Search
Search
Growing Tissues in the Lab
When challenged by surgeons to find better treatments for difficult-to-manage connective tissue diseases, Dr. David O’Gorman gladly accepted.
Dr. O’Gorman is a Molecular Biologist and Lawson Scientist based at St. Joseph’s Hospital, a part of St. Joseph’s Health Care London. His research focuses on understanding normal and abnormal connective tissue repair. He collaborates with researchers and clinicians working in many different disciplines, including those specializing in reconstructive surgery, orthopedics and urology.
Surgical reconstructions can be hampered by a lack of graft tissue, or graft tissue of insufficient quality, making it difficult to achieve optimal outcomes for the patients.
An example is a condition called urethral stricture disease (urethral scarring). This condition occurs in males and typically causes symptoms such as frequent and urgent urination, and slow urinary stream. In extreme cases, it can cause urinary tract infections, permanent bladder dysfunction and renal failure. Recurrence rates after minimally invasive treatments are high, and so many urologists recommend open surgical approaches.
Surgeons can use the patient’s own tissues to reconstruct the urethra after stricture removal. This tissue is normally sourced from the buccal cavity in the mouth but taking large tissue grafts can result in complications. In cases where buccal grafts have been used for previous reconstructions, there may not be enough intact tissue left.
Dr. O’Gorman sees a solution in growing sheets of human buccal tissues in the lab.
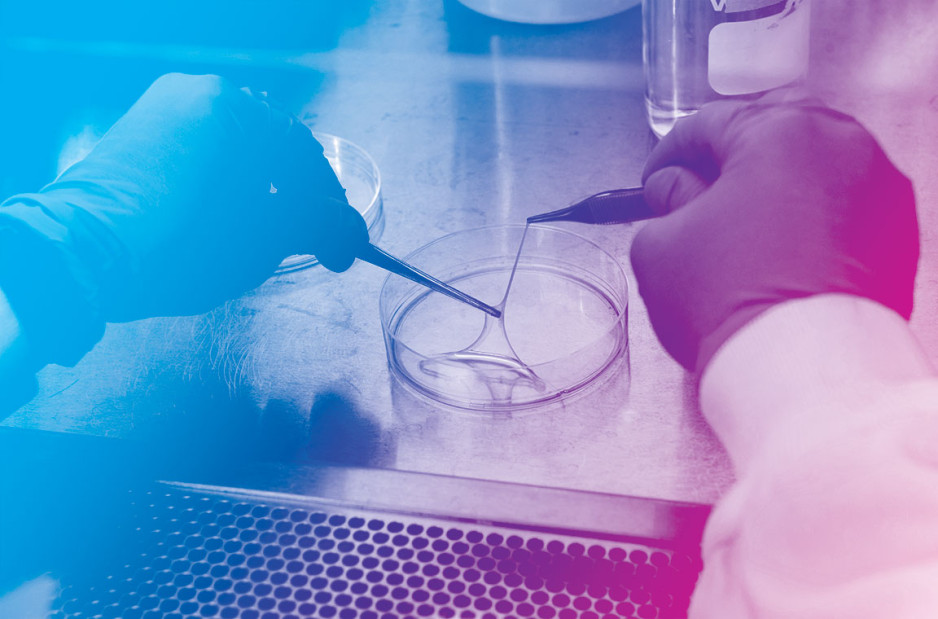
“We are currently using buccal graft trimmings as a source of cells, culturing them in a 3D environment and expanding them to create tissues of suitable size, density and elasticity.”
The patient’s own cells are used to generate a tissue graft for urethral reconstruction. While several research groups have developed this approach in the past, few have attempted to translate their models for clinical use.
“Our immediate goal is to provide proof of principle – that we can consistently generate grafts of suitable size and functional characteristics,” explains Dr. O’Gorman, “In the future, we could be providing bioengineered graft tissues for reconstructive surgeries here in London.”
Bioengineered human tissues can also be used as ‘mimetics’ – replications of human tissues – to study diseases, especially those difficult to model using routine laboratory methods.
