Search
Search
Addressing the impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic
As the COVID-19 pandemic has continued for a year and a half, many people from all walks of life are feeling the impacts especially when it comes to their mental health and wellbeing.
Hospital researchers through Lawson Health Research Institute, along with its hospital partners, have been studying the impacts for some key groups.
Health care workers have been at the forefront of the pandemic. These heroes have worked tirelessly through every wave and continue to provide excellent care to their patients and community. Dr. Kamia Honarmand, Critical Care Physician at London Health Sciences Centre (LHSC), remembers the stress that she and her colleagues were feeling, and know that something needed to be done.
“Our team wanted to better understand the impact of the pandemic on the lives of health care workers, both personally and professionally, and understand how they were coping when it came to their mental health,” says Dr. Honarmand who is also an Associate Scientist at Lawson. “There was a lot of reasons to be stressed even before the height of the first wave in our region. There was a lot of anxiety. The hospital wanted to find ways to support health care workers and identify resources that would assist them.”

Dr. Kamia Honarmand, Critical Care Physcian at LHSC and Lawson Associate Scientist
Frontline health care workers across the region were invited to take part in an online survey about their experiences during the pandemic. “We looked at both the impacts and the preferred coping strategies, and what supportive strategies they would like to have in the hospital in the future.”
The Veterans Care Program located at Parkwood Institute, a part of St. Joseph’s Health Care London, provides complex continuing and long-term care for Canadian war Veterans. Dr. Don Richardson, Director of the MacDonald Franklin OSI Research Centre at Parkwood Institute, has been treating and studying mental health among Veterans for many years. He believed this was a group was likely to be affected by the pandemic in unique ways.
“We know that Veterans in general are at a higher risk for depression, anxiety and PTSD,” explains Dr. Richardson, who is also a Scientist at Lawson. “We also knew the pandemic and forced restrictions would have significant impact on Veterans and their families who would be more isolated than they already are.”
More than 1,100 Veterans and around 250 spouses were recruited for the study, completing an online survey every three months for 18 months.
The study is still ongoing, but Dr. Richardson says the initial data has been telling. “We have been able to analyze some of the preliminary data and what we have found is that almost 50 per cent did not indicate their mental health had worsened during the pandemic but 40 to 50 per cent have had difficulty accessing care.”

Dr. Don Richardson, Director, Macdonald Franklin OSI Research Centre
The hope is that this study will lead to better preparedness in the future to safeguard the mental health of Veterans and ensure their access to care during a pandemic.
Many people have felt isolation during the pandemic, but that feeling may have even more of an impact for youth suffering from mood and anxiety disorders.
Dr. Elizabeth Osuch, Director of the First Episode Mood and Anxiety Program (FEMAP) at LHSC says the pandemic-led lockdown forced more than a hundred mental health clients out of in-person services.

Dr. Elizabeth Osuch, Director of FEMAP and Lawson Scientist
“They lost their resources for mental health services and support as soon as the quarantine was announced,” shares Dr. Osuch, who is also a Scientist at Lawson. “We were concerned that it would be devastating to people – and to some people it was. We wanted to make sure they had an avenue to connect with the program.”
Dr. Osuch and the FEMAP team created an online research platform to find out how patients were doing by having them fill out a symptoms and function questionnaire.
“We have analyzed the first wave so far and it shows that male patients were doing better and female patients were doing worse, which was a surprise. One of the risk factors for not doing well was the loss of their job.”
The pandemic added an extra layer of stress and worry for women who were having a baby.
“This has been an enormous and pivotal time for everyone in the world,” says Dr. Genevieve Eastabrook, Obstetrician-Gynecologist at LHSC. “The experiences during pregnancy and post-partum for both the birthing person and their baby can have effects later in life for children. For example, their overall cardiovascular and metabolic health, bonding experiences and the risk of mood disorders.”
Dr. Eastabrook, who is also an Associate Scientist at Lawson and Assistant Professor at Western University’s Schulich School of Medicine & Dentistry, is working with a team to examine the effects the pandemic may be having for mothers and their babies. As part of the study, the London research team is using an approach called ‘One Health’ which offers a holistic perspective to explore how various risk factors and social determinants of health interact.

