Search
Search
Study gives Ontario men access to advanced prostate cancer imaging
Prostate cancer can be elusive.
Wayne Smith’s journey with prostate cancer began 16 years ago when his family physician noticed increasing levels of prostate specific antigen (PSA) in his blood. PSA is a protein expressed by the prostate. A blood test is used to monitor levels of the protein as a screening tool for prostate cancer.
“My doctor referred me to Dr. Stephen Pautler, Urologist at St. Joseph’s Health Care London. Although we did a number of tests, we weren’t able to locate any spots of cancer,” says Wayne, a 71-year-old man from Ingersoll, Ontario. “We were able to manage my PSA levels for a number of years until they jumped up too high.”

Above: Wayne Smith
In 2012, Wayne was sent for a CT scan. This test finally revealed spots of cancer at the back of the prostate. “Dr. Pautler discussed my treatment options with me and I chose to have surgery to remove my prostate,” explains Wayne. “The team did a great job but we eventually realized some cancer remained. I asked about a PET scan to locate it but the technology was not available at that time.”
After consulting with Dr. Pautler and Dr. Glenn Bauman, Radiation Oncologist at London Health Sciences Centre, Wayne chose to postpone further treatment and monitor the cancer over time. It was undetectable for five years before his PSA levels started rising again. Earlier this year, the levels doubled.
“I was told a PET scan was available through research and that it could help locate the disease,” says Wayne. He went for the scan earlier this year at St. Joseph’s Hospital, part of St. Joseph’s Health Care London. “Nothing showed up on the scan, but that was good news; it meant the cancer was microscopically small.”
The PET scan helped Wayne and his care team in making decisions about his treatment. They decided on hormone therapy and radiation therapy to hopefully eradicate any cancerous cells. He was treated at London Health Sciences Centre’s (LHSC) London Regional Cancer Program.
“Early evidence suggests that a clear PET scan despite rising PSA levels is likely associated with persistent cancer at the original site,” explains Dr. Glenn Bauman, Lawson Scientist and Radiation Oncologist at LHSC. “Based on the scan, Wayne was able to do a much shorter round of hormone therapy – six months rather than being on hormone therapy indefinitely.”
“After the first hormone treatment, my PSA levels dropped significantly. With the added radiation, we’re confident this will be the end of my battle with prostate cancer,” says Wayne, who is currently enjoying retired life by spending time with his wife, two children and five grandkids. “Despite my diagnosis and treatments, I carried on with my life. I did what I had to do but still went places on weekends, did chores around the house and went golfing.”

Above: Dr. Glenn Bauman (left) and Wayne Smith (right)
Wayne is one of 1,500 Ontario men who will participate in the PSMA-PET Registry Trial. Led by researchers at Lawson Health Research Institute, the multi-centre registry trial is testing the use of a new imaging tracer, called a PSMA tracer, for early detection of recurrent prostate cancer. The registry gives patients access to a new type of imaging and will assess the impact on patient care.
PSMA tracers are used in positron emission tomography (PET) scans to target a protein found in prostate cancer cells called prostate specific membrane antigen (PSMA). Supported by Cancer Care Ontario and McMaster University’s Centre for Probe Development and Commercialization (CPDC), the goal of the registry trial is to capture detailed PET images to guide treatment decisions made by patients and their care teams.
Eligible participants are those with suspected prostate cancer that cannot be detected in conventional bone and CT scans. Participants have a PET scan using a specific PSMA tracer called 18F-DCFPyL. The tracer is injected and spreads out in the body to find spots of cancer which are then visible on the scan.
“With this trial, men in Ontario can access a promising test that could impact their treatment outcomes,” says Dr. Bauman. “The PSMA tracer may be able to locate prostate cancer that was once undiscoverable.”
Led by Dr. Bauman along with Drs. Ur Metser and Tony Finelli at University Health Network (UHN), the trial is currently available across multiple sites in Ontario: London Health Sciences Centre; St. Joseph’s Health Care London; St. Joseph’s Health Care Hamilton; Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre; Princess Margaret Cancer Centre (UHN); and Thunder Bay Regional Health Sciences Centre. The trial is also expected to open at The Ottawa Hospital this year.
The PSMA tracer is considered an investigational agent in Canada and is currently only available through clinical trials. After studying the accuracy of the tracer in detecting early cancer recurrence, the research team hopes to have enough data to recommend when it could be used in the clinic.
Patients from London, Ontario and region who are enrolled in the PSMA-PET Registry Trial have their scans performed at St. Joseph's Hospital. In 2016, Lawson researchers were the first in Canada to use the 18F-DCFPyL PSMA tracer to capture PET images with a patient at St. Joseph’s Hospital. The tracer is provided by CanProbe, a joint venture between CPDC and UHN located in Toronto, and was set up with funding from the Movember Foundation.
“We conducted an initial trial that included 20 men with prostate cancer who were having their prostate removed. The goal was to determine how effective the PSMA probe was in detecting disease at the time of initial treatment,” explains Dr. Bauman. “We found the PET scan was able to detect spots of cancer in almost all participants, which corresponded to spots of cancer identified in the prostate after it was removed and examined under the microscope.”
The initial trial was made possible with donor funding through London Health Sciences Foundation, which provided initial funding to hire Research Associate, Catherine Hildebrand, who set up citywide cancer imaging workshops and helped the team prepare successful grant applications to secure key funding from CIHR and OICR.
Dr. Bauman notes that conventional imaging tests like bone scans and computed tomography (CT) are not always effective for detecting prostate cancer. While other PET probes can be used to detect a number of different cancer types, they are unable to identify prostate cancer. The PSMA probe opens new avenues for prostate cancer diagnosis, prognosis and treatment guidance.
For patients like Wayne Smith, access to this advanced imaging is critically important.
“It’s fantastic we have access to this PET scan. It certainly gave me relief knowing nothing showed up on the scan and that, even if something did, it would light up to show us where to treat,” says Wayne. “I know PET scans are used for other cancers too and I think they’re imperative. They give you more of a chance through knowledge of where the disease is located.”