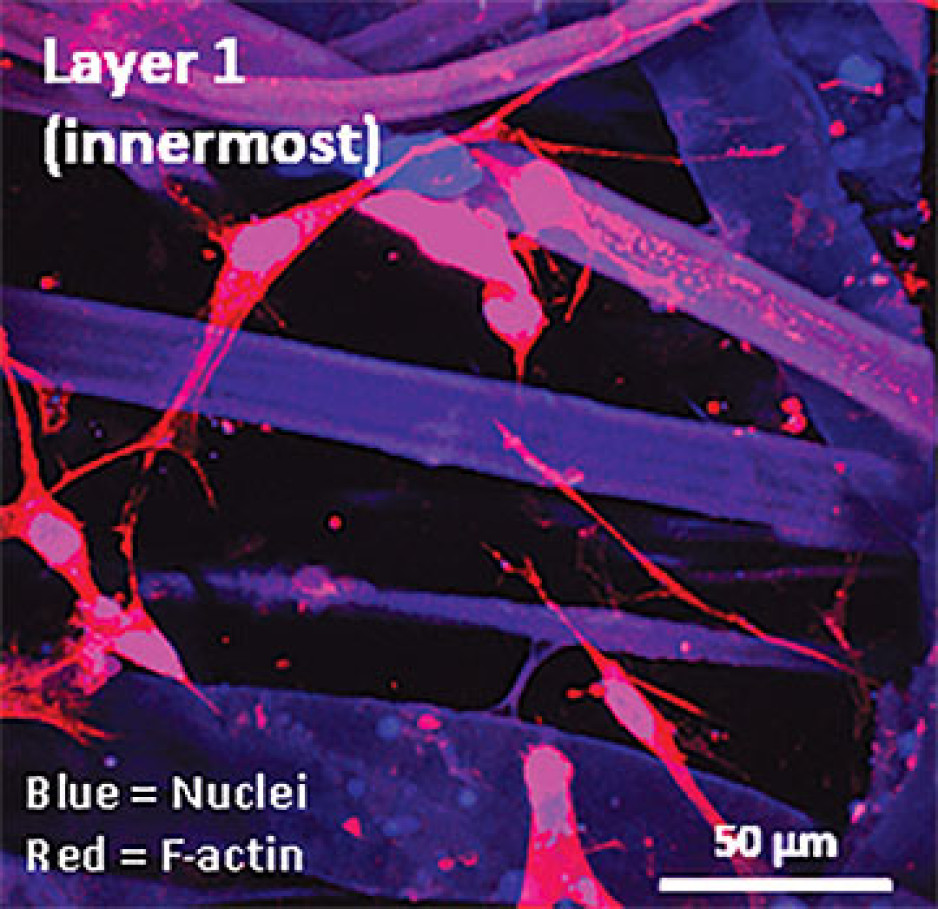
Instead of a using a growth media or sterile plastic dishes, 3D cell culture is achieved by embedding cells in a matrix of proteins and other molecules normally found in those tissues. In this environment, gene expression and growth is more similar to cells of connective tissues in the body being replicated.
Dupuytren’s disease (or Dupuytren’s Contracture) affects the palmar fascia in the hand, a connective tissue beneath the skin that extends from the base of the palm into the fingers. This disease can be understood as a type of excessive scarring, where normal tissue repair processes have gone awry and dense scar tissue forms, typically causing permanent palm or finger flexion that restricts hand function.
This condition is surprisingly common and may affect more than one million people in Canada. While there are surgical treatment options available, none consistently prevent this disease from recurring in at least a third of patients.
“Due to its high recurrence rate after treatment, Dupuytren’s disease is currently considered incurable. Our challenge is to understand it well enough to develop truly effective treatments,” says Dr. O’Gorman.