Dr. Genevieve Eastabrook, OBGYN at LHSC and Lawson Associate Scientist
“The unique aspect is that we have a comparative group to see if there are differences in markers such as risk of depression, perceived stress and social supports,” adds Dr. Eastabrook.
Study participants are asked to complete a 30-minute questionnaire at around 6-12 weeks after their delivery. The research team is still recruiting patients for this study.
Advancing research during the COVID-19 pandemic
From the moment the COVID-19 pandemic was declared in March 2020, our teams at Lawson Health Research Institute have been at the forefront. Researchers at London Health Sciences Centre (LHSC) and St. Joseph’s Health Care London immediately began to work towards understanding the new virus in an effort to discover lifesaving health-care solutions.
To date, dozens of research projects have been advanced through Lawson with some receiving international attention as ‘world firsts’. As we mark the three-year anniversary of COVID-19 being declared a global pandemic by the World Health Organization (WHO), we share with you COVID-19 research highlighted over the past year.
Study finds acute kidney injury associated with severe COVID-19 leads to high mortality rates
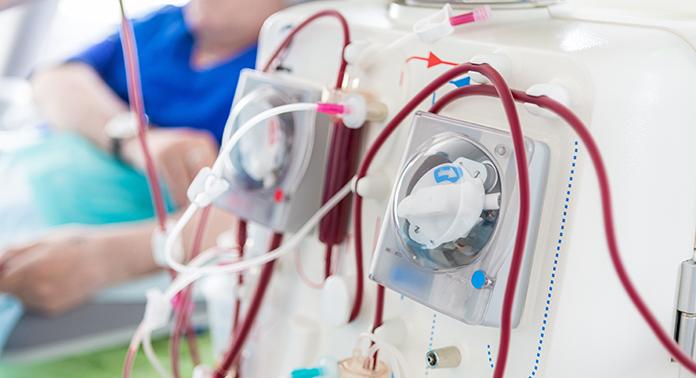
Severe cases of a COVID-19 infection can cause a host of serious complications, including acute kidney injury. In a published study, scientists at Lawson found that acute kidney injury in patients with a severe COVID-19 infection leads to a high mortality rate.
By accessing data collected through the Ontario Renal Network (ORN), Dr. Peter Blake, Lawson Researcher and Provincial Medical Director at the Ontario Renal Network, and his colleagues examined 271 people at 27 renal programs across the province, including patients at LHSC, who received dialysis for acute kidney injury due to a COVID-19 infection. Read more.
Study shows a decline in Veterans’ mental health throughout the pandemic

In published findings from Lawson, more than half of Canadian Veterans reported a decline in their mental health over the course of the COVID-19 pandemic.
When it comes to mental health conditions, Veterans are an at-risk population, often having higher rates of depression and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). When the COVID-19 pandemic hit, scientists at Lawson wanted to understand its effects on this already at-risk population.
To examine the potential impacts the research team launched a longitudinal study recruiting Canadian Veterans and spouses of Canadian Veterans. Participants complete online questionnaires every three months, with questions focused on mental health and virtual health care services. Read more.
Virtual care associated with significant environmental and patient cost savings

A study published in JAMA Network Open by researchers at ICES, Lawson and Western University found that virtual care during the COVID-19 pandemic led to a significant reduction in carbon dioxide emissions and patient travel-related expenses, such as gasoline, parking or public transit costs.
Findings show that for more than 10 million patients with at least one appointment during the study period (63 million visits in total), virtual care was associated with estimated savings of:
• 3.2 billion kilometers of patient travel;
• 545 to 658 million kilograms of carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions; and
• $569 to $733 million (Canadian [US $465-$599 million]) in expenses for gasoline, parking, or public transit. Read more.
London researchers discover novel method to diagnose long COVID

