of Canada, Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR) and other funding partners. CIHR is providing $31.6 million, and partners—including provincial agencies and non-profit organizations—are providing an additional $14.4 million for a total investment of $46 million over five years. The research on dementia prevention, diagnosis, treatment and care as part of Phase II of the CCNA will support the national strategy.
Related stories
New research showcased at third annual Parkwood Institute Research Spring Update Half Day
More than 100 researchers, staff and trainees attended the third annual Parkwood Institute Research (PIR) Spring Update Half Day on April 27, 2018 to share their innovative research and learn about work from across PIR through interactive workshops and poster presentations.
A program of Lawson Health Research Institute and located at St. Joseph’s Health Care London’s Parkwood Institute, PIR represents three major research programs: cognitive vitality and brain health, mobility and activity, and mental health. The event allowed guests to hear about new studies and recent research developments from across these three themes.
“Parkwood Institute Research covers different research areas but what we want to emphasize with this event is the overlap and collaboration between our programs. Having an inter-disciplinary approach that encourages partnerships ultimately helps us to incorporate new knowledge into patient care at Parkwood Institute,” says Dr. Cheryl Forchuk, Beryl and Richard Ivey Research Chair in Aging, Mental Health, Rehabilitation and Recovery, and Assistant Director, Lawson.
Five interactive workshops were held on a variety of different topics, such as clinical trials, systematic reviews, innovation in health care, practice-based research methods and evaluating SMART technology. The workshops were led by some of Parkwood Institute’s research leaders, including Drs. Cheryl Forchuk, Robert Teasell, Michael Borrie, Dalton Wolfe, and Arlene MacDougall.
Attendees also had the opportunity to visit poster presentations on recent PIR projects.

Ashrafunissa Janmohammad (above), Lawson research coordinator at Parkwood Institute’s Chronic Wound Management Clinic, was one of the poster presenters at the event. She presented on a study led by Lawson associate scientist Dr. David Keast, which assessed whether chitosan gelling fibre dressing could be effective in controlling bleeding after minor wound surgery. Chitosan is derived from chitin, the structural component of the cell walls of fungi and the shells of arthropods such as crabs, lobsters, shrimps and insects.

Juweiriya Ahmed (above), a MSc candidate at Lawson and Western University’s Schulich School of Medicine & Dentistry, was another presenter. Her poster outlined a study investigating the interaction between neuroanatomical and genetic risk factors that may contribute to the development of psychotic symptoms (delusions and hallucinations) in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Supervised by Lawson scientist Dr. Elizabeth Finger, the study could help inform the development of therapeutic targets and treatment plans.
New robotic 3D ultrasound may improve accuracy of liver cancer ablation therapy
LONDON, ON – A new system that turns ultrasounds into a 3D image could make treatment of liver cancer using thermal ablation more accurate, a new simulated study from Lawson Health Research Institute and Western University has found.
Liver cancer is the fourth leading cause of cancer death globally. While surgery is one treatment option, thermal ablation, using heat to destroy the cancerous tumour, can have fewer complications and a shorter recovery time. It can also be used for patients who are not surgical candidates.
Thermal ablation requires precise needle placement to treat the cancer without damaging the vital organs and blood vessels around it.
“It's very important that we get the needle right in the centre of the tumour,” says Dr. Derek Cool, Associate Scientist at Lawson, Assistant Professor at Western University’s Schulich School of Medicine & Dentistry and Interventional Radiologist at London Health Sciences Centre (LHSC). “If the treatment area doesn't fully cover the tumour, patients are left with a small amount of residual cancer, risking recurrence and the need for additional treatment.”