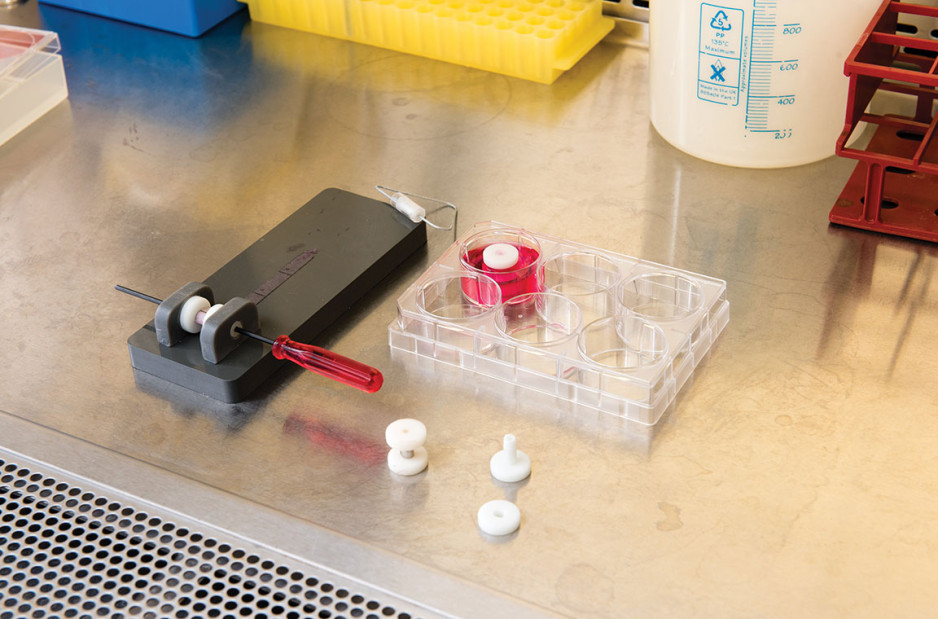
Human hands have unique characteristics not found in other species, making animal models impractical. Instead, Dr. O’Gorman’s team extracts cells from the diseased palmar fascia of patients undergoing hand surgeries and bioengineers them into palmar fascia ‘contractures’ in the lab.
“Since the cells from a single palmar fascia sample can be used to grow dozens of little contractures, we can test many different treatments simultaneously to see what works best for each patient.”
This approach may also allow them to determine if Dupuytren’s disease is truly one disease, or a group of similar diseases that cause palm and finger contractures.
“Often, Dupuytren’s disease is clearly heritable, but some individuals have no family history of it and develop apparently sporadic disease,” notes Dr. O’Gorman. “We want to determine if these are truly the same disease at the molecular level.”
Another major cause of abnormal connective tissue repair is infection, and tissue mimetics can play a role here, too. While rare, infections of artificial joint replacements are particularly devastating for patients, as they typically require readmission to hospital to remove the infected joint, weeks of antibiotic-based treatment, and an additional surgery to replace the artificial joint.
In addition to the associated pain and suffering, these procedures are technically challenging and costly to our health care system.
Artificial shoulder joint infections are most frequently caused by the microorganism Cutibacterium acnes (C. acnes). C. acnes infections disrupt normal tissue repair processes after surgery, cause shoulder tissues to die and promote loosening of the artificial joint. These infections are difficult to diagnose, and there is a lack of reproducible
models in which to study them. Dr O’Gorman’s team has set out to create the first human Shoulder-Joint Implant Mimetic (S-JIM) of C. acnes infection.
“While S-JIMs are more complex, they are 3D in vitro cell culture systems designed to mimic human tissues, like those that we use for studying Dupuytren’s disease.”
S-JIMs include layers of artificial human tissue, wrapped around cores of titanium alloy or cobalt chrome, the metals used to create artificial joints. They are co-cultured with C. acnes under low oxygen conditions similar to those that normally occur around artificial shoulder joints.
“We are bioengineering simple 3D cell cultures to more closely mimic the complexity of human tissues, with blood supply, nerves and interactions with other cells.” – Dr. David O’Gorman
Studying the connective tissue layers close to the infection allows researchers to investigate processes that promote infection, such as the formation of a biofilm that harbours and protects the bacteria from the body’s immune system. They are also able to test whether novel treatments can disrupt biofilm formation and increase the effectiveness of antibiotics.
Dr. O’Gorman predicts that in the future, medical researchers will routinely use bioengineered 3D human tissue and organ mimetics to accelerate our understanding of disease.
“The technology is in its infancy, but the potential for using bioengineered human tissues for surgical reconstructions or as disease models is huge. At Lawson, we’re ready to take on health care challenges and build on innovative approaches to improve the quality of life for patients.”
ONLINE EXCLUSIVE: What is 3D cell culture?
Medical researchers have grown human cells in culture media on or in sterile plastic dishes, such as Petri dishes, for more than 50 years.
Some cells, such as blood cells, can survive and grow in suspension, while others like smooth muscle cells need¬ to adhere to a surface to survive and grow. These are often called “2D cell cultures” because the cells grow horizontally across the bottom of the dish.