Published in Molecular Medicine, researchers at Lawson found that patients with post-COVID-19 condition (long COVID) have unique biomarkers in their blood. The team is now working on developing a first of its kind blood test that could be used to diagnose long COVID. The discovery could also lead to new therapeutics for this condition.
The researchers studied 140 blood samples from participants at LHSC and St. Joseph’s Health Care London, including St. Joseph’s Post-Acute COVID-19 Program. Participants were those with presumed long COVID, hospital inpatients with acute COVID-19 infection and healthy control subjects. Read more.
Researchers are combining new technologies to examine blood proteins in COVID-19 patients
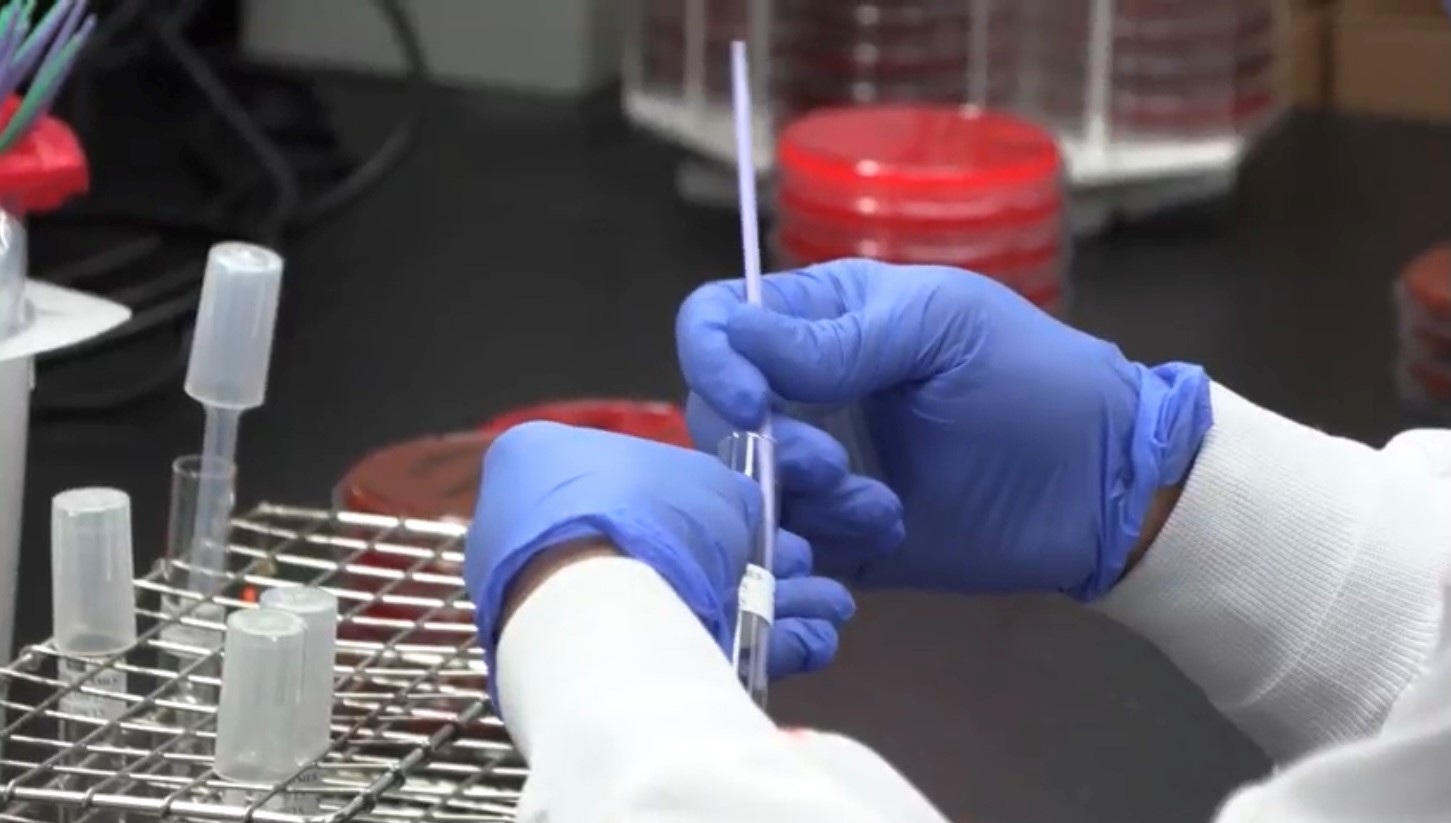

Published in the Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine, a team at Lawson discovered unique patterns of blood plasma proteins in critically ill patients that may help develop a more personalized approach to treating severe COVID-19.
Called the plasma proteome, the proteins studied are released by cells that often play an important role in the body’s immune response to viruses. The research team studied how they adapt and change to a COVID-19 infection. Read more.
Senior Media Relations Consultant
Communications & Public Engagement
T: 519-685-8500 ext. 73502
Celine.zadorsky@lhsc.on.ca
Advocating for health research during “H on the Hill”
HealthCareCAN held its third annual Lobby Day “H on the Hill” event on Parliament Hill in Ottawa, on Tuesday, October 30, 2018.
Canada’s hospital CEOs and vice presidents of health research joined HealthCareCAN - the national voice of Canada’s healthcare organizations, community and research hospitals - to meet with MPs, Senators and senior government staff.
Collectively, they issued a call for federal action to unlock the tremendous economic potential of the health and life sciences sector to support better health for Canadians.
Dr. David Hill, Scientific Director for Lawson and Integrated Vice President of Research for London Health Sciences Centre and St. Joseph’s Health Care London, participated in the lobby day. Dr. Hill currently sits on the Board of Directors for HealthCareCAN.

Image

“Minister of Crown Indigenous Relations @Carolyn_Bennett, Parliamentary Secretary for Science, Sport, and Accessibility @KateYoungMP, and Dr. David Hill, catching up over lunch at #HontheHill #CDNpoli #CDNhealth”

Meeting participants stressed the need for action on HealthCareCAN’s recommendations for the 2019 federal budget, specifically:
- Setting a minimum 25% funding floor for the indirect costs of research under the Research Support Fund;
- Granting eligibility to federal infrastructure funding competitions to healthcare organizations, and;
- Investing in digital health platforms to support care, training, and research in healthcare organizations.
Diverse areas of the health and life sciences sector and key health issues were discussed, including:
- Health and science research, granting councils;
- Hospital infrastructure;
- Health innovation;
- Electronic health technology;
- Opioid crisis response;
- Mental health;
- Aboriginal health; and,
- Home care.
Read Dr. Hill’s recent column in Hospital News on bridging the gap from discovery to patient care.

