Search
Search
Hospital-based research in London ranked in the top 10 for Canada
Lawson Health Research Institute is ranked eighth in the country according to the 2018 edition of “Canada’s Top 40 Research Hospitals List” by Re$earch Infosource. This strong position has been maintained by Lawson for the past five years and also keeps the institute within the top five institutions in Ontario.
The research institute of London Health Sciences Centre (LHSC) and St. Joseph’s Health Care London (St. Joseph’s), Lawson has also maintained the top ranking for research intensity among the large tier institutions, with $616,300 of research spending per researcher.
“As a hospital-based research institute, our innovation happens where care is delivered,” says Dr. David Hill, Lawson Scientific Director. “Every day, teams of researchers are working directly with clinicians and patients to improve treatments, or create entirely new ones. They find innovative methods of delivering services that drive efficiency and reduce costs.”
The top 40 list analyzes hospital-based research institutes from across the country on several metrics, including total research income from the previous fiscal year. The ranking looks at funds received from all sources, including both internal and external, to support research at the organization. According to the report, Lawson received $123,255 million in research income in 2017, which was a 0.8 per cent drop from the previous fiscal year.
Dr. David Hill advocates for increased scientific funding nationally. “We held our position despite the modest decrease in funding. Canada as a whole requires significant investment in scientific discovery to increase the well-being of Canadians and build a robust economy.”
This year, a special spotlight on intellectual property (IP) is showcasing the top Canadian organizations – universities, corporations, hospitals and government departments/agencies – patenting at the US Patent and Trademark Office.
Lawson, as the research institute of LHSC and St. Joseph’s, is featured in the top 10 list for Hospital Patent Leaders as measured by ownership of patents granted between 2013-2017. Lawson has ranked in the sixth spot with 13 patents owned.
Commercialization opportunities are managed through WORLDiscoveries®, the business development arm of London’s extensive research network. Born out of a partnership between Lawson, Robarts Research Institute and Western University, WORLDiscoveries® draws upon a mix of industry connections, sector-specific market knowledge, and business development expertise to help researchers and local inventors commercialize their discoveries through licensing and new company spin-offs.
“We support technology development and licensing agreements by taking local knowledge and discoveries to industry partners worldwide,” explains Dr. Hill. “Research-intensive hospitals are improving health care, creating jobs and contributing to the country’s growing knowledge economy.”
Featured Innovations
A Stroke of Genius

Based at St. Joseph’s Hospital in London, Dr. Ting-Yim Lee specializes in computed tomography (CT) imaging, a type of x-ray technology that captures images of slices of the body. As a young scientist, he dreamed of using CT imaging to measure how blood flows in the human body. The idea was to develop software that could be installed on existing CT scanners to make quick, easy work of a very complex algorithm. If a patient came to the emergency room suffering from a stroke, it would allow the doctor to quickly analyze and address the damage.
Thanks to decades of public and private sector support, Dr. Lee’s idea has evolved from concept to prototype to clinically-approved product. Through a licensing deal with GE Healthcare, his software is now installed on 70 per cent of the company’s new CT scanners on the market. It’s currently in use in more than 8,000 hospital imaging departments around the world.
Stroke is a situation where every minute of delay in treatment has grave consequences on the recovery of the patient, and this software allows physicians to quickly decide on the best treatment for the patient. Dr. Lee is extending his technology to measure blood flow in whole organs, including predicting and monitoring how cancer and heart attacks respond to treatment. The royalties from the licenses enabled Lawson to install Canada’s first PET/CT scanner to complement CT Perfusion with metabolic information from PET scanning.
Novel discovery in the field of Parkinson’s Disease

In addition to a busy neurosurgery practice, Dr. Matthew Hebb maintains a highly productive research program. Dr. Hebb is creating tools to advance Parkinson’s Disease research and therapeutics across the globe. Parkinson’s Disease is characterized by progressive neurological impairment caused by the death of cells in the nervous system. Dr. Hebb’s team provided a novel description of brain-derived progenitor cells (BDPCs) that could protect and stimulate re-growth of disease-affected neurons. This discovery may offer critical insight into the disease process and provide a new personalized source of brain-derived cells for delivering therapy back into the same individual.