Some cells derived from connective tissues, such as fibroblasts, are not only adherent, but also very sensitive to the stiffness of their environment (“biomechanically sensitive” cells). Plastic dishes are at least 10,000 times stiffer than most connective tissues, and when biomechanically sensitive cells detect stiff surfaces, they can change the expression of their genes and behave abnormally.
The most common proteins in these tissues - and in the entire human body - are collagens, and one routine 3D cell culture approach is to embed fibroblasts in a collagen gel (gelatin). Fibroblasts in this environment can grow in any direction they choose, and their gene expression is more similar to cells in connective tissues.
These simple 3D cell cultures represent tissue engineering in its most basic form.
“Our challenge is to bioengineer simple 3D cell cultures in the lab to more closely mimic the complexity of human tissues, which have blood supply, nerves and interactions with other cells and tissues that modify their function and ability to heal after injury,” explains Dr. O’Gorman.
Dr. David O’Gorman is a Lawson Scientist and Co-director, Cell and Molecular Biology Laboratory at The Roth | McFarlane Hand and Upper Limb Centre in London, Ontario. He is also an Assistant Professor at Western University.
History
Each hospital’s research mission has a rich history. At both hospital organizations, leaders recognized opportunities to leverage in-house experts to conduct research and improve care. However, they also recognized the challenge in supporting these activities without dedicated space and resources.
Through great foresight, our hospitals founded the official research institutes that serve as Lawson's foundation:
- 1983: Supported by Sister Mary Doyle, former Executive Director of St. Joseph's, the Sisters of St. Joseph's establish the hospital's official research institute. LHSC and Upjohn jointly open the Victoria Upjohn Clinical Research Unit at South Street Hospital (formerly Victoria Hospital), focusing on Phase I-III clinical trials.
- 1987: The St. Joseph's research institute is named the Lawson Research Institute (LRI) in honour of London businessman and philanthropist Colonel Tom Lawson and his wife, Miggsie Lawson - close friends of Sister Mary Doyle and major supporters of the research mission.
- 1990: Victoria Hospital takes over the operation of the clinical research unit at South Street, renaming it the Victoria Clinical Trials Centre.
- 1997: The Victoria Clinical Trials Centre is renamed London Health Sciences Centre Research Inc. and becomes a fully incorporated research institute overseeing all hospital-based research within London Health Sciences Centre sites: Victoria Hospital, University Hospital and South Street Hospital.
- 2000: LRI and LHSCRI merge to form a joint venture: Lawson Health Research Institute.
- 2014: Lawson Research Institute (re-)launches as the hospital-based research arm of St. Joseph's with the goal of transforming imagination to innovation to impact; and as LHSCRI is also embedded into LHSC.
Today, partnerships remain strong, allowing researchers to move seamlessly between hospital locations and Western University.
Milestones
Since forming in 2000, Lawson has pioneered breakthroughs across various disciplines of health research and reached several institutional milestones.
- 2019: Lawson led research team is the first in the world to develop a new imaging tool, showed that MRI can be used to measure how the heart uses oxygen.
- 2019: New studies from Lawson and Western University found for the first time that HIV can be transmitted through the sharing of equipment used to prepare drugs before injection and that a simple intervention can destroy the HIV virus, preventing that transmission.
- 2019: In the first genomic analysis of head and neck cancer by smoking status, researchers at Lawson, in collaboration with researchers at the Ontario Institute for Cancer Research and UCLA Cancer Centre, carried out a comprehensive genetic analysis of HPV-negative tumours to better understand the link between smoking and cancer recovery.
- 2019: Lawson scientists develop molecular diagnostic tool to analyze epigenetic patterns, facilitating diagnosis of rare, unknown hereditary disorders. London Health Sciences Centre is the first site in the world to offer this type of testing.
- 2018: Research shows high-dose radiation can improve survival in patients with cancer that has spread to give or less sites. The SABR-COMET study was the first randomized phase II clinical trial of its kind.
- 2018: An international collaborative study between Lawson Health Research Institute, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, the Royal Marsden and Epic Sciences is one of the first to demonstrate that a blood test can predict how patients with advanced prostate cancer will respond to specific treatments, leading to improved survival.