HealthCareCAN provides high-quality policy research advocacy and leadership development services to our members while championing healthcare system transformation in Canada. Visit www.healthcarecan.ca to learn about our solutions to health and healthcare challenges. Follow us on Twitter: @HealthCareCAN
An innovative year: Top 12 research stories of 2023
It’s been another year of transformational research at Lawson Health Research Institute. Our teams have published groundbreaking findings and launched new studies that will have a profound impact on patient care.
The following are 12 highlights of research and innovation from across London Health Sciences Centre (LHSC) and St. Joseph’s Health Care London (St. Joseph’s). From trialing new cancer treatments to advancing understanding of mental health, our research teams have achieved a number of important milestones.

1. New study suggests blood plasma proteins hold answers to better understanding long COVID
Lawson researchers continued to advance understanding of COVID-19 this past year. In one study, researchers found that unique patterns in blood plasma proteins of patients with suspected long COVID could act as a drug target to improve patient outcomes. Read more.
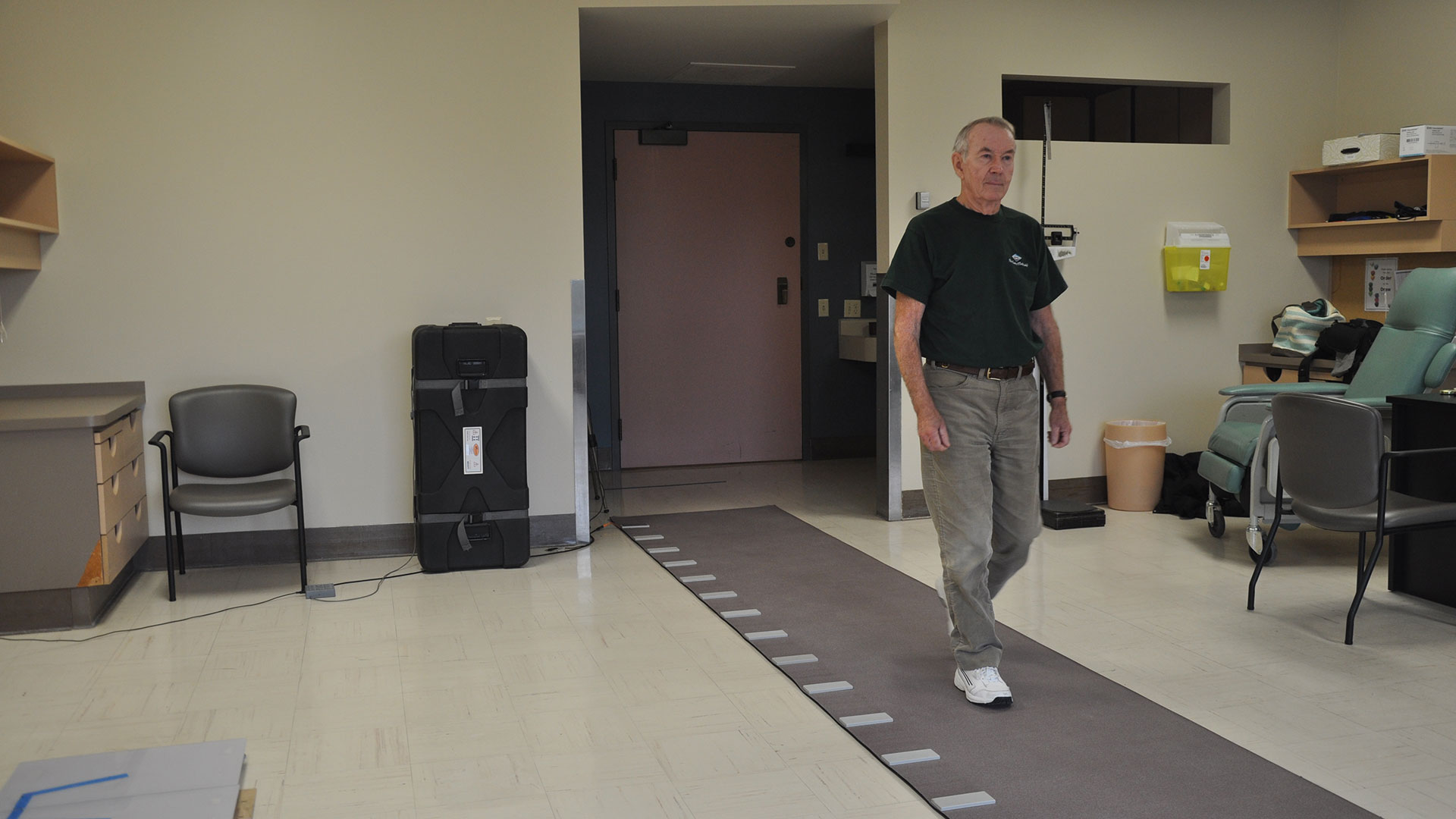

2. New study finds exercise, cognitive training combo boosts mental sharpness in seniors
A study from Lawson and Western University found that a combination of computerized cognitive training and aerobic-resistance exercises can improve functions like memory, attention, recognition and orientation in older adults with mild cognitive impairment. The results suggest a new way to address declining mental sharpness in older adults. Read more.