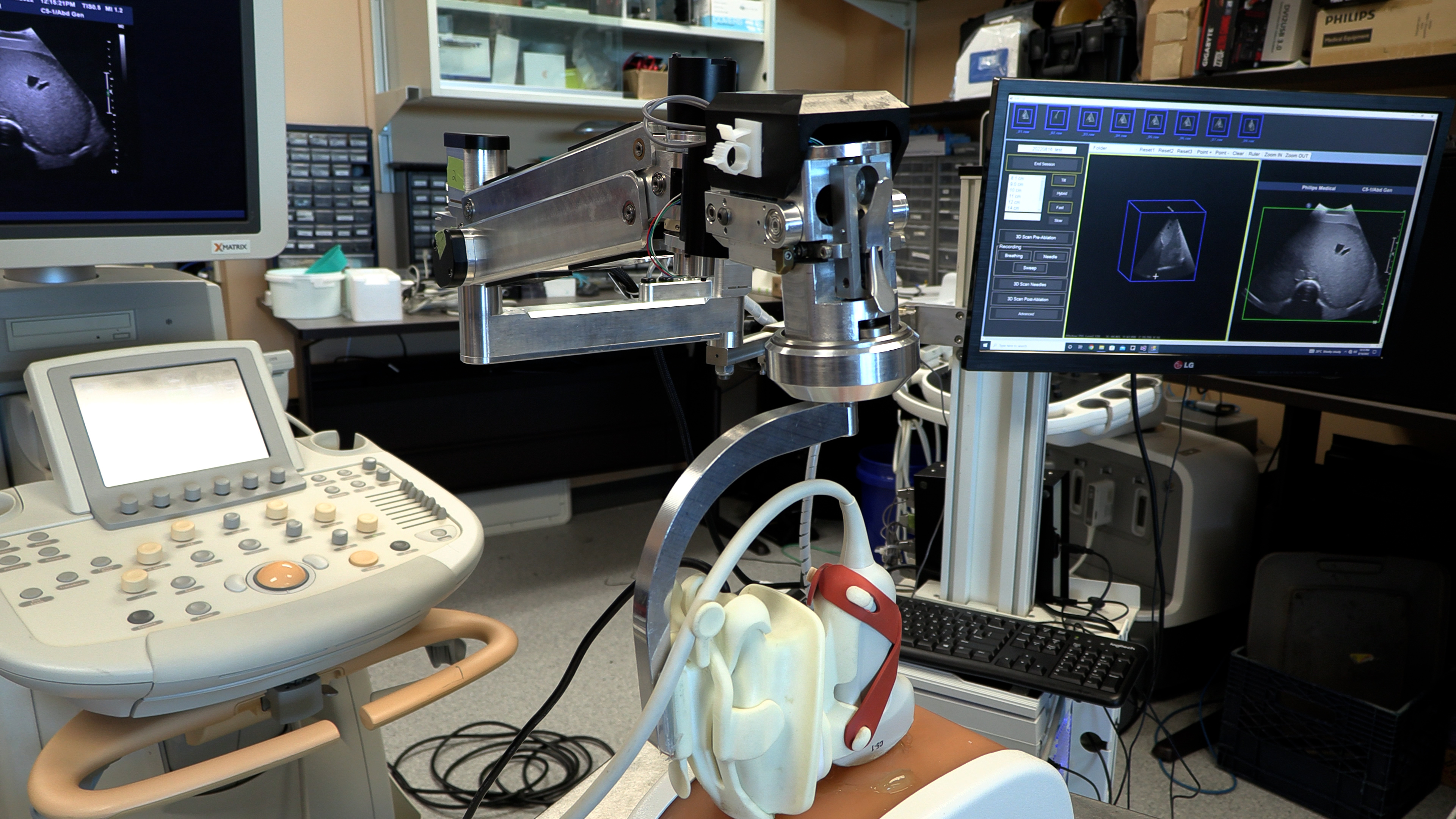
Ultrasound or CT (computerized tomography) imaging is normally used to guide needle placement, but both are limited. Ultrasound is widely available and can be done in real-time, but only delivers a 2D image. While a CT scan provides a 3D image, it isn’t in real-time and can be a lengthy process.
“We developed a new 3D ultrasound method that shows promise in analyzing whether the complete liver tumour will be ablated by the procedure,” explains Dr. Aaron Fenster, a Professor at Schulich and Scientist at Robarts Research Institute. “And we're now using the same system to guide the needle directly into the centre of the tumor.”