- 2018: In collaborative study between Lawson and Stanford University, scientists develop and test a new synthetic surfactant that could lead to improved treatments for lung disease and injury.
- 2018: Scientists use brain MRI to develop first ever method examining young people before they become ill to reliably identify who will develop acute psychosis and who will not.
- 2018: Research team develops clinically-validated, open-source 3D printed stethoscope for areas with limited access to medical supplies.
- 2018: Lawson opens Clinical Research and Chronic Disease Centre (CRCDC) at St. Joseph’s Hospital to tackle chronic disease and improve patient care.
- 2018: Lawson researchers receive $4.4 million to study personalized medicine at LHSC, examining the value of prescribing treatments based on a patient’s genetics.
- 2017: In one of the largest microbiota studies conducted in humans, researchers at Western University, Lawson Health Research Institute and Tianyi Health Science Institute in Zhenjiang, Jiangsu, China have shown a potential link between healthy aging and a healthy gut.
- 2017: Lawson researchers develop transition program to help young adults with type 1 diabetes move from paediatric to adult care.
- 2017: Innovative study brings next-generation genome sequencing to London cancer patients, contributing to province-wide database of genomic and clinical data.
- 2017: Technology developed at Western University and Lawson Health Research Institute can provide a new window into whether or not patients are responding to treatment for advanced ovarian cancer.
- 2017: Dr. Alan Getgood and his team at Western University and Lawson Health Research Institute are the first in Canada to participate in an investigative trial to determine the safety and efficacy of using a patient’s own cartilage cells to repair knee cartilage injuries.
- 2016: Lawson Researchers at Parkwood Institute are the first in Canada to develop clinical practice guidelines for managing neuropathic pain with patients who have experienced a spinal cord injury.
- 2016: Researchers at Lawson are the first in Canada to use a Prostate Specific Membrane Antigen (PSMA) probe in Positron Emissions Tomography (PET) scans to provide improved and highly specific images used for better diagnosis and management of prostate cancer.
- 2015: Lawson scientists, in collaboration with Ceresensa Inc., produce novel PET-transparent MRI head coil, a world first in imaging technology
- 2015: Lawson announces partnership with STEMCELL Technologies for commercialization of tools for Parkinson’s disease research
- 2015: Novare Pharmaceuticals and Lawson announce issuance of a U.S. patent for the composition-of-matter and use of RHAMM-binding peptides with a wide range of potential therapeutic uses. The patent also has claims for the diagnosis and prognosis of cancer, and for prescribing a course of treatment for the diagnosed cancer.
- 2014: Lawson announces licensing agreement with Yabao Pharmaceutical Group in China to develop and test a new life-saving drug to treat sepsis
- 2014: Lawson researchers are part of a Canadian team who have developed a way to produce a key medical isotope, technetium-99m (Tc-99m), using hospital based cyclotrons
- 2013: The Institute for Clinical Evaluative Sciences (ICES) Western opens at Lawson
- 2012: Lawson installs Canada's first PET/MRI at St. Joseph's Hospital
- 2011: Lindros Legacy Research Building officially opens at University Hospital
- 2010: Lawson opens the Cyclotron and PET Radiochemistry facility at St. Joseph's Hospital
- 2009: Lawson receives a record $7 million donation to support the Canadian Research & Development Centre for Probiotics
- 2008: Lawson establishes an experimental anti-thrombolitic clinic to calculate personalized dosage of drugs based on a patient's genetics
- 2007: The first totally endoscopic closed-chest robotic coronary artery bypass surgery on a patient's beating heart is performed at University Hospital
- 2006: Lawson opens the Aging, Rehabilitation & Geriatric Care Research Centre, the first centre of its kind in Canada, at Parkwood Institute
- 2005: Lawson creates the first Ontario Cardiac Rehabilitation Registry
- 2004: Lawson scientists release a three-year study on the effects of the Walkerton water disaster
- 2003: Lawson opens the Victoria Research Laboratories at Victoria Hospital, the first collaboration of its kind in Canada bringing together research from cancer, children's health and vascular biology
- 2002: Lawson installs the first Positron Emission Tomography and Computer Tomography (PET/CT) scanner in Canada at St. Joseph's Hospital
- 2001: St. Joseph's is one of five sites in the world piloting the Diabetes Electronic Management Systems