3. $7.55 million in funding to take LHSC-developed technology global
Technology to diagnose rare genetic disorders developed by researchers at Lawson and LHSC will be going global thanks to $7.55 million in funding from Genome Canada grant and Illumina Inc. The new artificial intelligence-led technology could allow rare diseases to be diagnosed with a simple blood test. Read more.

4. Fecal transplants show promise in improving melanoma treatment
Fecal microbiota transplants (FMT) from healthy donors are safe and could improve response to immunotherapy in patients with advanced melanoma, according to results from a world-first multi-centre clinical trial led by Lawson researchers. Read more.

5. New study shows technology could play an important role in mental health support
A team of Lawson researchers found that the use of ‘smart home’ technology like touch screen devices, activity trackers, weigh scales and medication dispensers may lead to better outcomes for those living with both mental health and physical disorders. The study found that participants using the technology started logging more exercise, making healthier food choices and not missing medication doses. Read more.

6. Canadian children’s hospital visits for suicidal thoughts, self-poisoning and self-harm up during pandemic, study finds
A national study with Lawson researchers found that during the first two years of the COVID-19 pandemic, adolescent emergency department (ED) visits and hospitalizations for suicidal thoughts, self-harm and self-poisoning increased across Canada, with the greatest increase occurring among adolescent girls. Read more.
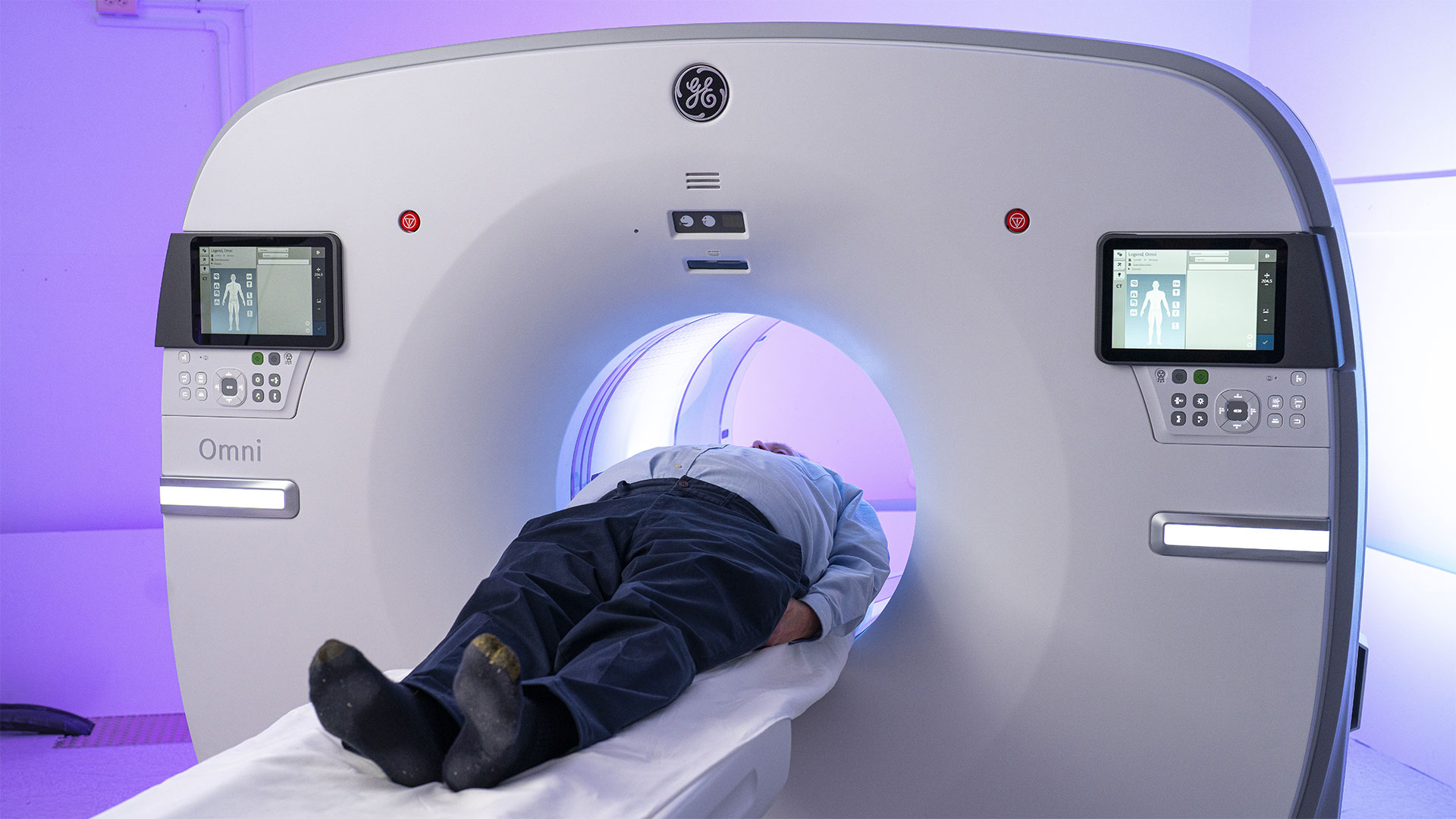
7. St. Joseph’s to become Canada’s first centre of excellence in molecular imaging and theranostics
A partnership between Lawson, St. Joseph’s Health Care London and GE HealthCare will create Canada’s first centre of excellence in molecular imaging and theranostics at St. Joseph’s. The centre will focus on using precision diagnostic imaging and targeted therapy to advance personalized treatment of cancer and other diseases. Read more.
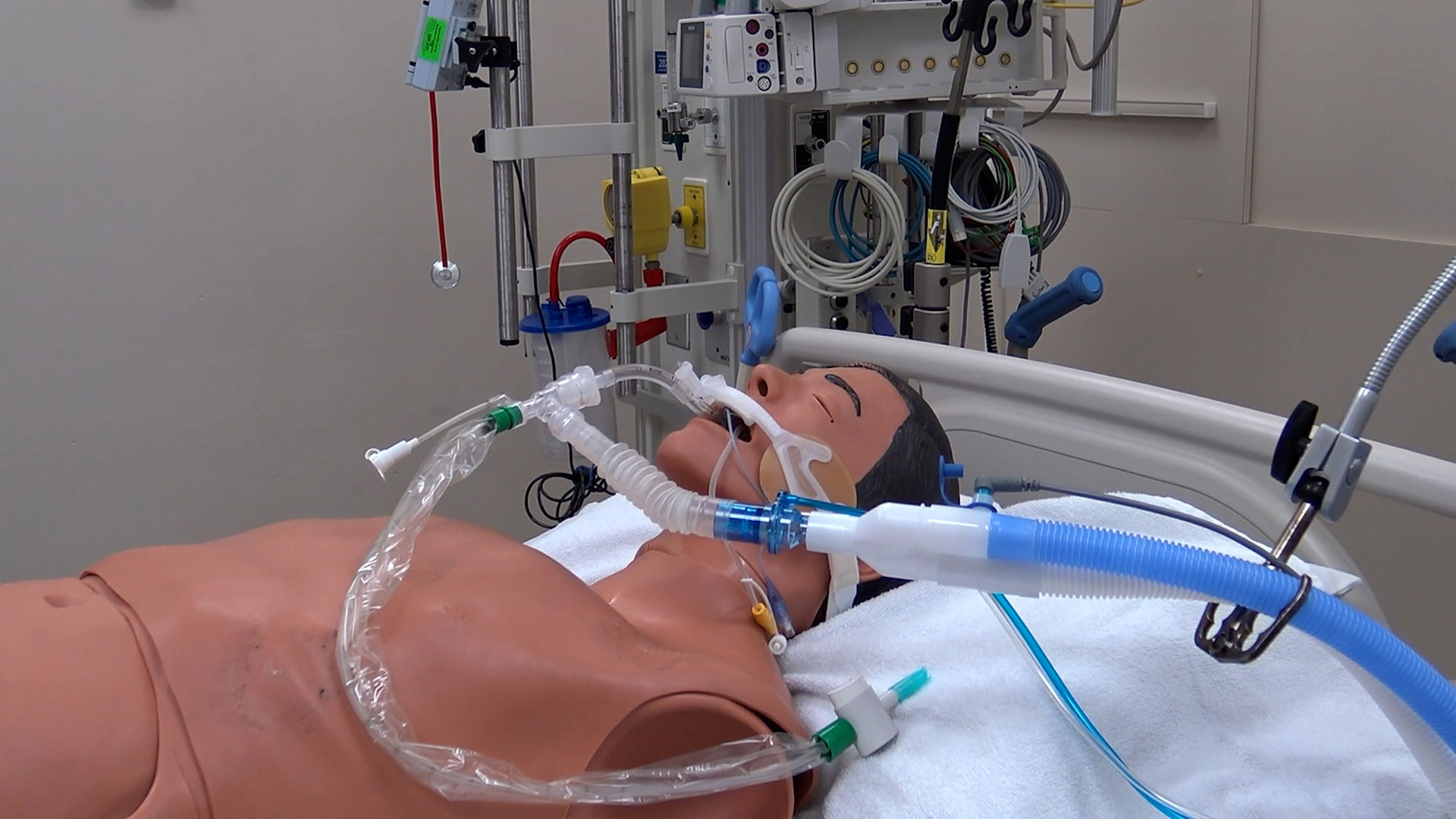