By using a patient’s own BDPCs, Dr. Hebb hopes to slow or halt disease progression and stimulate regeneration of damaged brain circuitry. BDPCs may further advance drug, genetic and functional screening across broad patient populations. This work also resulted in a patent and partnership with STEMCELL Technologies to develop innovative research tools for Parkinson’s Disease and other incurable neurological diseases.
Computer assisted surgical techniques and technologies
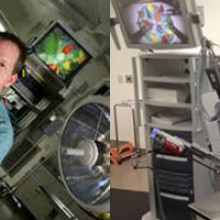
Dr. Christopher Schlachta is Medical Director of CSTAR, the Canadian Surgical Technologies & Advanced Robotics, at LHSC. His current research interests are focused on development of computer-assisted surgical techniques and technologies to enhance care and training. Along with his team, he has demonstrated how computer-assisted technologies in the operating room can enhance communication among surgeons and trainees to produce better outcomes for patients. He is currently partnering with industry to commercialize operating room technology developed with engineers at CSTAR.
His Wireless Hands-free Surgical Pointer system incorporates infrared and inertial tracking technologies to address the need for hands-free pointing during minimally invasive surgery. The combination of these technologies allows for optimal movement of the pointer and excellent accuracy while the user is located at a realistic distance from the surgical monitor.
Smart tech, smart treatment for movement disorders
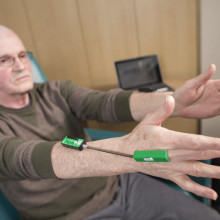
Dr. Mandar Jog operates the London Movement Disorders Centre and has driven the development of TremorTek, a wearable sensor technology that has already successfully treated hundreds of research patients who suffer from tremors in their arms and hands. These tremors, typically caused by Parkinson’s disease or essential tremor, are a common movement disorder symptom yet there is no effective treatment. Neurotoxin therapy has been identified as a possible treatment for tremors; however, an injection in the wrong place or at the wrong dose can cause negative side effects. Everyone experiences tremors in different ways – the location and strength of the movements, and how often they occur varies widely.
Using commercially available sensor technology, Dr. Jog and his team were able to isolate independent muscle movements. They created a system that matched the muscle activity pinpointed by the sensors with the correct amount of toxin to administer. This kinematic technology can be applied to the pre-treatment assessment of patients and the information generated can guide the placement of botulinum toxin. The technology has been taken by a spinoff company MDDT Inc. that has been working with numerous stakeholders interested in its applications.
ICU patients with non-brain-related injuries may suffer undetected cognitive dysfunction
LONDON, ON - A new study led by Western University and Lawson Health Research Institute has found that most patients entering hospital intensive care units (ICU) for non-brain-related injuries or ailments also suffer from some level of related cognitive dysfunction that currently goes undetected in most cases.
The findings were published today in the influential scientific journal, PLOS One.
Many patients spend time in the ICU for reasons that have nothing to do with a known brain injury, and most health care providers and caregivers don’t have any evidence to believe there is an issue with the brain. For example, a patient may have had a traumatic injury that does not involve the brain, yet still requires breathing support to enable surgeons to fix damaged organs, they may have issues with their heart or lungs, they may contract a serious infection, or they may simply be recovering from a surgical procedure like an organ transplant that has nothing directly to do with their brain.
For the study, Western researchers from the Schulich School of Medicine & Dentistry and the Brain and Mind Institute and researchers from Lawson assessed 20 such patients as they left the ICU and every single patient had detectible cognitive deficits in two or more cognitive areas of investigation, including memory, attention, decision-making and reasoning. Again, this is in spite of the fact that, on the face of it, they had no clear brain injury.
The discovery was made using online tests, developed by renowned Western neuroscientist Adrian Owen and his teams at the Brain and Mind Institute and BrainsCAN, which were originally designed to examine cognitive ability in patients following brain injuries but for this purpose, are being used to detect cognitive deficits in people who have spent time in an intensive care unit without a diagnosed brain injury.
“Many people spend time in an intensive care unit following a brain injury and, of course, they often experience deficits in memory, attention, decision-making and other cognitive functions as a result,” explains Owen, a professor at Schulich Medicine & Dentistry. “In this study, we were interested to see how patients without a specific brain injury fair after leaving the ICU. The results were astonishing.”
Why cognitive ability declines even in non-brain related visits to the ICU likely varies from patient to patient, but Dr. Kimia Honarmand from Schulich Medicine & Dentistry says the lesson to be learned is that many conditions affect brain function, even though they might not directly involve the brain.