Study shows a decline in Veterans’ mental health throughout the pandemic
MEDIA RELEASE
For immediate release
February 16th, 2022
LONDON, ON – In newly-published findings from Lawson Health Research Institute, more than half of Canadian Veterans report a decline in their mental health over the course of the COVID-19 pandemic.
When it comes to mental health conditions, Veterans are an at-risk population, often having higher rates of depression and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). When the COVID-19 pandemic hit, scientists at Lawson wanted to understand its effects on this already at-risk population.
“We anticipated the ongoing pandemic would have impacts to multiple domains of life such as loneliness, isolation, depression and PTSD,” says Associate Scientist at Lawson and the MacDonald Franklin Operational Stress Injury (OSI) Research Centre, Dr. Anthony Nazarov.
To examine the potential impacts the research team launched a longitudinal study in early 2021, recruiting Canadian Veterans and spouses of Canadian Veterans. A total of 1,136 Veterans have participated in the study which spans over 18 months. Participants complete online questionnaires every three months, with questions focused on mental health and virtual health care services.
“We looked at use of care services, including virtual care services, which we know have been on the rise during the pandemic,” says Lawson Associate Scientist and Scientific Director of the Macdonald Franklin OSI Research Centre, Dr. Don Richardson.
The team recently published preliminary findings based on the Veterans portion of the study, which confirm a decline in mental health amongst the Veterans that took part.
“One of the important preliminary findings demonstrated a little more than 55 per cent of Veterans (55.9 per cent) have indicated that their mental health has worsened over the pandemic.” explains Dr. Richardson.
The findings also revealed that nearly one in five Veterans used virtual health care and telepsychiatry services and found them to be helpful.
“Veterans have been having positive experiences with virtual care for mental health support,” adds Dr. Nazarov. “Most found it helpful, and more importantly, many would like to continue to use this form of health care services even post pandemic.”
The preliminary study findings have been published in the European Journal of Psychotraumatology. The longitudinal study will wrap up this summer, and then the team hopes to use the information to improve and innovate different forms of mental health supports for Veterans and their spouses in the future.
-30-
About Lawson Health Research Institute: Lawson Health Research Institute is one of Canada’s top hospital-based research institutes, tackling the most pressing challenges in health care. As the research institute of London Health Sciences Centre and St. Joseph’s Health Care London, our innovation happens where care is delivered. Lawson research teams are at the leading-edge of science with the goal of improving health and the delivery of care for patients. Working in partnership with Western University, our researchers are encouraged to pursue their curiosity, collaborate often and share their discoveries widely. Research conducted through Lawson makes a difference in the lives of patients, families and communities around the world. To learn more, visit www.lawsonresearch.ca.
For more information, please contact:
Celine Zadorsky
Communications Consultant & External Relations
Lawson Health Research Institute
T: 519-685-8500 ext. 75664
C. 519-619-3872
@email
www.lawsonresearch.ca/news-events
Senior Media Relations Consultant
Communications & Public Engagement
T: 519-685-8500 ext. 73502
Celine.zadorsky@lhsc.on.ca
The invisible world inside us
The human microbiome is a wonder of nature.
Trillions of microbes call our body home. They live in our gut and many other places throughout our body. They are involved in virtually every aspect of how we function and we are learning that they are essential to staying healthy. An unhealthy microbiome has been linked to many diseases from allergies to cancer and even mental health.
Most people out there have heard about probiotics and fermented foods, and chances are you’re trying to get more of them in your diet.
Drinking kombucha or eating yogurt, anyone?
Join Lawson Health Research Institute for our next Café Scientifique event, "The invisible world inside us: Exploring the human microbiome."
Hear from a panel of researchers who are unraveling the mysteries about the microbiome and using that knowledge to improve health and health care. They will also bust some myths and share the important facts when it comes to probiotics, prebiotics and the microbiome.
Image

