Search
Search
Lawson study validates new biopsy method for breast cancer patients
In a newly published study in the American Journal of Roentgenology, a team at Lawson Health Research Institute was the first in North America to find that a new breast cancer biopsy method may offer a more accurate and comfortable option for patients.
The method is a new form of mammography software that combines contrast enhanced mammography (CEM) with mammography guided biopsy technology at St. Joseph’s Health Care London’s Breast Care Program. These tools were combined in an effort to make the biopsy procedure more streamlined, accurate, and easier for patients and technicians.
CEM is a relatively new form of mammography that uses contrast iodine injected intravenously, which acts like a dye that allows radiologists to spot potential cancerous lesions more effectively. If potential lesions are found, a biopsy is often the next step.
Before this option was made available to patients through this research, suspicious lesion detection that was only seen on contrast enhanced mammography were biopsied under MRI. This meant longer procedures, and working with limited MRI availability.
“If a lesion is detected only by CEM we usually offer an MRI guided biopsy, but we first need to find the same lesion on an MRI,” says Dr. Anat Kornecki, Lawson Associate Scientist and Breast Radiologist Lead at St. Joseph’s Health Care London. “The problem is that it is sometimes hard to find the same lesion and the MRI itself can be uncomfortable for the patient. Also, some lesions that are close to implants or chest walls cannot be reached with MRI guided biopsy.”
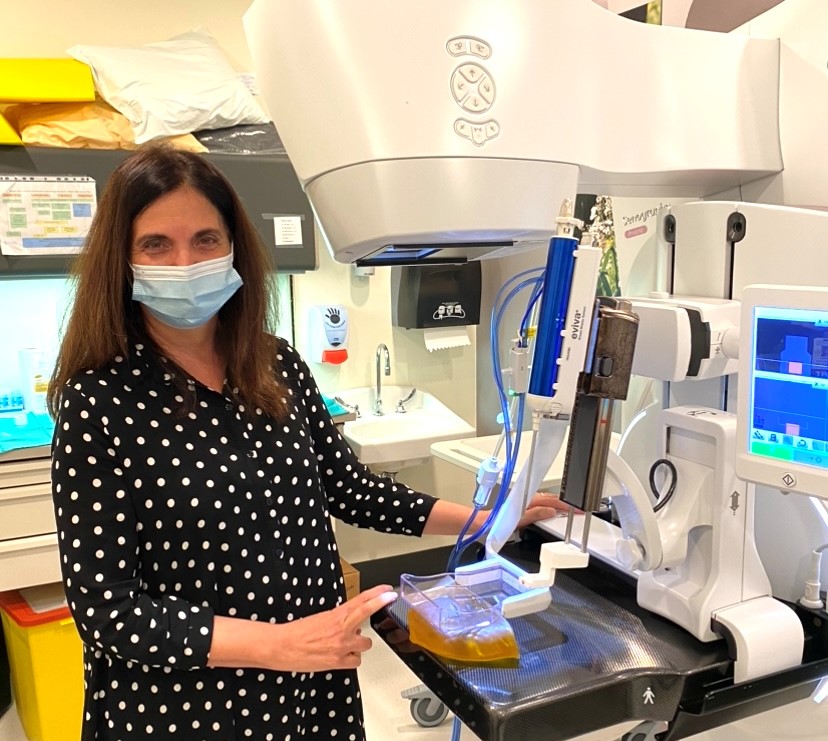
Dr. Kornecki and her research team therefore decided to study this new method. They were the first in North America to trial CESM-guided biopsies by using new technology created by GE HeathCare.This software means that patients can have the biopsy done with the exact same modality, avoiding the need for an MRI.
The study included 50 patients through St. Joseph’s Breast Care Program. The research team found 51 potentially cancerous breast lesions. Biopsies were successfully performed for 46 of the lesions. The results showed that 11 were breast cancer, 10 were high-risk lesions, and the remaining were benign lesions.
“These are very similar results that were reported through MRI-guided biopsies, which means that this new method can replace the MRI,” explains Dr. Kornecki.
Patients also reported having a more comfortable experience with the CEM-guided biopsy method.
Researchers in London and at two other centres in Europe were the first to pilot this technique which has now been cleared by Health Canada and the FDA commercially. St. Joseph’s Breast Care Program was the first site in North America to offer this procedure as a clinical standard of care.
“It is a game changer with certainty,” adds Dr. Kornecki. “This is now a great added component for patients, which makes it a very good tool.”
Currently, CEM- guided biopsy can be offered to patients with lesions that were initially detected by MRI where a biopsy is not feasible due to the lesion location. While it is currently being used as a diagnostic tool only, Dr. Kornecki is hopeful that eventually CEM-guided biopsies will be approved as an initial breast cancer screening tool as well.