“If you are having trouble breathing, your brain may be starved of oxygen. If you have a serious infection, the inflammation that occurs as a result of infection may affect brain function. If you are undergoing major surgery, you might be given drugs and have procedures that may affect your breathing, which in turn may affect the flow of oxygen to the brain,” explains Dr. Honarmand. “What we have shown here is that all or any of these events can lead to deficits in brain function that manifest as impairments in cognition. And healthy cognition is a vital determinant of functional recovery.”
Dr. Marat Slessarev, Lawson Scientist, says these findings can shift how the medical community treats incoming patients and more importantly, outpatients following ICU visits.
“Historically, the clinical focus has been on just survival. But now we can begin to focus on good survival,” says Dr. Slessarev, also an associate member at the Brain and Mind Institute and an assistant professor at Schulich Medicine & Dentistry. “These sensitive tests will enable doctors to both detect cognitive impairment and track cognitive performance over time, which is the first step in developing processes for optimizing brain recovery.”
-30-
Western delivers an academic experience second to none. Since 1878, The Western Experience has combined academic excellence with life-long opportunities for intellectual, social and cultural growth in order to better serve our communities. Our research excellence expands knowledge and drives discovery with real-world application. Western attracts individuals with a broad worldview, seeking to study, influence and lead in the international community.
The Schulich School of Medicine & Dentistry at Western University is one of Canada’s preeminent medical and dental schools. Established in 1881, it was one of the founding schools of Western University and is known for being the birthplace of family medicine in Canada. For more than 130 years, the School has demonstrated a commitment to academic excellence and a passion for scientific discovery.
Lawson Health Research Institute is one of Canada’s top hospital-based research institutes, tackling the most pressing challenges in health care. As the research institute of London Health Sciences Centre and St. Joseph’s Health Care London, our innovation happens where care is delivered. Lawson research teams are at the leading-edge of science with the goal of improving health and the delivery of care for patients. Working in partnership with Western University, our researchers are encouraged to pursue their curiosity, collaborate often and share their discoveries widely. Research conducted through Lawson makes a difference in the lives of patients, families and communities around the world. To learn more, visit www.lawsonresearch.ca.
Senior Media Relations Consultant
Communications & Public Engagement
T: 519-685-8500 ext. 73502
Celine.zadorsky@lhsc.on.ca
Improving palliative cancer treatment with existing diagnostic scans: Study reveals promising results
A recent study from London Health Sciences Centre and Lawson Health Research Institute suggests that using existing diagnostic CT scans in planning simple palliative radiation treatments can significantly cut down the waiting time for urgent treatment, resulting in a better experience for cancer patients.
“Reducing the time patients spend in a cancer centre has far-reaching benefits,” said lead study author Melissa O’Neil an Advanced Practice Radiation Therapist at London Health Sciences Centre’s (LHSC) London Regional Cancer Program (LRCP). “Faster treatment initiation means quicker relief from symptoms for patients. Utilizing existing scans is also cost-effective and frees up appointment slots or staff, allowing us to accommodate and assist more patients in need.”

Palliative radiation therapy is used to relieve symptoms in patients whose cancers cannot be cured. It’s often used when tumours cause pain, neurological issues or breathing problems such as blocked airways.
In the current standard practice, patients referred for palliative radiation typically require a CT simulation scan before starting their treatment. This scan creates 3D images that the patient's health care team uses to develop a customized radiation treatment plan. Unfortunately, this process often takes several hours, even with efforts to speed it up.
However, many of these patients have undergone previous diagnostic CT scans as part of their routine medical care. Previous research has shown that radiation oncology teams can create suitable palliative treatment plans for patients with bone and soft tissue metastases using these existing scans. This approach is less time-consuming than the more intensive simulation scans.
In the current study, O’Neil and her colleagues explored whether using existing CT scans to plan treatment before a patient arrives at the cancer centre could reduce their wait time while still ensuring appropriate care. They randomly assigned 33 patients who needed palliative radiation for tumours in their chest, abdomen or pelvis to either the standard treatment planning with on-site CT simulation scans or to treatment planning using diagnostic CT scans taken within the previous 28 days.
The study found that patients who didn't need the extra CT simulation scan spent much less time at the cancer centre on the day of their treatment – just under 30 minutes compared to nearly five hours for the others. Treatments were delivered successfully, and patient perception on time spent at the cancer centre was improved for those whose treatment planning used diagnostic CT scans taken without the previous 28 days.