SPEAKERS
- Dr. Gregor Reid, Lawson Scientist and Professor of Microbiology & Immunology and Surgery at Western University.
Presenting: Probiotics and Prebiotics - Look beyond the fake news - Dr. Michael Silverman, Lawson Associate Scientist, Chair of Infectious Diseases, Schulich School of Medicine & Dentistry at Western University and Chief of Infectious Diseases for St. Joseph’s Health Care London and London Health Sciences Centre.
Presenting: Fecal Transplants: What does this crap have to do with me? - Dr. Jeremy Burton, Lawson Scientist and Assistant Professor of Surgery (Urology) and Microbiology & Immunology at Western University.
EVENT DETAILS
Date: Wednesday, November 27, 2019
Time: 7-9 pm (doors open at 6:30 pm)
Location: Best Western Plus Lamplighter Inn & Conference Centre (Regency Room), 591 Wellington Rd, London, ON N6C 4R3
Map and directions.
Parking: Free on-site parking
This is a free event and online registration is REQUIRED.
Registration for this evengt is now FULL.
Please fill out the form here to be added to the waitlist.
You will be notified should a spot open up.

Third clinical trial launched to study whether type 2 diabetes can go into remission
Since launching two years ago, an innovative study that aims to induce remission of type 2 diabetes has captured the attention of hundreds of Londoners. For those with type 2 diabetes like Greg Ackland and Jocelyne Chauvin, the idea of stopping all medications has translated from a dream to a reality through participation in the REMIT study at Lawson Health Research Institute (Lawson).
With a family history of type 2 diabetes, Greg Ackland was first diagnosed over six years ago when he underwent an operation for a hernia. He developed a mild infection and, while being treated, his care team discovered his blood sugar levels were high.
Ackland started treatment and was eventually taking four pills per day. “I watched the progression of my medications and thought ‘I’m losing this battle,’” says 51 year-old Ackland.

Above: Greg Ackland, research participant in the REMIT study
He saw information about the REMIT study on the local news and after meeting the criteria he was enrolled. The outcomes have been incredible. Ackland has now stopped all medications and his blood sugar levels are good. He has recommitted to exercise which has resulted in weight loss and muscle gain.
“I’m glad I jumped at the opportunity to participate in this trial,” says Ackland. “I’ve reset myself.”
Lawson is one of seven Canadian sites taking part in the REMIT study, which is considered a significant departure in strategy in the care of people with type 2 diabetes. The study consists of a series of clinical trials that tests an aggressive approach in recently diagnosed patients. The first two trials in London saw significant interest in participation from those with type 2 diabetes. A third REMIT trial is now being launched providing another opportunity for individuals with type 2 diabetes to take part.
“The goal of the REMIT study is to take a proactive approach to help people early in the disease, normalize their blood sugars for a period of 12 weeks and then slow the progression of the disease and the need for additional medications,” says Dr. Irene Hramiak, Lawson researcher, endocrinologist, and Chief of the Centre for Diabetes, Endocrinology and Metabolism at St. Joseph’s Health Care London. “We want to know if we can induce remission, for how long and whether it matters what combination of medications we use.”
The standard treatment for people with type 2 diabetes is to start on a single medication, which is then followed by the addition of more drugs and insulin as the disease progresses. In the REMIT study, patients receive intensive treatment early in their care journey that consists of two diabetes medications plus insulin at bedtime for three months to see if remission can be induced. In addition, patients are supported to make lifestyle changes with a diet and 30 minutes of exercise each day.
“When I saw a gentleman on the news talking about the REMIT study and how it allowed him to stop taking all medications, I thought ‘cool!’” says Jocelyne Chauvin. The 62 year-old Londoner was first diagnosed with type 2 diabetes three years ago after a regular checkup. While it was difficult news, she had a family history of the disease and health issues before her diagnosis.

Above: Jocelyne Chauvin, research participant in the REMIT study
“I started taking one pill a day and was told I’d be up to four pills a day within six months,” says Chauvin. “But with good nutrition and exercise I worked hard to stay on one pill a day for three years.”
After hearing about the study, she contacted the research team and, after meeting the criteria, was enrolled in April 2017. Chauvin has now stopped all medications and says she feels much better. She exercises more and her blood sugar levels are close to normal.
“This is my first time participating in a clinical trial and I’m very excited about my experience,” says Chauvin.
REMIT is being led by the Population Health Research Institute (PIHR), a joint institute of McMaster University and Hamilton Health Sciences. The study follows a PHRI pilot study of early aggressive treatment that resulted in up to 40 per cent of intervention group participants with type 2 diabetes going into remission and not needing any diabetes treatment for at least three months.
“The idea of putting type 2 diabetes into remission is changing the way we think about the disease. It has a strong appeal to both those with type 2 diabetes and clinicians,” says Dr. Hramiak. “It’s changing the paradigm of when and how to use medication for type 2 diabetes.”
Those who would like more information about the trial can call 519-646-6100 ext. 65373.
This will be a huge benefit for society because sepsis is the leading cause of death worldwide
It’s a discovery that has been more than ten years in the making: the use of a human protein to potentially treat patients with sepsis.
Lawson Scientist Dr. Qingping Feng noticed that a human protein called annexin A5 showed positive results with sepsis back in 2007.