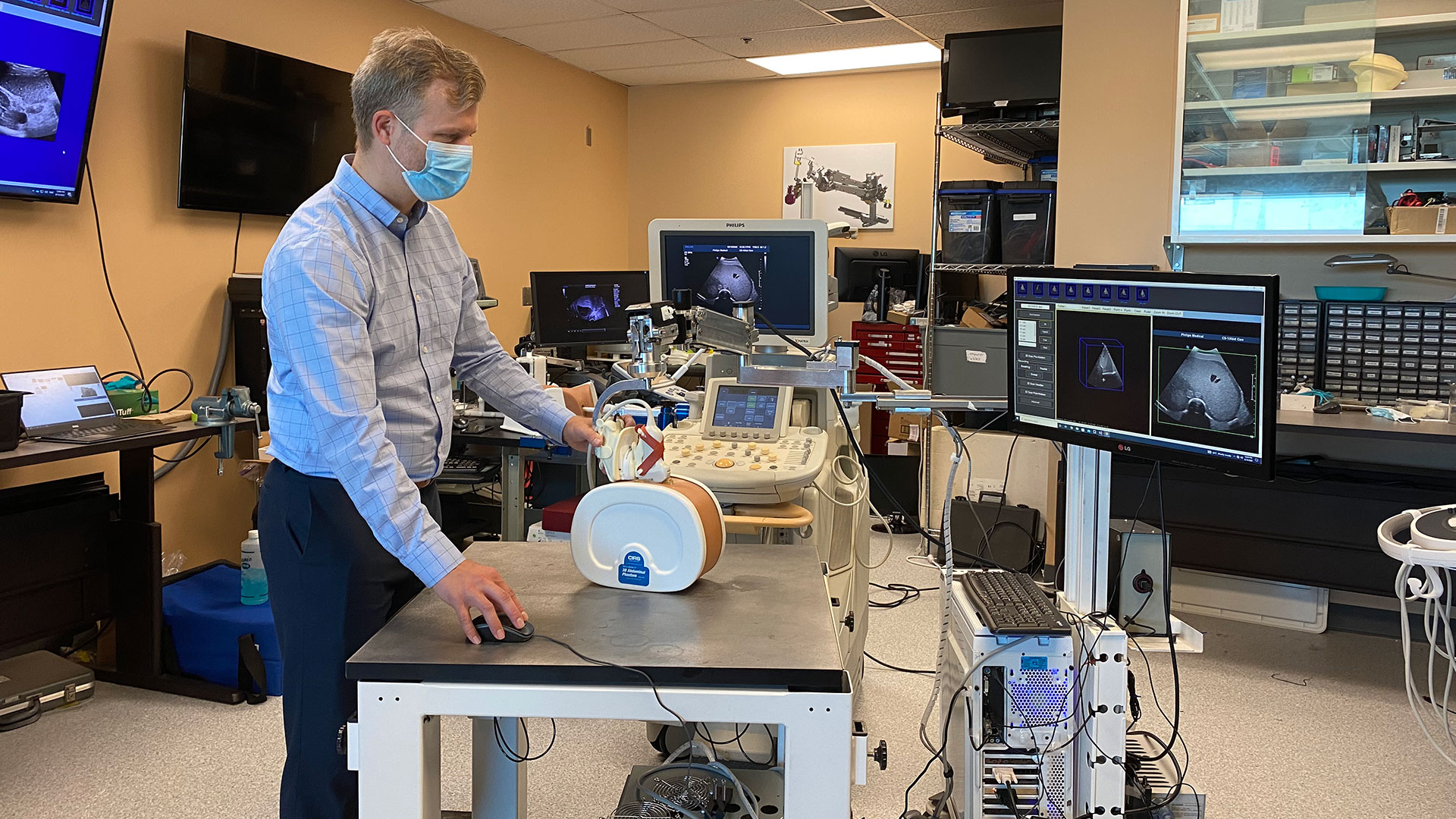
To create the 3D ultrasound images, a robotic cradle moves a standard ultrasound probe, collecting images and stacking them like puzzle pieces.
The simulated study, published in IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, used data from 14 patient cases at LHSC to analyze accuracy of the technology. It found that while 64.3 per cent of cases showed complete tumour coverage with standard imaging methods, the new system could result in complete coverage for 92.9 per cent of cases (13 of 14 cases). The researchers found that the remaining case could benefit from increasing the ablation time or intensity.

“Our next step is to move from simulation studies to a clinical trial,” says Dr. Cool.
If proven effective, the robotic ultrasound system’s portability could potentially allow for more widespread use of 3D ultrasound imaging, including in smaller health care centres. By eliminating the need for CT scans, it could also help to reduce imaging wait times.
“If a clinical trial shows the approach is more accurate and more precise than conventional techniques, there would be a direct impact on patient care,” says Dr. Fenster. “We hope to explore commercialization to license the technology and distribute it worldwide.”

Lawson Health Research Institute is one of Canada’s top hospital-based research institutes, tackling the most pressing challenges in health care. As the research institute of London Health Sciences Centre and St. Joseph’s Health Care London, our innovation happens where care is delivered. Lawson research teams are at the leading-edge of science with the goal of improving health and the delivery of care for patients. Working in partnership with Western University, our researchers are encouraged to pursue their curiosity, collaborate often and share their discoveries widely. Research conducted through Lawson makes a difference in the lives of patients, families and communities around the world. To learn more, visit www.lawsonresearch.ca.
Western delivers an academic experience second to none. Since 1878, The Western Experience has combined academic excellence with life-long opportunities for intellectual, social and cultural growth in order to better serve our communities. Our research excellence expands knowledge and drives discovery with real-world application. Western attracts individuals with a broad worldview, seeking to study, influence and lead in the international community.
The Schulich School of Medicine & Dentistry at Western University is one of Canada’s preeminent medical and dental schools. Established in 1881, it was one of the founding schools of Western University and is known for being the birthplace of family medicine in Canada. For more than 130 years, the School has demonstrated a commitment to academic excellence and a passion for scientific discovery.