"For patients who need radiation to help treat symptoms of cancer, it's important for us to get them treated quickly and to minimize the time they spend waiting for medical appointments,” said Dr. David Palma, Radiation Oncologist at LHSC and Associate Scientist at Lawson. “This trial shows that this new approach not only saves resources by reducing the number of scans we do, but also substantially reduces the time patients spend waiting for urgent radiation.”
"These findings are incredibly promising, especially in light of the nationwide shortage of radiation therapists," said Dr. Michael Ott, Physician Department Executive for Oncology at LHSC. “Work like this has benefits that can reach far beyond London, offering more relief for patients across the country."
The findings were presented at the American Society for Radiation Oncology’s Annual Meeting on Oct. 3, 2023. This meeting is recognized globally as the leading radiation oncology scientific event, drawing more than 8,500 attendees each year.
While the study shows promise, the research team said it's important to note that using prior diagnostic scans may not be suitable for every type of cancer or patient. It depends on the specific area being treated and the technique used.
For more information, please contact:
Jessica Rabaey
Communications Consultant
London Health Sciences Centre
T: 519-685-8500 ext. 77728
Jessica.rabaey@lhsc.on.ca
Lawson Health Research Institute is one of Canada’s top hospital-based research institutes, tackling the most pressing challenges in health care. As the research institute of London Health Sciences Centre and St. Joseph’s Health Care London, our innovation happens where care is delivered. Lawson research teams are at the leading-edge of science with the goal of improving health and the delivery of care for patients. Working in partnership with Western University, our researchers are encouraged to pursue their curiosity, collaborate often and share their discoveries widely. Research conducted through Lawson makes a difference in the lives of patients, families and communities around the world. To learn more, visit www.lawsonresearch.ca.
Improving surgery for wrist arthritis
Wrist arthritis can cause debilitating pain, weakness and decreased range of motion. When patients are first diagnosed, the condition can often be managed with activity modification and pain medication. However, as symptoms progress, patients eventually require surgery.
Surgeons typically perform a procedure called four-corner fusion to preserve wrist motion and provide pain relief. This surgery involves removing one of the carpal bones and fusing four of the remaining carpal bones. Although this procedure is one of the most common treatments for wrist arthritis, it is not known how the position of the fusion of the wrist bones affects range of motion and joint contact.
Lawson associate scientist Dr. Nina Suh is leading a study with the goal of improving the surgical technique for four-corner fusion to maximize wrist function and symptom relief, and delay wrist arthritis progression.
Dr. Suh and her team will use a customized active-motion wrist simulator to create different carpal bone fusion positions. They will then assess how these positions affect wrist motion and joint contact area.
“We hope this research will lead to new surgical techniques that will help us to more effectively manage wrist arthritis with four-corner fusion,” says Dr. Suh, who is also an orthopaedic surgeon at the Roth McFarlane Hand and Upper Limb Centre (HULC) at St. Joseph’s Health Care London and an assistant professor at Western University’s Schulich School of Medicine & Dentistry. “The project will also advance our understanding of wrist biomechanics, providing a foundation for the development of enhanced patient-specific surgical tools, such as custom wrist fusion devices and implants.”
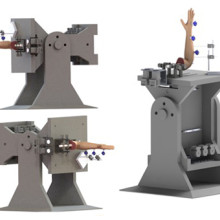
Image of the customized active-motion wrist simulator Dr. Nina Suh and her team are using to create different carpal bone fusion positions. They will then assess how these positions affect wrist motion and joint contact area.
The study is being funded through the Lawson Internal Research Fund (IRF), designed to allow scientists the opportunity to obtain start-up funds for new projects with exciting potential.
“The IRF program is valuable for scientists as external funding sources routinely require preliminary data to strengthen applications,” says Dr. Suh. “Particularly for new scientists such as myself, these grants provide seed funding that allows us to demonstrate the validity of our methodology and the clinical usefulness of our results.”
The IRF is designed to provide Lawson scientists the opportunity to obtain start-up funds for new projects with the potential to obtain larger funding, be published in a high-impact journal, or provide a clinical benefit to patients. Funding is provided by the clinical departments of London Health Sciences Centre and St. Joseph’s Health Care London, as well as the hospital foundations (London Health Sciences Foundation and St. Joseph’s Health Care Foundation).