Lawson welcomes nursing students from South Korea
Dr. Dalton Wolfe, scientist, Lawson Health Research Institute, led a tour of the physiotherapy gym at St. Joseph Health Care London’s Parkwood Institute for 14 nursing students from Kyungil University in South Korea.
The nursing students have spent six weeks in Canada as part of the Health Care and English as a Second Language Program at King’s University College, during which they focused on English as a language instruction with a focus on medical terminology.
Dr. Wolfe showcased various physiotherapy tools, including a locomat and exoskeleton and explained how holistic and practice-based research can lead to better patient outcomes.

Lens of compassion improves health care
Keynote speaker at joint mental health research day says compassion in action has proven benefit
Compassion in mental health care – and in all health care – is “what separates good from really great” patient outcomes, Calgary-based researcher Shane Sinclair, PhD, told mental health researchers during a conference Oct. 30, 2024, in London.
Sinclair, who heads the Compassion Research Lab at the University of Calgary, was the invited keynote speaker at the Joint Mental Health Research and Innovation Day, attended by about 130 people.
The event was hosted by Lawson Research Institute, London Health Sciences Centre Research Institute and Schulich School of Medicine & Dentistry.
The day also featured 17 poster presentations and 17 oral presentations on different aspects of mental health research. It’s one of the premier annual education-and-development events in mental health science regionally.
This year’s event showcased how compassion could transform health policy, partnerships, systems, care, research and service delivery.
Compassion, respect and excellence are core values of St. Joseph’s Health Care London.
Sinclair noted that the key role of compassion – responding to someone’s suffering with understanding and action – is evidence-based.
“We do patient-informed and patient-targeted research. And we’ve found compassion makes a difference in how people heal.”
-Shane Sinclair, PhD, compassion researcher
His lab examined the outcomes and satisfaction among patients at 14 emergency rooms across Alberta and found compassion to be the greatest predictor of quality care ratings.
“What separates good from really great comes down to compassion. These things matter,” Sinclair said.
“It improves their health and their quality of life. It reduces health-care costs, reduces adverse medical outcomes and helps build patients’ trust in the medical information and direction they receive,” he said.
Leveraging technology to diagnose psychiatric disorders
Psychiatric disorders are often difficult to diagnose. As research advances, we are learning there are multiple subtypes of illness that differ in symptoms and treatment needs, making classification even harder. Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is one example. Individuals with the more common type of PTSD experience active defensive responses like hyperarousal or outbursts of emotion while those with the dissociative subtype experience additional passive defensive responses like ‘shutting down’ or out-of-body experiences.
In a new study from Lawson Health Research Institute and Western University, researchers combined brain imaging and machine learning to classify with 92 per cent accuracy whether individuals had PTSD and whether or not it was the dissociative subtype. The results highlight the promise of brain imaging as a tool for early diagnosis of psychiatric illness, helping to predict symptom development and treatment needs.
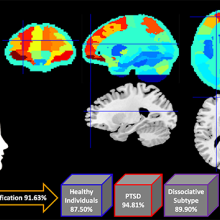
Brains scans and machine learning were combined to classify PTSD with 92 per cent accuracy.
The study involved 181 research participants, including those diagnosed with the more common form of PTSD, the dissociative subtype of PTSD, and healthy individuals with no history of PTSD. They participated in functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) at St. Joseph’s Health Care London and Robarts Research Institute.
Researchers used the high-powered imaging to analyze patterns of resting-state brain activity where participants simply remained in a state of restful wakefulness in an fMRI scanner. The team found that unique patterns of brain activity differed significantly between the three groups.
“Our research group has been leading a number of studies that have shown differences in brain activity and neural connections between healthy individuals and those with different subtypes of PTSD,” says Dr. Ruth Lanius, a researcher at Lawson, professor at Schulich School of Medicine & Dentistry at Western University and psychiatrist at London Health Sciences Centre. “This study further validates that unique patterns of brain activity are associated with different forms of PTSD.”
In the second part of the study, the research team inputted the patterns of brain activity into a machine learning computer algorithm. They found the machine learning system could analyze brain scans to predict whether an individual had PTSD, the dissociative subtype of PTSD or no PTSD with 92 per cent accuracy.
“Our study suggests brain activity can be used to assist diagnosis of psychiatric disorders and help predict symptoms,” says Andrew Nicholson, PhD, lead author on the study and a post-doctoral fellow at Schulich Medicine & Dentistry who is conducting research at Lawson. “Patterns of brain activity are objective biomarkers that could be used to diagnose PTSD and, with more research, even predict response to treatment.”