8. Researchers investigate a new method of sedation for paediatric patients
Intravenous sedatives are normally used to sedate critically ill children. However, they can contribute to a complication called delirium, which includes symptoms of confusion, disorientation, agitation, excessive drowsiness and poor attention. To improve outcomes, scientists at Children’s Health Research Institute (a program of Lawson), Sunnybrook Research Institute and The Hospital for Sick Children (SickKids) are collaborating on a pilot study to understand whether inhaled sedation could be a better alternative to keep critically ill children sedated and comfortable. Read more.
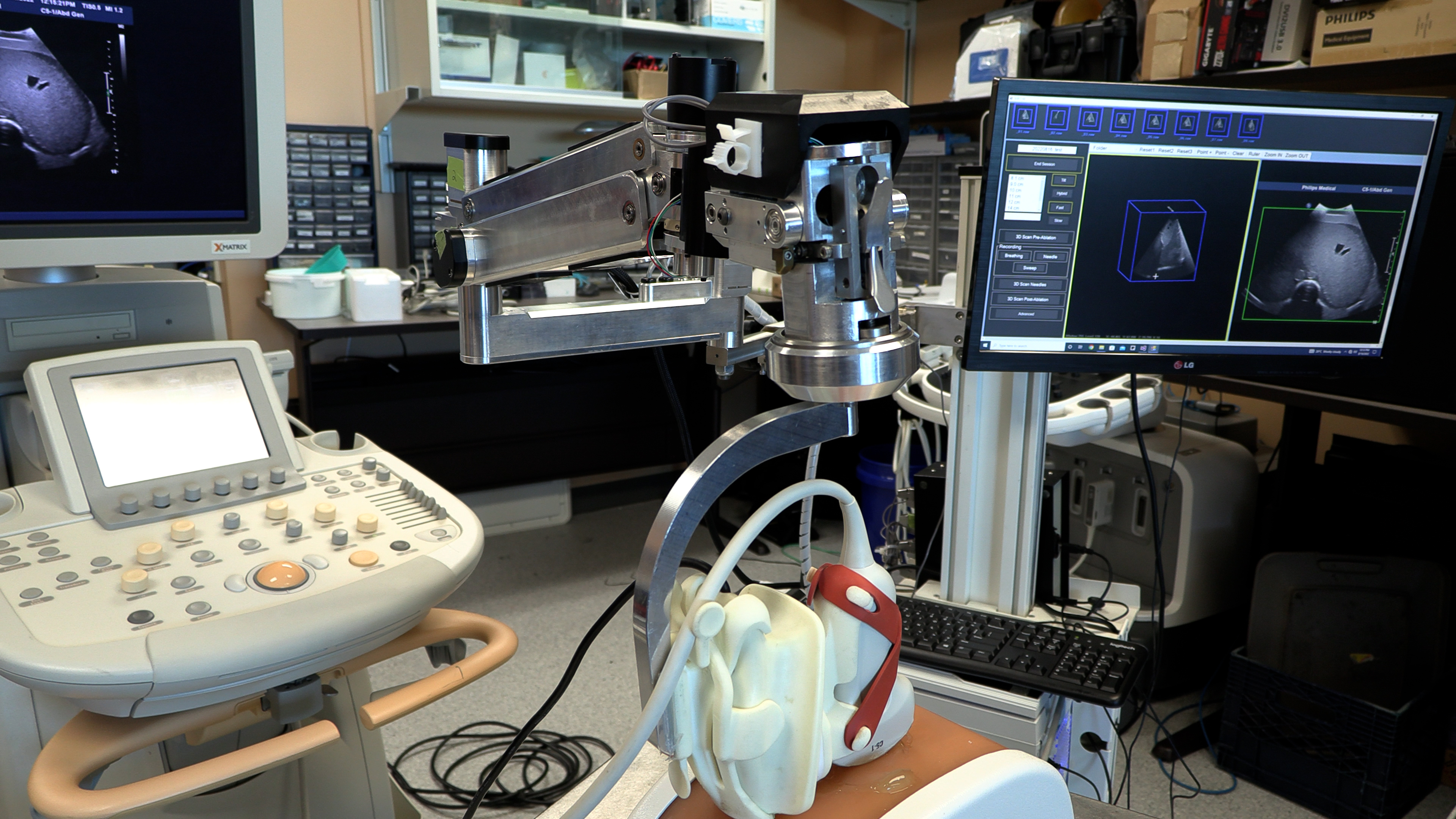
9. New robotic 3D ultrasound may improve accuracy of liver cancer ablation therapy
A technique that turns a normal ultrasound into a 3D image is showing promise in making thermal ablation for liver cancer treatment more accurate in a study from Lawson and Western University. Thermal ablation – using heat to destroy a cancerous tumour – can have fewer complications and a shorter recovery time than surgery. Read more.