Fast forward 14 years later to now, and this discovery could very well be the first ever viable treatment for sepsis patients, including severe COVID-19 patients who develop sepsis. “With COVID initially, it is in the airway and then in the lungs, then from there the inflammatory response in fact spreads to the whole body,” says Dr. Feng, Ivey Chair in Molecular Technology at Western University's Schulich School of Medicine & Dentistry. “Sepsis causes major organ dysfunction and carries a high mortality unfortunately.”
It has become a challenging issue for Intensive Care Physician at London Health Sciences Centre (LHSC), Dr. Claudio Martin, who can only do so much to treat severe COVID-19 patients that develop sepsis.
“What we have seen is a very primary severe respiratory failure to the lungs for severe COVID patients,” says Dr. Martin, Associate Scientist at Lawson. “We have used steroids and other treatments to try to help, but the results and effects aren’t dramatic and we see patients who have these treatments and still progress and end up in the ICU.”
However, Dr. Feng and his team has found in a pre-clinical study, that annexin A5 can inhibit inflammation, improve organ function, and survival when treating sepsis.
Another potentially deadly situation for COVID-19 patients is cell death and blood clots, specifically near the lungs. The good news is that the research team also believes the annexin A5 drug will prevent these complications through the drugs anti-apoptotic (cell death prevention) and anti-coagulant (blood clot prevention) properties.

Supported by provincial funding through Ontario's COVID-19 Rapid Research Fund, the research team has launched a clinical trial with critically ill COVID-19 patients at LHSC, using a manufactured form of annexin A5. The goal is to enroll a total of 60 patients for the clinical trial, and enrollment has already begun. “Patients are receiving standard treatment and then those enrolled will also receive the annexin,” says Dr. Martin. “It’s a placebo blinded clinical trial, so patients will either get a lower dose of annexin, a higher dose of annexin, or a placebo.”
If the clinical trial shows promising results, Dr. Feng says the team plans on expanding into a larger phase three trial with not just COVID-19 patients with sepsis, but other sepsis patients as well. “If in fact annexin A5 is shown to be effective in sepsis, then this will be a huge benefit for society because sepsis is the leading cause of death worldwide.”
The drug is currently being produced through a partnership with Suzhou Yabao Pharmaceutical R&D Co., Ltd., based in China, Lawson Health Research Institute, and WorldDiscoveries. “Our long-standing partnership with Suzhou Yabao has enabled annexin A5 drug development to proceed to this point,” says Kirk Brown, Manager of Business Development, Lawson Health Research Institute. “We are now in a unique position through this trial to offer a potential life-saving treatment for this emergent global disease, with the objective of soon expanding to all cause septic patients.”
Top 12 research stories of 2022
As the research institute of London Health Sciences Centre (LHSC) and St. Joseph’s Health Care London, our teams impact the lives of people in Ontario, Canada and around the globe with groundbreaking studies, world firsts and translational research that enhances care, health and wellbeing. Here are some of Lawson Health Research Institute’s top research highlights of 2022.
Researchers looking to better personalize treatment for PTSD

In a new study through Lawson and Western University’s Schulich School of Medicine & Dentistry, scientists are looking at a form of treatment called deep brain reorienting (DBR) for those suffering from post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Read more.
Virtual care associated with significant environmental and patient cost savings

A new study by researchers at ICES, Lawson and Western finds that virtual care during the COVID-19 pandemic led to a significant reduction in carbon dioxide emissions and patient travel-related expenses, such as gasoline, parking or public transit costs. Read more.
Novel test that could easily diagnose blast injury created by local scientists