Communications Consultant & External Relations
Lawson Health Research Institute
T: 519-685-8500 ext. ext. 64059
C: 226-919-4748
@email
New study looking at advanced imaging to optimize treatments for prostate cancer patients
Advanced imaging will help better guide radiation treatments
MEDIA RELEASE
For Immediate Release
January 12th, 2022
London, Ontario- Prostate cancer is the most common cancer among Canadian men, and it is estimated that one in eight men will be diagnosed with prostate cancer within their lifetime. Researchers at both Lawson Health Research Institute and Sunnybrook Research Institute, are teaming up on a study which is pairing advanced imaging technology with high precision short course radiotherapy, that could lead to better outcomes for patients.
“We have started to look at ways to integrate advanced imaging to help better understand the amount of cancer in the prostate and the location of cancer in the prostate to help guide radiation treatments,” says Lawson Scientist, and Radiation Oncologist at London Health Sciences Centre’s (LHSC) London Regional Cancer Program (LRCP), Dr. Glenn Bauman.
Currently when radiation is done, a computer tomography scan (CT) gives radiologists the location and boundary of the prostate, but it doesn’t give details about the location of the cancer within the prostate.
“What we are doing in the study is integrating two other forms of imaging; magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and prostate specific membrane antigen (PSMA) PET scans, both of which can give information on the exact location of the cancer,” explains Dr. Bauman. “This will allow us to refine the radiation treatment and to target the cancer with more intensified radiation.”
Scientist at Sunnybrook Research Institute, Dr. Andrew Loblaw says using advanced imaging will also pinpoint if the cancer has moved into other areas of the pelvic region, which helps target all possibilities and lessens the chance of the cancer coming back. The type of radiation being used for this study is called stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) which is more accurate, and reduces both radiation side effects to adjacent organs, while also reducing treatment visits.
“The combination of PSMA and SBRT gives us the ability to save some normal tissue and dramatically reduce treatment times,” explains Dr. Loblaw. “If we know the cancer is in one place and not another, we can spare radiation from areas not needing it which spares side effects.”
The team plans to recruit 50 men for the study that have advanced prostate cancer and need more intense treatments. Participants will undergo the advanced PSMA PET imaging at St. Joseph’s Health Care London. The same imaging techniques will be used to determine and track if the cancer is responding well to treatments.
“This is a smarter tool that will help us more accurately know what patients have,” says Dr. Loblaw. “We will know if they have more of a metastatic disease and who has localized disease. Cure rates are better when you know exactly what you are trying to cure.”
Study participants will be closely monitored for five years, to determine the success of the more targeted and intense radiation treatments. Dr. Bauman says this will also help quickly identify the potential need for more advanced therapies.
“Our treatments are good, but If there is a man we haven’t cured we want to know as soon as possible.”
The study has received funding by the Ontario Institute for Cancer Research (OICR) as part of the Institute’s new initiative that supports pre-clinical research and new clinical trials that focus on early stage, and recurrent cancers.
-30-
About Lawson Health Research Institute: Lawson Health Research Institute is one of Canada’s top hospital-based research institutes, tackling the most pressing challenges in health care. As the research institute of London Health Sciences Centre and St. Joseph’s Health Care London, our innovation happens where care is delivered. Lawson research teams are at the leading-edge of science with the goal of improving health and the delivery of care for patients. Working in partnership with Western University, our researchers are encouraged to pursue their curiosity, collaborate often and share their discoveries widely. Research conducted through Lawson makes a difference in the lives of patients, families and communities around the world. To learn more, visit www.lawsonresearch.ca.
About Sunnybrook Research Institute: Sunnybrook Research Institute (SRI) is the research arm of Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre, an internationally recognized academic health sciences centre fully affiliated with the University of Toronto. SRI is one of the fastest growing hospital-based research enterprises in Canada with well-established programs in basic and applied sciences which span across three scientific platforms and ten clinical programs, developing innovations in care for the more than 1.3 million patients the hospital cares for annually. Recognized as a Centre of Excellence in focused ultrasound, SRI has one of the most comprehensive and successful focused ultrasound research programs in the world, with technical, scientific and clinical experts accelerating progress in the field.
FOR MORE INFORMATION, PLEASE CONTACT:
Celine Zadorsky
Communications Consultant & External Relations
Lawson Health Research Institute
T: 519-685-8500 ext. 75664
C. 519-619-3872
@email
www.lawsonresearch.ca/news-events
Senior Media Relations Consultant
Communications & Public Engagement
T: 519-685-8500 ext. 73502
Celine.zadorsky@lhsc.on.ca
New study shows technology could play an important role in mental health support
LONDON - In a study published in MDPI Journal, a team of researchers at Lawson Health Research Institute have shown that the use of technology may assist in better outcomes for those living with both mental health and physical disorders.