Objective biomarkers hold promise for transforming psychiatric medicine.
“The field of psychiatry does not currently have objective biomarkers like those used to diagnose and understand other illnesses or diseases like cancer,” says Nicholson. “By discovering and validating patterns of brain activity as biomarkers, we can bring objective measures to psychiatry and transform patient care.”
The study, “Machine learning multivariate pattern analysis predicts classification of posttraumatic stress disorder and its dissociative subtype: A multimodal neuroimaging approach,” is published in Psychological Medicine.
LHSC and St. Joseph’s introduce new research institutes
Lawson Research Institute at St. Joseph’s and London Health Sciences Centre Research Institute will strengthen hospital-based innovation in London, Ontario
LONDON, Ont. – Today, London Health Sciences Centre (LHSC) and St. Joseph’s Health Care London (St. Joseph’s) unveiled new research institutes designed to strengthen hospital-based innovation. Lawson Research Institute (Lawson) at St. Joseph’s and London Health Sciences Centre Research Institute (LHSCRI) will leverage each hospital’s unique areas of clinical focus while further integrating research with care, helping to advance discoveries that lead to improved patient outcomes.
The new institutes were announced at a launch event with guided open house tours taking place across LHSC’s Victoria Hospital, Children’s Hospital and University Hospital, as well as at St. Joseph’s Hospital and Parkwood Institute. Attendees were able to experience signature research areas, including aging, mental health and microbiome research at Lawson, as well as cancer, children’s and mental health research at LHSCRI. The day included demonstrations of discoveries that are reshaping care in Ontario and around the world, including a new robotic, body-weight support for people with mobility difficulties and studies using artificial intelligence (AI) to diagnose rare diseases.
“When research takes place in a hospital context, scientists have more direct connection to the needs of the patients they serve,” said Roy Butler, President and CEO of St. Joseph’s. “There’s data to show that patients treated in research-intensive hospitals live longer because they have access to cutting-edge science. All patients benefit, not just those involved in clinical trials – and that’s the power of health research. That’s why this milestone day and the discoveries to come are real cause for celebration.”
LHSC and St. Joseph’s have been innovating for more than 150 years. The research institutes will build on the legacy of scientific excellence at both organizations. Their launch marks the completion of the transition from Lawson Health Research Institute, a research brand shared between the two organizations since 2000.
“We’re building on our history while introducing the next era in health research excellence, ensuring we will continue to attract the brightest minds in science and that patients will receive world-class, innovative care,” said David Musyj, Supervisor, LHSC. “We will continue to collaborate with each other, Western University, and health research partners across the country and around the world, bolstering London’s position as a national hub for health research.”
Research teams across Lawson and LHSCRI will continue to collaborate closely on projects and large scientific initiatives. LHSC and St. Joseph’s will also continue to share administrative support for research activities.
Learn more about the new research institutes and their transformative work at:
Lawson Research Institute
London Health Sciences Centre Research Institute
-30-
For more information, please contact:
Celine Zadorsky
Senior Media Relations Consultant
London Health Sciences Centre
(226) 927-2309
OR
Debora (Flaherty) Van Brenk
Communications Consultant
St. Joseph’s Health Care London
226-577-1429 or 519-318-0657
About Lawson Research Institute: Lawson Research Institute, the health innovation arm of St. Joseph’s Health Care London, is committed to making and sharing discoveries that improve lives locally and internationally. Every day, Lawson’s 250-plus scientists work to transform imagination to innovation to patient impact. Lawson leads health-care research. Find us online at sjhc.london.on.ca/research and on social media @stjosephslondon
About London Health Sciences Centre Research Institute: At London Health Sciences Centre Research Institute (LHSCRI), our teams pioneer discoveries that transform the health of adult and paediatric patients around the world. As the research institute of London Health Sciences Centre (LHSC), we conduct research where patient care is delivered, working alongside patients, families, health-care providers and academic partners like Western University. We are leaders in advancing the understanding, diagnosis, treatment and management of diseases and health conditions through a diverse research program that ranges from laboratory-based science to clinical trials. Our research has a global impact as we build on LHSC’s 150-year legacy of health innovation and drive forward medical breakthroughs that make a difference in the lives of patients and their families. Find us online at www.lhscri.ca and on social media @LHSCRI.
LHSC and St. Joseph’s Research Institutes Launch Day

Join us and the London community as we celebrate the launch of our new research institutes at London Health Sciences Centre (LHSC) and St. Joseph’s Health Care London (St. Joseph’s).