In a world first, researchers at Lawson and Defence Research and Development Canada have developed a breath test that could be used to diagnose repetitive blast injury – a mild traumatic brain injury resulting from pressure changes that occur during explosions. The device will soon go through clinical trials to validate its efficacy. Read more.
Local researchers using artificial intelligence to lead the way in bedside lung imaging
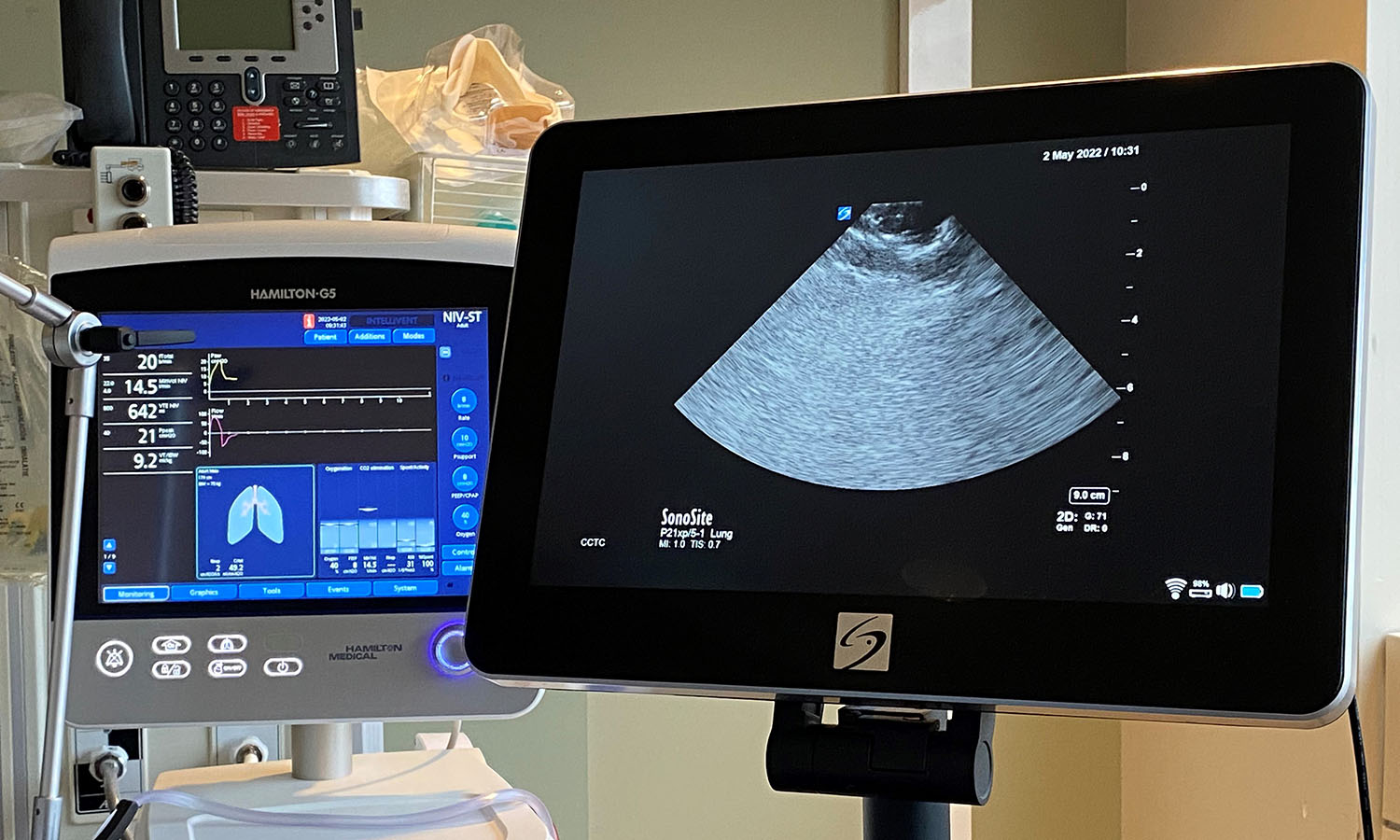
A team at Lawson is testing a new form of artificial intelligence (AI), paired with portable ultrasound machines, to image and identify lung concerns in real time, right at the beside of critically ill patients. Approximately 100 critical care patients at LHSC will be part of this study. Read more.
New tool shows promise in helping people manage traumatic brain injuries one pace at a time
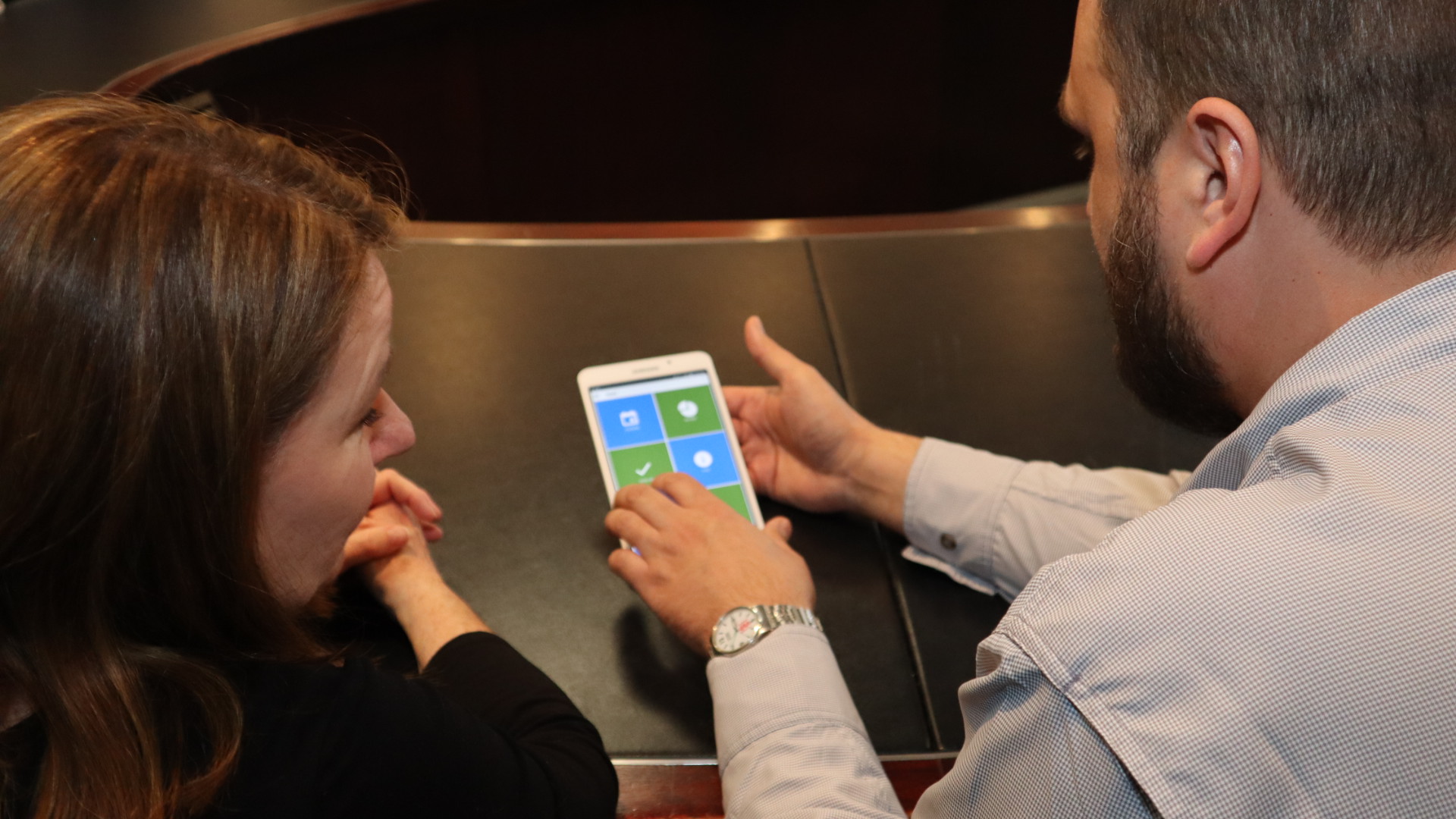