Dr. Cheryl Forchuk, Assistant Scientific Director at Lawson, and her team embarked on a pilot study that used smart home monitoring solutions to assist those living with both a mental health disorder and other health challenges. The purpose of this pilot study was to see if technology could improve overall lifestyle and wellbeing.
“We began our research by using hospital prototype apartments – apartment style care spaces within hospital settings – that were equipped with smart home technology solutions such as a screen device, activity trackers, weigh scales and medication dispensers,” says Dr. Forchuk who is also the Beryl and Richard Ivey Research Chair in Aging, Mental Health, Rehabilitation and Recovery at St. Joseph’s Health care London. “Once we tested it in a hospital setting, we wanted to find a way to take this idea out into the community in different kinds of housing and living situations to see if it would be beneficial.”
The research team partnered with the Canadian Mental Health Association (CMHA) and the London and Middlesex Community Housing (LMCH) to work together to retrofit the homes of the 13 study participants.
“We worked together with the participants and their care providers to choose what combination of technology they felt would be best for them,” says Dr. Forchuk. “No matter their health condition each participant wanted to be more active and independent, with the goal of staying out of hospital.”
All smart devices were connected to the Lawson Integrated Database, which is a database that can securely collect data from multiple sources such as health devices. This allowed care providers to send reminders to participants, while also tracking usage and results.
“The key benefits we noted was that study participants started to live healthier lives,” says Jonathan Serrato, Lawson Research Associate. “Participants logged going for walks and exercising more often, as well as making healthier food choices. Those who used the medication dispensers did not miss a single dose. The touch screen devices also allowed participants to easily communicate with care providers and support networks, and access more resources.”
Following the pilot study, the research team also published a subsequent paper, as a ‘how-to guide’ for utilizing smart home technology interventions as a health care tool.
“This paper is a helpful resource that outlines implications and considerations when it comes to smart home technologies,” adds Serrato. “There are many areas we touch upon such as security, privacy and feasibility as well as hardware and software information for those who would like to take on their own similar type of smart home technology project.”
Lawson Health Research Institute is one of Canada’s top hospital-based research institutes, tackling the most pressing challenges in health care. As the research institute of London Health Sciences Centre and St. Joseph’s Health Care London, our innovation happens where care is delivered. Lawson research teams are at the leading-edge of science with the goal of improving health and the delivery of care for patients. Working in partnership with Western University, our researchers are encouraged to pursue their curiosity, collaborate often and share their discoveries widely. Research conducted through Lawson makes a difference in the lives of patients, families and communities around the world. To learn more, visit www.lawsonresearch.ca.
Senior Media Relations Consultant
Communications & Public Engagement
T: 519-685-8500 ext. 73502
Celine.zadorsky@lhsc.on.ca
New study uncovers negative effects from vaping
LONDON, ON- A recently published preclinical study by researchers at Lawson Health Research Institute and Western University’s Schulich School of Medicine & Dentistry show that vaping may negatively affect pulmonary surfactant in the lungs.
Surfactant, which is made of lipids and proteins, is a critical layer in the lungs that allows people to breathe with minimal effort by reducing surface tension. Without surfactant, it would take more effort to breathe and a person would need mechanical help to do so.
“Vaping continues to be popular but not much is known about what happens with the aerosol when it enters the lungs,” says Dr. Ruud Veldhuizen, Lawson Scientist and Professor at Schulich Medicine & Dentistry. “We realized that the first thing the vapor aerosol comes in contact with in the lungs is pulmonary surfactant, which is an area our team specializes in.”
The research team was able to study the effects by placing a film of surfactant inside a syringe and, then using a vaping device to push aerosol into the syringe. This allowed the vapor to directly interact with the surfactant. The researchers then mimicked inhaling and exhaling vapor into the syringe 30 times to resemble a standard vaping session.
“In particular we were looking at the surface tension in the surfactant,” explains Emma Graham, Master’s student at Schulich Medicine & Dentistry. “After vaping, we saw high surface tension which suggests the surfactant would not be as effective at supporting proper lung functioning.”
The team also examined different vaping devices, flavours, additives and nicotine to see if there were any difference in effects.
“Nicotine didn’t have any worse effects on surface tension of surfactant compared to other e-liquids, but some flavourings like menthol e-liquid did,” says Graham.
While his team intends to study this further, Veldhuizen says these findings could provide an indication as to why people that vape have a susceptibility to develop lung injury, including those with respiratory viruses such as COVID-19.