10. Assessing neurofeedback in stroke survivors
Functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS) is used to detect changes in brain oxygen levels using light, but more recently it has also been used to develop brain-computer interfaces – allowing patients with brain injuries to control a device with their thoughts. Researchers at Lawson launched a new study to assess whether fNIRS can be used to improve patient outcomes during stroke rehabilitation. Read more.

11. Specific type of inflammation may be linked to risk of colorectal cancer
A preclinical study found that a specific type of inflammation may be linked to an increased risk of colorectal cancer. Previously, the degree of inflammation caused by illnesses like colitis, Crohn’s disease and other forms of inflammatory bowel disease were shown to be an important indicator of the development of colorectal cancer. However, this new study found the type of inflammation, rather than the severity and duration, may be more important in determining cancer risk. Read more.
12. New study examining if probiotics can improve outcomes in knee replacement surgeries
Lawson researchers launched a study to assess whether daily probiotics can improve outcomes in patients undergoing a total knee replacement surgery. Of the more than 70,000 knee replacement surgeries in Canada each year, nearly 10 per cent of patients experience complications. With patients who are considered healthy likely to have better outcomes, the research team is interested in improving the gut microbiome as a way to support patients’ overall health. Read more.
Communications Consultant & External Relations
Lawson Health Research Institute
T: 519-685-8500 ext. ext. 64059
C: 226-919-4748
@email
An online approach to care
With an aging population, neurological conditions like stroke, brain injury and multiple sclerosis (MS) are on the rise in Canada. Those living with neurological conditions face many long-term challenges that can affect both their physical and cognitive functioning. They are also at an increased risk for mental health challenges such as depression and anxiety.
“While mental health challenges are common for those with neurological conditions, they often go untreated for a number of reasons,” says Dr. Swati Mehta, Scientist at Lawson Health Research Institute. “For example, those living in remote areas often do not have access to specialized services and many patients are concerned about stigma.”
Yet seeking mental health care is critically important for patients with neurological conditions. “Research suggests that depression among these patients can impair recovery, leading to decreased quality of life and increased health care costs.”
To improve patient outcomes, Dr. Mehta and a collaborative research team are developing an internet-delivered cognitive behavioural therapy (ICBT) program.

Cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT) is a specialized type of therapy that involves patients learning strategies and skills to self-manage mental health symptoms. It’s one of the most widely used therapies for the treatment of depression and anxiety.
A panel of researchers, persons with lived experience of neurological conditions and community organizations are working collaboratively to develop an accessible ICBT program that meets the needs of persons with neurological conditions and mild cognitive impairment who are also experiencing symptoms of depression or anxiety. The program, called The Neuro Course, will be a modified version of an existing course developed in Australia by the eCentreClinic.
“Through co-development with patients and experts in the field, the ICBT program will meet the specific needs of persons with neurological conditions who are also experiencing mental health challenges,” explains Dr. Mehta. “With online delivery, it can provide personalized treatment while being flexible and easily accessible.”
The Neuro Course will be piloted with a small group of research participants, including patients from Parkwood Institute, a part of St. Joseph’s Health Care London. Eligible participants can sign up to be notified of the course’s availability at https://www.onlinetherapyuser.ca/neuro.
The free online course consists of six easy-to-understand CBT lessons and will take approximately 10 weeks to complete. In addition to the six lessons, participants will be encouraged to work through various activities during the week.

Participants will also receive regular support from a designated online guide. Guides will be health educators who are certified providers or graduate students working under the supervision of certified providers. All guides will have training in psychology or social work. The participant’s guide will review the participant’s progress and answer any questions or comments through a secure messaging system.
Participants in the study will be asked to complete brief questionnaires before they begin the course, on a weekly basis throughout the course and then again three months after treatment ends. The research team will use the questionnaires to assess patient outcomes and improve future versions of the course.
The goal of the program is to overcome barriers to face-to-face therapy, such as limited access to specialized care and concerns about stigma related to seeking care, by providing an effective online alternative. By reaching those in need, the research team hopes to improve patient outcomes and overall wellbeing.
“The long term goal would be to implement the ICBT program into clinical practice to provide increased access to mental health services among this population,” says Dr. Mehta. “The program could be used to provide care to those with mild to moderate mental health concerns or those waiting to access face-to-face programs.”
The team is being funded for this project through Lawson’s Internal Research Fund (IRF) competition. “As an early career researcher, receiving funding from Lawson’s IRF is a great honour. It’s a great opportunity to help researchers obtain funding for small feasibility studies to develop evidence for larger grants that can be used to translate knowledge across the community,” states Dr. Mehta.