A team at Lawson has developed a new app called MyBrainPacer™ which aims to better assist and treat those living with mild traumatic brain injuries (mTBI), including concussions. mTBI may come with lasting effects that can alter a person’s life. Although a person with a mTBI may appear fine on the outside, many have to pace their day-to-day activities in order to allow the time needed for the brain to properly heal. Much like point tracking used by dieters to monitor food choices, through MyBrainPacer™ App, users can assign values to tasks like driving, grocery shopping, screen use and exercise so they can plan and pace their daily activity. Read more.
Study shows a decline in Veterans' mental health throughout the pandemic

When it comes to mental health conditions, Veterans are an at-risk population, often having higher rates of depression and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). When the COVID-19 pandemic hit, scientists at Lawson wanted to understand its effects on this already at-risk population. They found that more than half of Canadian Veterans reported a decline in their mental health. Read more.
Growing evidence that PSMA imaging improves prostate cancer detection
Scientists at Lawson are leading the way in using specialized imaging to detect prostate cancer – the fifth leading cause of cancer death in men around the world. Early evidence indicates that PSMA PET scans have changed how prostate cancer is being treated, but more work is underway to understand the impact of those treatment changes. Read more.
Leveraging virtual reality to manage pain in paediatric patients
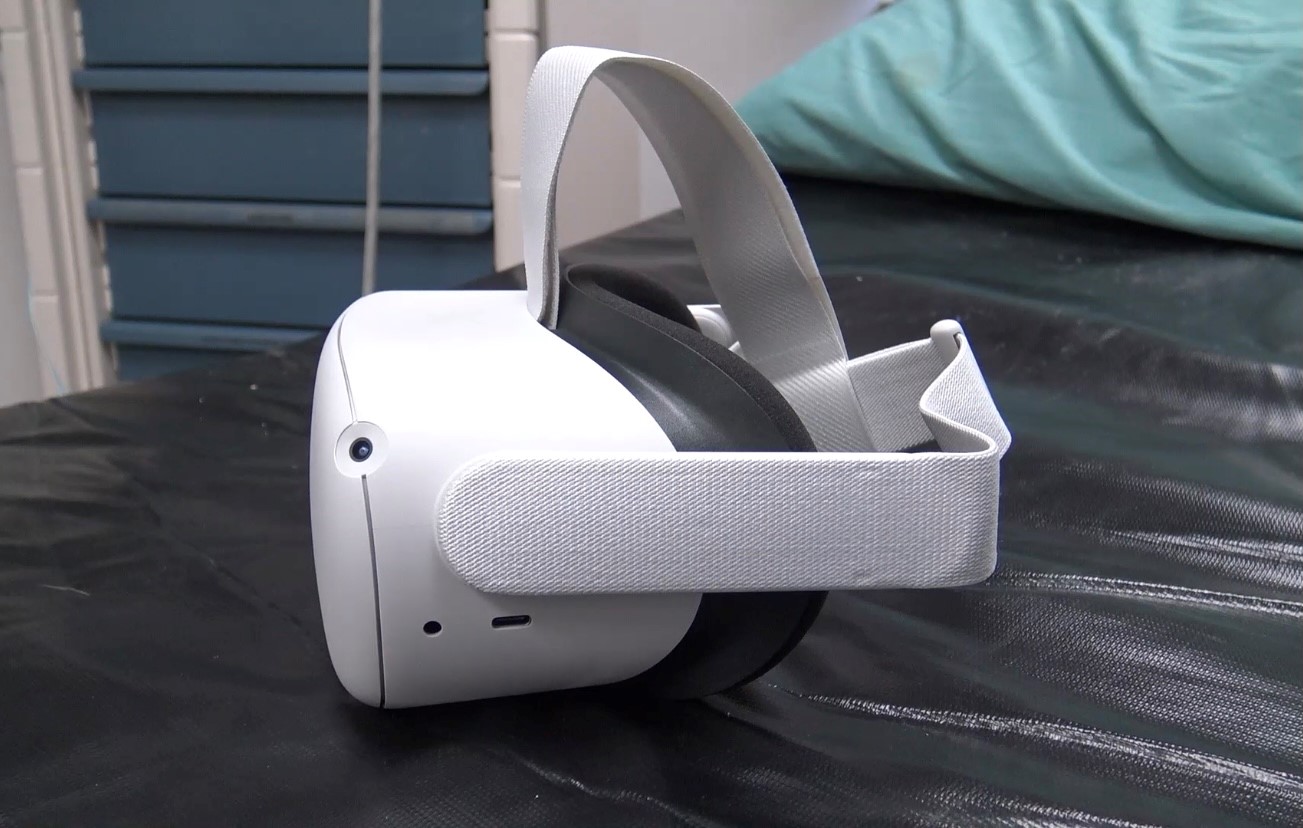

A study underway through Lawson and Children’s Hospital at LHSC is using virtual reality (VR) to help paediatric patients during painful and distressing procedures. The study is focusing on paediatric patients who need port access. A port is a little reservoir that sits underneath the skin that allows access to blood or medication with the use of a needle. Ports are most commonly used in paediatric cancer patients. Read more.
Team players: FMT and microbiome research could have widespread impact