“We would like to get this information out there so that people know vaping may be damaging to the lungs,” says Veldhuizen. “As a next step, we hope to further investigate the effects of vaping on the lungs and how we can treat resulting injury.”
The study has been published in the PLOS ONE Journal. These findings build on a body of research about the impacts of vaping through Lawson and Schulich Medicine & Dentistry. Our researchers were the first in the world to report on a potential new type of vaping-related injury in 2019.
Lawson Health Research Institute is one of Canada’s top hospital-based research institutes, tackling the most pressing challenges in health care. As the research institute of London Health Sciences Centre and St. Joseph’s Health Care London, our innovation happens where care is delivered. Lawson research teams are at the leading-edge of science with the goal of improving health and the delivery of care for patients. Working in partnership with Western University, our researchers are encouraged to pursue their curiosity, collaborate often and share their discoveries widely. Research conducted through Lawson makes a difference in the lives of patients, families and communities around the world. To learn more, visit www.lawsonresearch.ca.
Western delivers an academic experience second to none. Since 1878, The Western Experience has combined academic excellence with life-long opportunities for intellectual, social and cultural growth in order to better serve our communities. Our research excellence expands knowledge and drives discovery with real-world application. Western attracts individuals with a broad worldview, seeking to study, influence and lead in the international community.
The Schulich School of Medicine & Dentistry at Western University is one of Canada’s preeminent medical and dental schools. Established in 1881, it was one of the founding schools of Western University and is known for being the birthplace of family medicine in Canada. For more than 130 years, the School has demonstrated a commitment to academic excellence and a passion for scientific discovery.
Senior Media Relations Consultant
Communications & Public Engagement
T: 519-685-8500 ext. 73502
Celine.zadorsky@lhsc.on.ca
New study using nuclear medicine and rare isotopes in the fight against cancer
London - In a national multicentre study, scientists at Lawson Health Research Institute and Western University are working to create rare isotopes that will be used as an important tool to help treat cancer.
Currently, radiation therapy is a staple in cancer treatment, with approximately 50 per cent of cancer patients receiving radiation at some point in their cancer journey. Although a very effective tool, traditional radiation therapies rely on intense beams of energy. These beams can kill cancer cells, but their use is limited to select locations, making them less suited for difficult-to-treat metastatic cancers that have spread to multiple sites.
“Cancer treatment has evolved over the years with targeted drugs that go straight to the cancer and advanced radiation therapy. However, radiation comes from an external source that can damage other areas in the body,” says Dr. Len Luyt, Lawson Scientist and Professor at Western. “We are now working to advance treatment further by combining radiation and targeted drug therapy.”
The therapies work like a homing device — using specially designed molecules to seek out and deliver radioactive isotopes directly to cancer cells, wherever they might be in the body.
The multidisciplinary research team involves researchers at Lawson, Western University, University of British Columbia, BC Cancer, TRIUMF, Simon Fraser University, Université Laval, Université de Sherbrooke, University of Toronto and University of Alberta.
“This is the holy grail of cancer treatment. These disease-targeting molecules circulate throughout the body, binding tightly to cancer cells in order to eliminate them with a highly localized blast of energy,” explains principal investigator Dr. François Bénard, Professor of Radiology and Associate Dean at UBC’s Faculty of Medicine, and Senior Executive Director of the BC Cancer Research Institute.
The London, Ontario team will focus on developing the radio pharmaceuticals at labs in the London Regional Cancer Program at LHSC, the Cyclotron located at St. Joseph’s Health Care London, and at Western.
“The radio pharmaceuticals we are designing will be very specific to certain receptor proteins that are on cancer cells and not elsewhere on the body. This allows us to bring the isotopes to the cancer cells and clear it from the body so you have less side effects in other areas,” says Dr. Luyt. “This approach is showing promise in prostate cancer and now this team-based approach is looking at targeting any metastatic cancer.”
This collaborative research project has received $23.7 million in federal funding through the New Frontiers Research Fund (NFRF) over six years.
“We will establish Canada as a world leader in the field of nuclear medicine and ensure Canadian patients are the ones who benefit,” adds Dr. Bénard. “By developing these medicines in Canada and bringing them into local clinical trials, we will ensure Canadians have access to innovative cancer treatments sooner.”
The team hopes to bring multiple drug candidates into clinical trials in the coming years with the ultimate goal of developing an effective treatment for metastatic cancer patients.
Lawson Health Research Institute is one of Canada’s top hospital-based research institutes, tackling the most pressing challenges in health care. As the research institute of London Health Sciences Centre and St. Joseph’s Health Care London, our innovation happens where care is delivered. Lawson research teams are at the leading-edge of science with the goal of improving health and the delivery of care for patients. Working in partnership with Western University, our researchers are encouraged to pursue their curiosity, collaborate often and share their discoveries widely. Research conducted through Lawson makes a difference in the lives of patients, families and communities around the world. To learn more, visit www.lawsonresearch.ca.