This full-day event that is open to the public will showcase the legacy and future of hospital-based research in London. It’s a chance to engage in cutting-edge research, interact with research teams and take part in the unveiling of our new research brands.
LHSC and St. Joseph’s Research Institutes Launch Day
Date: Wednesday, October 16, 2024
Formal presentation:
- 9:30 am to 10:00 am | Parkwood Institute Main Building Auditorium, 550 Wellington Road South, Zone B, Room B2-109 (Entrance C)
Open houses:
- 11:00 am to 1:00 pm | St. Joseph’s Parkwood Institute, 550 Wellington Rd. S. Main Building (entrance C) and Mental Health Care Building (entrance F)
- 12:30 pm to 2:30 p.m. | LHSC’s Victoria Hospital, 800 Commissioners Rd. E. (Zone B entrance)
- 1:30 pm to 3:30 pm | St. Joseph’s Hospital (Cheapside entrance 4)
- 2:30 pm to 4:30 pm | LHSC’s University Hospital, 339 Windermere Rd. (Main entrance)
Local COVID-19 research supported by St. Joseph's Health Crisis Fund
St. Joseph’s Health Care London and Lawson Health Research Institute have announced plans to move forward with clinical trials testing a drug that could potentially be used to prevent and treat COVID-19. St. Joseph’s Health Care Foundation will accelerate the creation of the studies by providing seed funding to get the research started through donor support. Based on the immediate need, The St. Joseph’s Health Crisis Fund has been created by St. Joseph’s Health Care Foundation to enable these and other research studies currently in development through Lawson, the research arm of St. Joseph’s.
While supporting urgent COVID-19 clinical trials will be an immediate focus, The St. Joseph’s Health Crisis Fund will also support critical patient care equipment and care and comfort items for healthcare staff and volunteers working on the frontlines of the pandemic across St. Joseph’s.
Led locally by Dr. Michael Silverman, Medical Director of St. Joseph’s Infectious Diseases Care Program, one trial will assess the safety and efficacy of using hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) to prevent COVID-19 in health care workers recently exposed to the virus. This trial will also assess the drug as a treatment for non-hospitalized patients with mild cases of the illness. St. Joseph’s will be one of many participating sites in the trial, which is being led by the Research Institute of the McGill University Health Centre.
“There is much debate surrounding the drug hydroxychloroquine. We do not yet know whether it’s safe or effective, and it should not be routinely recommended until we do,” says Dr. Silverman, also a Lawson Associate Scientist and city-wide Chair/Chief of Infectious Diseases. “We plan to carefully study the drug through a randomized controlled trial and assess whether it can help combat COVID-19.”
Dr. Silverman is also partnering with Dr. Michael Borrie, Geriatrician at St. Joseph’s and Lawson Scientist, on a prevention trial to test the safety and efficacy of the drug for patients and residents at Parkwood Institute who have been exposed to COVID-19. They are at a higher risk of infection, as well as serious complications and potential admission to acute care.
“There are two critical goals with this prophylactic trial,” explains Dr. Borrie. “First, we want to see if the drug, taken for five days, is safe for the participants in the study. We will then look to see whether it is effective to prevent illness or lessen symptoms and complications.”
They are testing whether HCQ may inhibit the coronavirus similar to how the antiviral drug Tamiflu is used to prevent influenza after exposure. The research team will recruit patients and residents who have been accidentally exposed to the virus by a confirmed or presumed case of COVID-19, but who aren’t yet experiencing symptoms. In addition to cardiograms and blood tests for safety, they are collaborating with Dr. Saman Maleki, Lawson Scientist and Immunologist, to analyze the blood for a variety of indicators including the presence of antibodies and immune response. They will collect clinical data and information on common health conditions to gain insights into why some vulnerable individuals get the disease and others don’t.
“We are aware of two small studies that were published rapidly last week, one in France and the other in China, testing the use of chloroquine for potentially treating COVID-19. Further studies are greatly needed,” adds Dr. Borrie. “This study at Parkwood Institute is a good start and we hope to have other Canadian sites join us in recruiting participants so that we can offer statistically significant results as soon as possible.”
Those interested in donating to St. Joseph’s Health Crisis Fund are asked to visit St. Joseph’s Health Care Foundation’s website to learn more at sjhcfoundation.org. Donations can be made online, through direct mail submissions or by calling the Foundation directly at 519-646-6085.
“The Sisters of St. Joseph, who founded our organization, faced contagious diseases and other pandemics at different times in our 150+ year history,” says Michelle Campbell. “Today, it’s a different time, and a new disease. Now, more than ever, we ask our community to help us address the crisis facing us all.”