There is still much to learn about the human microbiome and its role in fighting disease, but ongoing studies at Lawson, including a focus on fecal microbial transplants (FMT), are making strides in harnessing this complex system. FMT is being studied in connection with conditions as varied as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, rheumatoid arthritis, atherosclerosis, HIV, cancer and multiple sclerosis. Read more.
London researchers adapt MRI technology to image salt within the kidneys
Scientists at Lawson have adapted PET/MRI technology to accurately image salt within the kidneys of patients with kidney disease. Imaging salt within the kidneys has never been accurately accomplished in patients with kidney disease, but Dr. McIntyre and his team developed new technology and software that was adaptable to a PET/MRI machine at St. Joseph’s. Read more.
London researchers discover novel method to diagnose long COVID
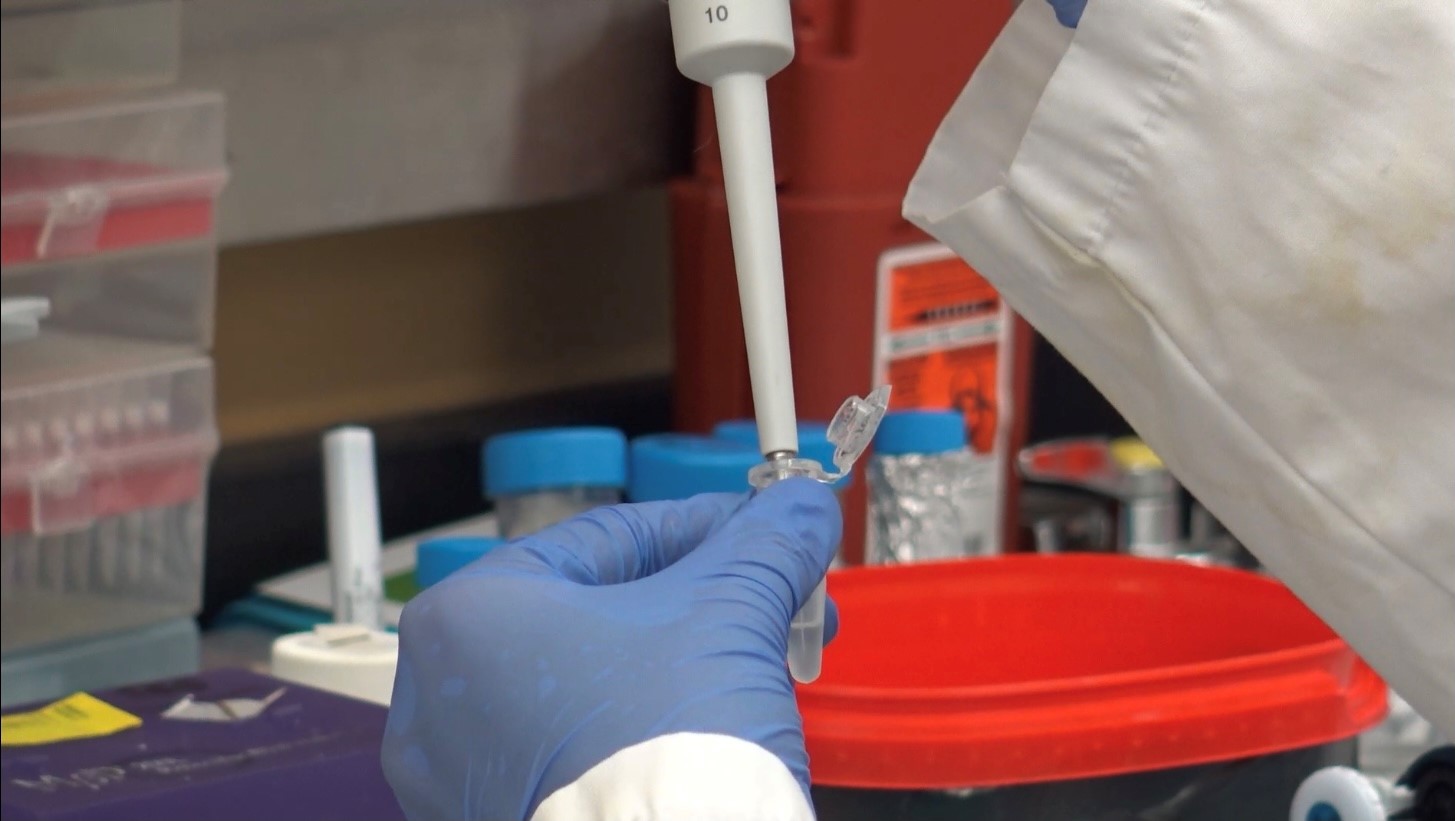
Published in Molecular Medicine, researchers at Lawson have found that patients with post-COVID-19 condition (long COVID) have unique biomarkers in their blood. The team is now working on developing a first of its kind blood test that could be used to diagnose long COVID. The discovery could also lead to new therapeutics for this condition. Read more.
Largest trial ever done in hemodialysis care examines optimal dialysis temperature
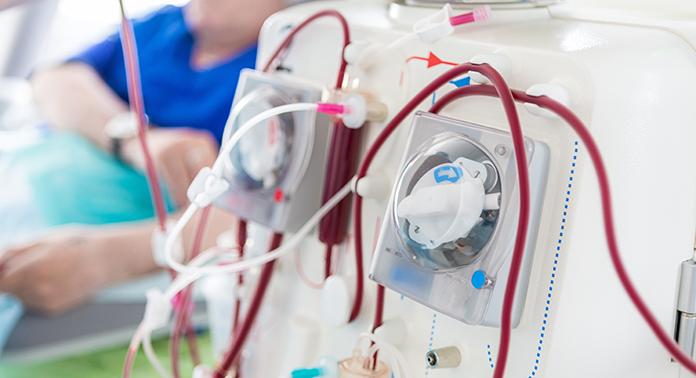
Published in the Lancet findings from a large clinical trial through Lawson, ICES Western and Western University suggest that lowering dialysis temperatures does not lead to improved patient outcomes, despite previous studies suggesting otherwise. Read more.
To learn more about Lawson research studies, please visit our News and Media page
Senior Media Relations Consultant
Communications & Public Engagement
T: 519-685-8500 ext. 73502
Celine.zadorsky@lhsc.on.ca