Western delivers an academic experience second to none. Since 1878, The Western Experience has combined academic excellence with life-long opportunities for intellectual, social and cultural growth in order to better serve our communities. Our research excellence expands knowledge and drives discovery with real-world application. Western attracts individuals with a broad worldview, seeking to study, influence and lead in the international community.
Senior Media Relations Consultant
Communications & Public Engagement
T: 519-685-8500 ext. 73502
Celine.zadorsky@lhsc.on.ca
New study using nuclear medicine and rare isotopes in the fight against cancer
In a national multicentre study, scientists at Lawson Health Research Institute and Western University are working to create rare isotopes that will be used as an important tool to help treat cancer.
Currently, radiation therapy is a staple in cancer treatment, with approximately 50 per cent of cancer patients receiving radiation at some point in their cancer journey. Although a very effective tool, traditional radiation therapies rely on intense beams of energy. These beams can kill cancer cells, but their use is limited to select locations, making them less suited for difficult-to-treat metastatic cancers that have spread to multiple sites.
“Cancer treatment has evolved over the years with targeted drugs that go straight to the cancer and advanced radiation therapy. However, radiation comes from an external source that can damage other areas in the body,” says Dr. Len Luyt, Lawson Scientist and Professor at Western. “We are now working to advance treatment further by combining radiation and targeted drug therapy.”

The therapies work like a homing device — using specially designed molecules to seek out and deliver radioactive isotopes directly to cancer cells, wherever they might be in the body.
The multidisciplinary research team involves researchers at Lawson, Western University, University of British Columbia, BC Cancer, TRIUMF, Simon Fraser University, Université Laval, Université de Sherbrooke, University of Toronto and University of Alberta.
“This is the holy grail of cancer treatment. These disease-targeting molecules circulate throughout the body, binding tightly to cancer cells in order to eliminate them with a highly localized blast of energy,” explains principal investigator Dr. François Bénard, Professor of Radiology and Associate Dean at UBC’s Faculty of Medicine, and Senior Executive Director of the BC Cancer Research Institute.
The London, Ontario team will focus on developing the radio pharmaceuticals at labs in the London Regional Cancer Program at LHSC, the Cyclotron located at St. Joseph’s Health Care London, and at Western.
“The radio pharmaceuticals we are designing will be very specific to certain receptor proteins that are on cancer cells and not elsewhere on the body. This allows us to bring the isotopes to the cancer cells and clear it from the body so you have less side effects in other areas,” says Dr. Luyt. “This approach is showing promise in prostate cancer and now this team-based approach is looking at targeting any metastatic cancer.”
This collaborative research project has received $23.7 million in federal funding through the New Frontiers Research Fund (NFRF) over six years.
“We will establish Canada as a world leader in the field of nuclear medicine and ensure Canadian patients are the ones who benefit,” adds Dr. Bénard. “By developing these medicines in Canada and bringing them into local clinical trials, we will ensure Canadians have access to innovative cancer treatments sooner.”
The team hopes to bring multiple drug candidates into clinical trials in the coming years with the ultimate goal of developing an effective treatment for metastatic cancer patients.
New transportation resource for youth in crisis
LONDON, ON – Transitional aged youth in Middlesex County now have access to a free transportation resource to access mental health services. Called the County Transport initiative, it will help youth ages 16 to 25 in Lucan, Parkhill, Exeter and Strathroy-Caradoc get the mental health care they need, when they need it.
County Transport is being coordinated by MINDS of London-Middlesex, a program of Lawson Health Research Institute, in partnership with the Canadian Mental Health Association (CMHA) of Elgin-Middlesex, Star Taxi and Middlesex County through the Lucan and Parkhill Libraries.
“Through our collaborative work, we’ve heard from many youth that transportation is a barrier for them when trying to access mental health services when in crisis. Youth in rural areas find this very challenging since most services are not close to their location,” says Romaisa Pervez, Research Assistant at MINDS of London-Middlesex.
MINDS, a Mental Health INcubator for Disruptive Solution, is a social innovation lab with a mission to address the complexity of the mental health care system. Youth with lived experience, community members and researchers work together to understand and help those living with mental health challenges in London-Middlesex by designing, piloting and testing innovative solutions developed locally.
“We do not have the exact numbers of Transitional Aged Youth (TAY) living in rural Middlesex who would benefit from access to the County Transport Initiative, but we know that mental health services in rural communities are limited and that access to the services available in larger city centres is challenging due to transportation difficulties,” explains Cathy Burghardt-Jesson, Warden for Middlesex County. “Transportation from Middlesex to London, where the majority of mental health resources are located, is underdeveloped as there are limited bus routes and schedules. This leaves little in the way of affordable transit options for TAY in crisis.”
Youth in crisis who connect with CMHA’s Reach Out 24/7 line at www.reachout247.ca or by phone at 519-433-2023 will be supported and assessed by the Crisis Line staff. If it is determined that a visit to the London Crisis Centre is needed, the CMHA Crisis worker will ensure a smooth transition from the Crisis Line to the Star Taxi Service. The youth will be provided with free transportation to and from CMHA’s Mental Health and Addictions Crisis Centre located at 648 Huron Street.
To ensure the safety and wellbeing of the youth accessing this service, Star Taxi drivers have received training developed by CMHA regarding mental health and crisis de-escalation, as well as suicide prevention training by Living Works.
Funding for the initiative has been provided by St. Joseph’s Health Care Foundation and the generous support of individual donors in the community.
“With additional funding, the initiative could be scaled up to reach as many youth as possible in Middlesex County and beyond. We want to see all youth in rural areas who want to access mental health services able to do so, by removing the barriers of location and transportation,” adds Pervez. They will be collecting information regarding use of the transportation service and youth experience to refine and improve the initiative.
-30-
Lawson Health Research Institute is one of Canada’s top hospital-based research institutes, tackling the most pressing challenges in health care. As the research institute of London Health Sciences Centre and St. Joseph’s Health Care London, our innovation happens where care is delivered. Lawson research teams are at the leading-edge of science with the goal of improving health and the delivery of care for patients. Working in partnership with Western University, our researchers are encouraged to pursue their curiosity, collaborate often and share their discoveries widely. Research conducted through Lawson makes a difference in the lives of patients, families and communities around the world. To learn more, visit www.lawsonresearch.ca.
Senior Media Relations Consultant
Communications & Public Engagement
T: 519-685-8500 ext. 73502
Celine.zadorsky@lhsc.on.ca
New transportation resource for youth in crisis
Transitional aged youth in Middlesex County now have access to a free transportation resource to access mental health services. Called the County Transport initiative, it will help youth ages 16 to 25 in Lucan, Parkhill, Exeter and Strathroy-Caradoc get the mental health care they need, when they need it.
County Transport is being coordinated by MINDS of London-Middlesex, a program of Lawson Health Research Institute, in partnership with the Canadian Mental Health Association (CMHA) of Elgin-Middlesex, Star Taxi and Middlesex County through the Lucan and Parkhill Libraries.
“Through our collaborative work, we’ve heard from many youth that transportation is a barrier for them when trying to access mental health services when in crisis. Youth in rural areas find this very challenging since most services are not close to their location,” says Romaisa Pervez, Research Assistant at MINDS of London-Middlesex.

Romaisa Pervez, Research Assistant at MINDS of London-Middlesex, is leading the County Transport initiative.
MINDS, a Mental Health INcubator for Disruptive Solution, is a social innovation lab with a mission to address the complexity of the mental health care system. Youth with lived experience, community members and researchers work together to understand and help those living with mental health challenges in London-Middlesex by designing, piloting and testing innovative solutions developed locally.
“We do not have the exact numbers of transitional aged youth living in rural Middlesex who would benefit from access to the County Transport Initiative, but we know that mental health services in rural communities are limited and that access to the services available in larger city centres is challenging due to transportation difficulties,” explains Cathy Burghardt-Jesson, Warden for Middlesex County.
“Transportation from Middlesex to London, where the majority of mental health resources are located, is underdeveloped as there are limited bus routes and schedules. This leaves little in the way of affordable transit options for youth in crisis.”
Youth in crisis who connect with CMHA’s Reach Out 24/7 line at www.reachout247.ca or by phone at 519-433-2023 will be supported and assessed by the Crisis Line staff. If it is determined that a visit to the London Crisis Centre is needed, the CMHA Crisis worker will ensure a smooth transition from the Crisis Line to the Star Taxi Service. The youth will be provided with free transportation to and from CMHA’s Mental Health and Addictions Crisis Centre located at 648 Huron Street.
To ensure the safety and wellbeing of the youth accessing this service, Star Taxi drivers have received training developed by CMHA regarding mental health and crisis de-escalation, as well as suicide prevention training by Living Works.
Funding for the initiative has been provided by St. Joseph’s Health Care Foundation and the generous support of individual donors in the community.
“With additional funding, the initiative could be scaled up to reach as many youth as possible in Middlesex County and beyond. We want to see all youth in rural areas who want to access mental health services able to do so, by removing the barriers of location and transportation,” adds Pervez.
They will be collecting information regarding use of the transportation service and youth experience to refine and improve the initiative.